Dementia
Context :
- According to a 2020 report, there are around five million people in India living with dementia.
- Worldwide, 47.5 million people have dementia, and up to 135.5 million could by 2050.
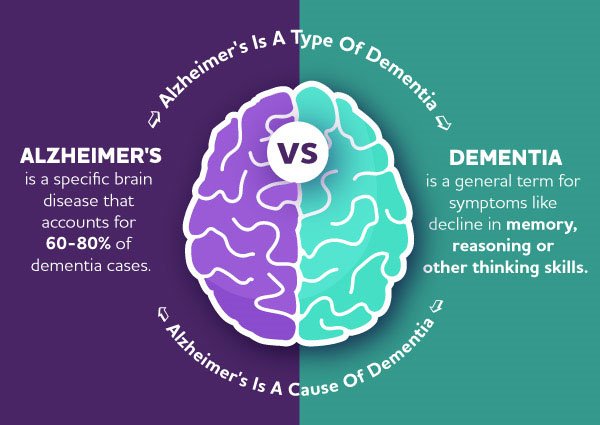
What is Dementia?
- Dementia is a clinical syndrome caused by a range of diseases or injuries to the brain.

- The most common cause of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, which is implicated in up to 70% of dementia diagnoses.
Symptoms :
- Early symptoms include absentmindedness, difficulty recalling names and words, difficulty retaining new information, disorientation in unfamiliar surroundings, and reduced social engagement.

Signs and symptoms of Dementia
- Atypical symptoms include impairment in recognising visually presented objects despite a normal visual field, acuity and colour vision.
- Some might also experience wordfinding difficulties.
- As the disease progresses, there is a marked memory loss and loss of other cognitive skills, including reduced vocabulary and less complex speech patterns.
- This may be accompanied by mood swings, apathy, a decline in social skills, and the emergence of psychotic phenomena.
- Advanced disease is characterised by monosyllabic speech, psychotic symptoms, behavioural disturbance, loss of bladder and bowel control, and reduced mobility.
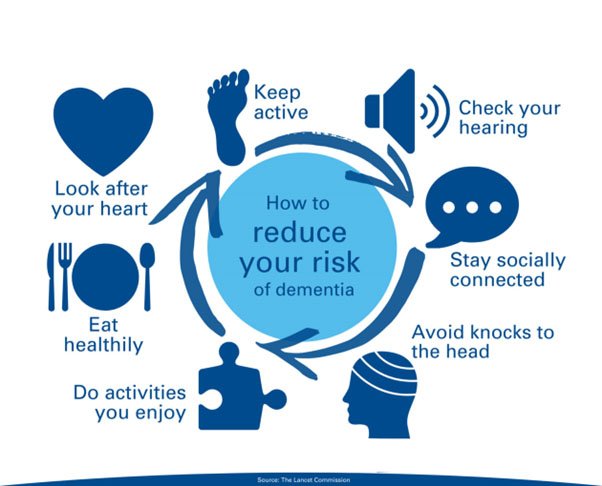
How to prevent Dementia?
- The WHO has identified preventing Alzheimer’s disease to be key to fighting the world’s dementia epidemic.
- Economic analyses have found that delaying the onset of the disease by even one year could reduce its prevalence by 11%.
- Prevention programmes usually focus on lifestyle risk factors together with mental wellbeing and risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Regular exercise helps offset cardiovascular health risks and improves cerebral perfusion, synaptic function, and stimulates the growth of new brain cells in the hippocampus.
Who are more vulnerable?
- At least two large studies, in 1996 and 2009, have demonstrated a strong relationship between midlife hypertension and dementia in later life.
- Current smokers have a 50% higher risk of developing dementia relative to those who have never smoked.
- Smoking cessation is known to reduce the risk to the level of never-smokers.
- There is also a robust link between depression in late life and the incidence of sporadic dementia. Having depression almost doubles the risk of developing dementia.
Treatment of Dementia :
- Dementia care has four pillars.
- The first two include managing the important aspects of the disease, with a goal to reverse their effects or to delay its progression in the brain as well as managing the cognitive, neuropsychiatric, and functional symptoms.
- The other two pillars involve providing systematic, evidence-based supportive care to patients and to carers.
Way forward :
We will need a cultural transition moving from dementia to a framework of brain health will destigmatise cognitive decline, empower people to take more responsibility towards prevention, and encourage society to adopt inclusive solutions to maintain functional independence.
SOURCE : THE HINDU
Syllabus : GS3 – Health; Diseases

