Kashi Vishwanath Temple Complex
Indian Express
GS 1: Indian Culture
Context:
- Recently, Prime Minister will inaugurate the Kashi Vishwanath Corridor connecting the ancient Kashi Vishwanath Temple in Varanasi to the ghats of the Ganga.
- The corridor has been built over an area of 5,000 hectares, and seeks to not only decongest but to also transform the temple complex.
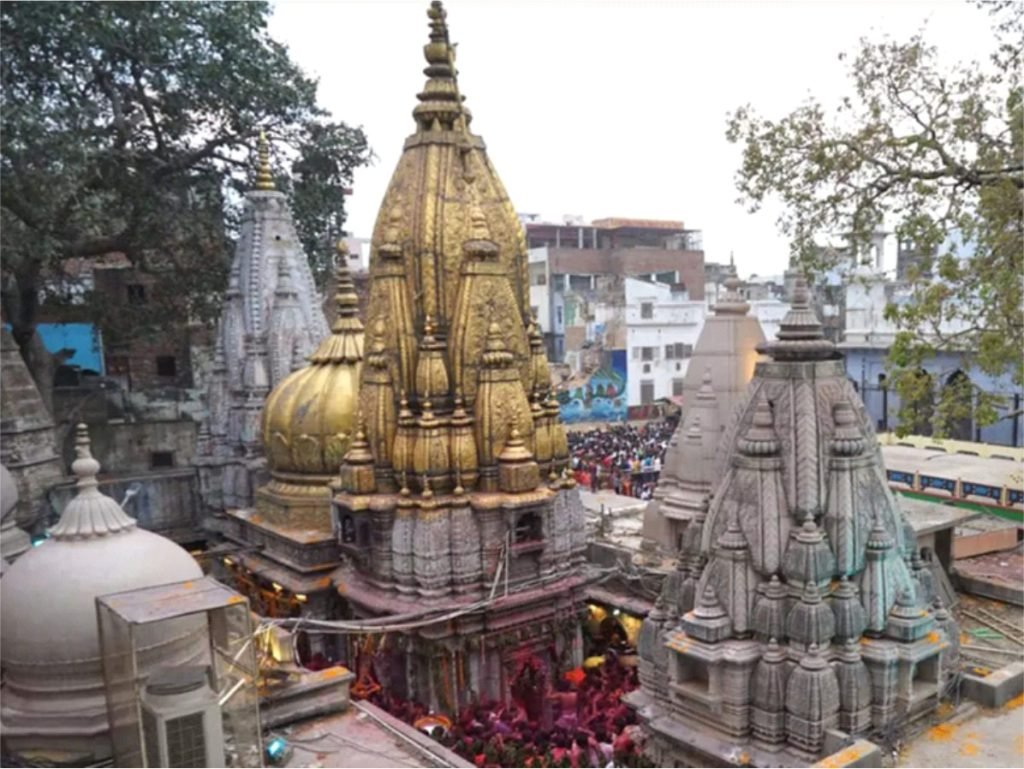

About:
- The Rs-800-crore project was launched by the PM in his parliamentary constituency in March 2019, with the aim of restoring the “lost glory” of the spiritual centre.
- The Kashi Vishwanath temple lacked direct access to the Ganga, and a 20-foot-wide corridor was envisaged to connect Lalita Ghat on the holy river to Mandir Chowk on the temple premises.
The tourism push
- The improvement of the infrastructure in Varanasi is expected to give a boost to tourism in the holy city as well as in the region, including the Buddhist pilgrimage site of Sarnath.
- The Rudraksh Convention Centre, designed like a Shiva lingam, can seat 1,200 people, and has divisible meeting rooms, an art gallery, and multipurpose pre-function areas.
- Ganga cruises are planned for tourists, road infrastructure has been upgraded, and the Banaras railway station in the city’s Manduadih area has been revamped with the addition of an air-conditioned waiting lounge.
- Elsewhere in the city, LED screens will display information for tourists, including on the history, architecture, and art of Kashi. The famous Ganga Aarti and the aarti at the Kashi Vishwanath temple will be shown on the screens throughout the city.
- The Deen Dayal Hastkala Sankul, a trade facilitation centre for weavers, craftsmen, and artisans of Varanasi that was opened in 2017, acts as both a public place and a marketing platform for local artisans.
Heritage restoration
- During demolition of the buildings, more than 40 ‘lost’ temples like the Gangeshwar Mahadev temple, the Manokameshwar Mahadev temple, the Jauvinayak temple, and the Shri Kumbha Mahadev temple were discovered. Each of these temples has a history going back a few centuries.
- A gallery has been devoted to showcase some of the excavated remains at the National Museum in New Delhi, and to run a narrative on their histories on screens alongside.
- In Varanasi, “smart signages” have been erected to provide information on the cultural importance of heritage sites and the city’s 84 ghats, which are known for their antiquity and architectural significance.
VL-SRSAM
Indian Express
GS 3: Defence
Context:
- The Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile (VL-SRSAM) designed for Indian Naval warships was successfully flight tested recently by India for the second consecutive time since February earlier this year.
