BRAIN COMPUTER INTERFACE (BCIs)
WHY IN NEWS ?
- Recently, Neuralink has implanted a brain chip in a patient who is recovering well.
WHAT IS BRAIN-COMPUTER INTERFACE (BCI) ?
- Brain-computer interface (BCI) is a collaboration between a brain and a device, which enables signals from the brain to direct some external activity, such as control of a cursor or a prosthetic limb.
- It enables a direct communications pathway between the brain and the object to be controlled.
- BCI systems are a fast-growing technology, which involve hardware and software communication systems that control external devices through the brain activity.
- BCI devices that replace or restore function have been shown to provide competitive alternatives to other assistive communication and control technologies in some very severe cases.
- One of the most important applications of BCI technology is to provide assistance to disabled people like paralytic patients.
HOW DO BCIs WORK ?
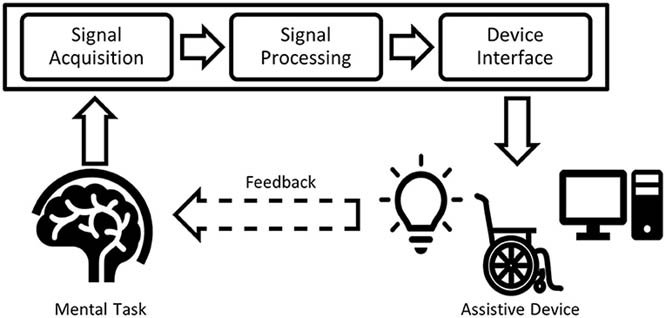
- These systems acquire brain signals, and decode and translate them into intended actions.
- The BCI then transmits these decoded signals to devices like computers, phones, robotic and prosthetic limbs.
- A BCI can use any of the three non-invasive techniques such as:
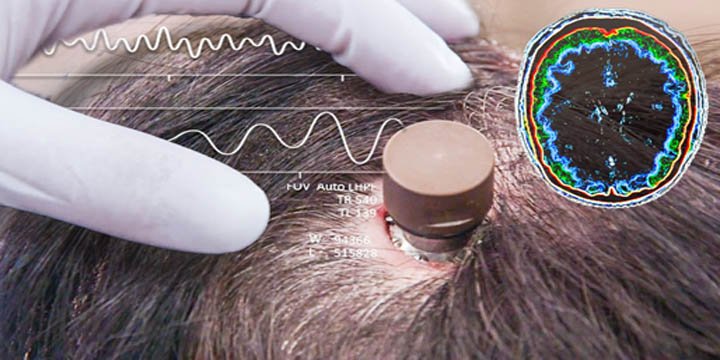
- Electroencephalography (EEG) that uses electrodes on the scalp to acquire brain signals
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG) that captures magnetic fields from brain activity but is expensive
- Real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to acquire non-invasive brain scans.
- Neuralink implants electrodes, which offer the highest signal resolutions but are invasive in nature.
ABOUT NEURALINK:
- Neuralink’s BCI product known as ‘Telepathy’, is fully implantable and comprises an implant that records neural activity through 1,024 electrodes, a surgical robot and a user app.
- Neuralink is accepting patients (22 years and above) with quadriplegia(limited function in all four limbs) due to spinal cord injury or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
- However, neuralink will not accept individuals with devices like pacemakers or deep brain stimulators (DBS), or a history of seizures.
OTHER BCIs IN MARKET:
- Other companies are also working on BCIs such as Paradromics, Synchron, Kernel, Emotiv, CTRL-labs (Meta), MindMaze and Blackrock Microsystems.
- Their innovations range from neuroimaging headsets to EEG headsets for gaming and wrist-worn devices for intuitive computer interaction.
- Some companies also offer solutions for healthcare and virtual reality, and even implantable BCIs.
BENEFITS OF BCIs:
- They can revolutionize healthcare for individuals with paralysis or severe motor disabilities to control devices with their thoughts.
- They also offer immersive experiences in entertainment and gaming.
- BCIs can monitor brain activity and provide real-time feedback for stress management or anxiety reduction.
- BCIs can train pilots to improve their cognitive performance and response times.
- They have the potential to improve the quality of life for many individuals affected by debilitating disorders of the brain, spine, limbs, and sensory organs through direct interface with the nervous system.
- Potential uses of the BCI technology include secure communication and control of unmanned vehicles; and educational content based on the learner’s cognitive state, making learning more effective.
CONCERNS REGARDING BCIs:
- Though the long-term effects on the brain are still being tested.
- These brain chip implants can be hacked, raising privacy and security concerns.
- Safeguards against unauthorized access is a solution.
- There are possible issues of bias in algorithms and questions about autonomy and personal identity emerge as BCIs could alter cognitive abilities, raising ethical concerns too.
- Ensuring equitable access to such technologies is critical too.
- Those with religious leanings could see gene editing and BCI implants as “meddling with nature”.
- The intrinsic neurophysiological instability of brain dynamics poses critical challenges for making BCI systems efficient.
WAY AHEAD:
- The future of BCI technology will rely largely on addressing the following key aspects:
- Analysing the underlying psychophysiological and neurological factors that potentially influence BCI performance.
- Designing less invasive sensors with reliable signal acquisition and resolution and considering portability, easy maintenance, and affordability at the same time.
- Establishing broad consensus on ethical issues and beneficial socioeconomic application of this technology.