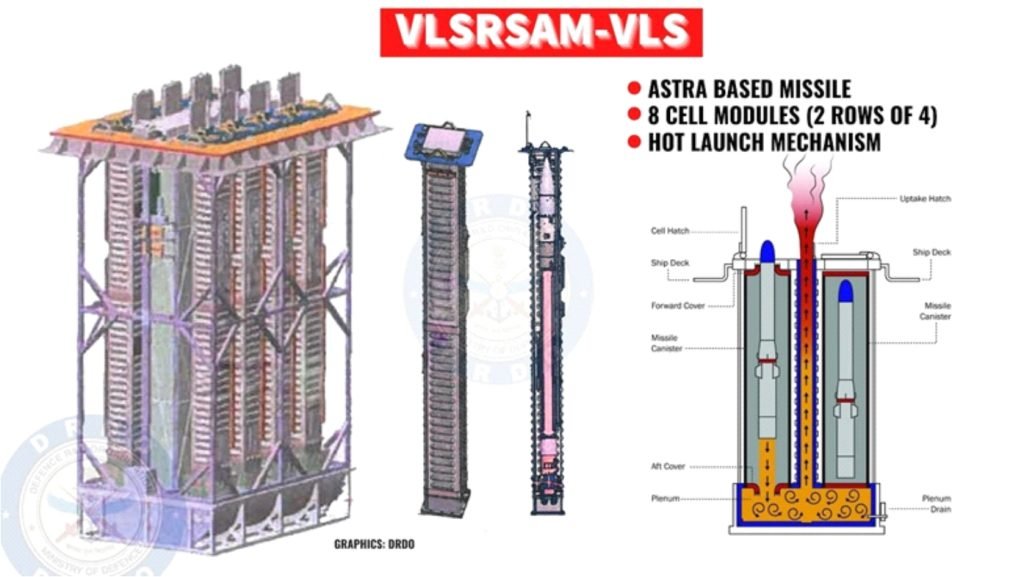
About:
- VL-SRSAM has been designed and developed jointly by three facilities of the Defence Research and Development Organisation for deployment of Indian Naval warships.
- The missile has the capability of neutralising various aerial threats at close ranges including sea-skimming targets.
- The tactic of sea skimming is used by various anti-ship missiles and some fighter jets to avoid being detected by the radars onboard warships. For this, these assets fly as close as possible to sea surface and thus are difficult to detect and neutralise.
The design of VL-SRSAM
- The missile has been designed to strike at the high-speed airborne targets at the range of 40 to 50 km and at an altitude of around 15 km. Its design is based on Astra missile which is a Beyond Visual Range Air to Air missile.
- Two key features of the VL-SRSAM are cruciform wings and thrust vectoring. The cruciform wings are four small wings arranged like a cross on four sides and give the projective a stable aerodynamic posture.
- The thrust vectoring is an ability to change the direction of the thrust from its engine control the angular velocity and the attitude of the missile.
- It is a canisterised system, which means it is stored and operated from specially designed compartments. In the canister, the inside environment is controlled, thus making its transport and storage easier and improving the shelf life of weapons.
International Solar Alliance
Business Standard
GS 3: Environmental Pollution Degradation
Context:
- The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) has granted Observer Status to International Solar Alliance (ISA).
About:
- ISA has become an example of positive global climate action through partnerships to benefit global energy growth and development.
- The granting of Observer Status to ISA in the General Assembly would help provide for regular and well-defined cooperation between the Alliance and the United Nations that would benefit global energy growth and development.
- It would help ISA to expand its network through setting up a trans-national grid — One Sun One Work One Grid (OSOWOG).
ISA:
- Its launch was announced by current Prime Minister of India, and former French President Francois Hollande in November 2015, at the 21st session of the UN Climate Change Conference of the Parties in Paris, France.

- Headquarters: India
- The Assembly is the apex decision-making body of the ISA. It meets annually at the Ministerial level at the seat of the ISA.
- Membership: A total of 80 countries have signed and ratified the ISA Framework Agreement and 101 countries have only signed the agreement
- ISA provides a dedicated platform for cooperation among Governments, multilateral organisations, industry, and other stakeholders to help achieve a common goal.
- It assists member countries in finding suitable bilateral or multilateral funding.
- ISA does not explicitly provide funds or technology and it helps create conditions that make funding, developing and deploying solar applications on a large scale possible.

75 Years of Constituent Assembly’s 1st Sitting
PIB
GS 1: Modern Indian History
GS 2: Polity and Governance
Context:
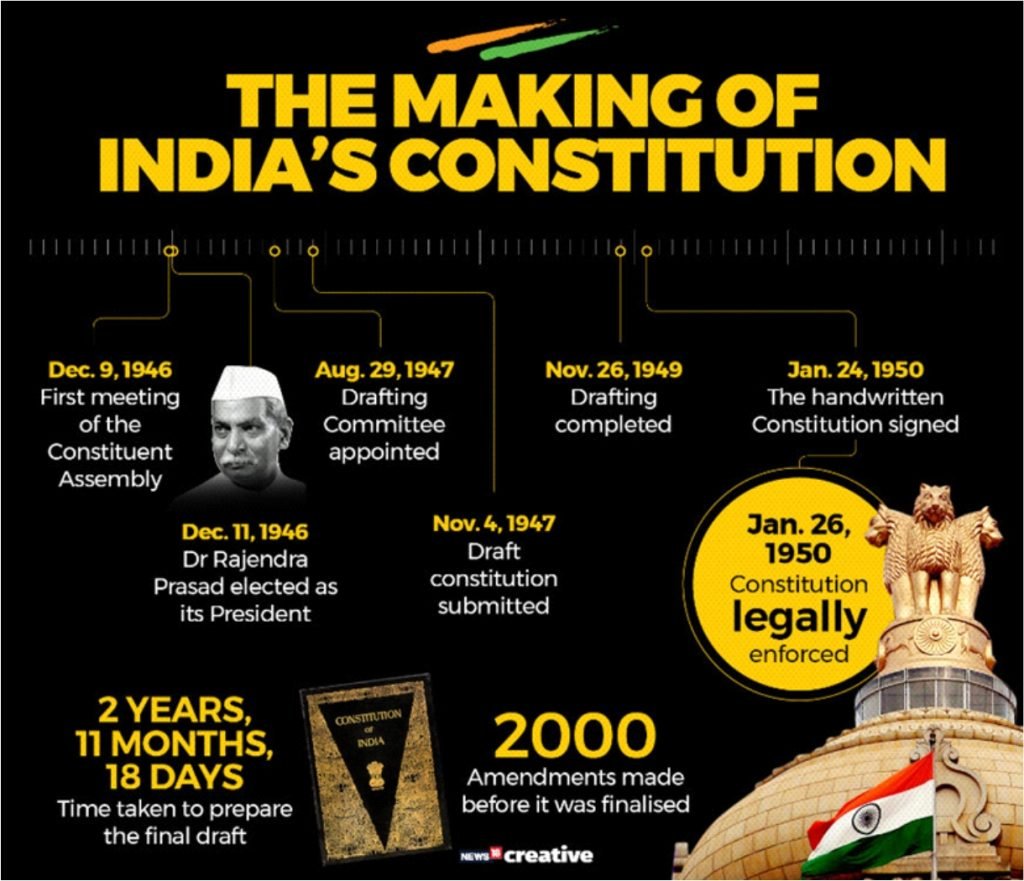
- The Constituent Assembly of India had held its first meeting 75 years ago on December 9, 1946.
About:
- Distinguished people from different parts of India, different backgrounds and even differing ideologies came together with one aim- to give the people of India a worthy Constitution.
- The first sitting of the Constituent Assembly was Presided over by Dr Sachchidananda Sinha, who was the eldest member of the Assembly. He was introduced and conducted to the Chair by Acharya Kripalani.

CA:
- Took 2 years, 11 months & 17 days for drafting the Constitution of India.
- Dr Sachchidananda Sinha : 1st President of CA.
- Dr Rajendra Prasad : chairman of the Constituent Assembly.
- Jawaharlal Nehru (PM) made the ‘Objectives Resolution’ on 13th December 1946, later adopted as Preamble on 22nd Jan 1947.
- It acted as the temporary legislature until a new one was to be constituted.
- Partly elected and partly nominated.
- Indirect election by provincial assemblies who themselves were elected on a limited franchise.
- Though an indirect mode of election, it included representatives from all sections of the society.
- Muslim League did not participate in the first meeting.
Criticism:
- Not a representative body since members were not directly elected.
- It was not a sovereign body since it was established based on British order.
- It took an unduly long time to make the constitution.
- It was dominated predominantly by the congress party.
- It was dominated by lawyer-politicians to a greater degree.
- It was dominated by Hindus predominantly.
Chinese Project at Balochistan Port
GS 2: India and foreign relations
Indian Express
Context:
- There have been continuous protests for 26 days in Gwadar, Balochistan against mega-development plans of the port city as part of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
About:
- With the announcement of the CPEC in 2015, Gwadar has been showcased as the gateway to a new era of Chinese investments meant to change the fate of both Pakistan and the region as a whole.
- It is a part of China’s ambitious One Belt One Road (OBOR) Initiative to link China with Europe.
- The CPEC project would link Pakistan’s southern Gwadar port in Balochistan on the Arabian Sea to China’s western Xinjiang region.
- It also includes plans to create road, rail and oil pipeline links to improve connectivity between China and the Middle East.
- Gwadar is a small port town on the coastline of the Arabian Sea in Pakistan’s southwestern Balochistan province, has been in news since then.
- China has spent billions of dollars on building the port town, opening a 300-megawatt coal-fired power plant, and building an international airport at the cost of $230 million, alongside other projects that come under the CPEC umbrella.
- The authorities have continued to ignore the basic demands of the locals.
- Balochistan has the lowest access to drinking water, electricity, and even gas that is the main resource of the region.
- They still don’t have basic necessities, despite the influx of billions of dollars in Chinese investment.
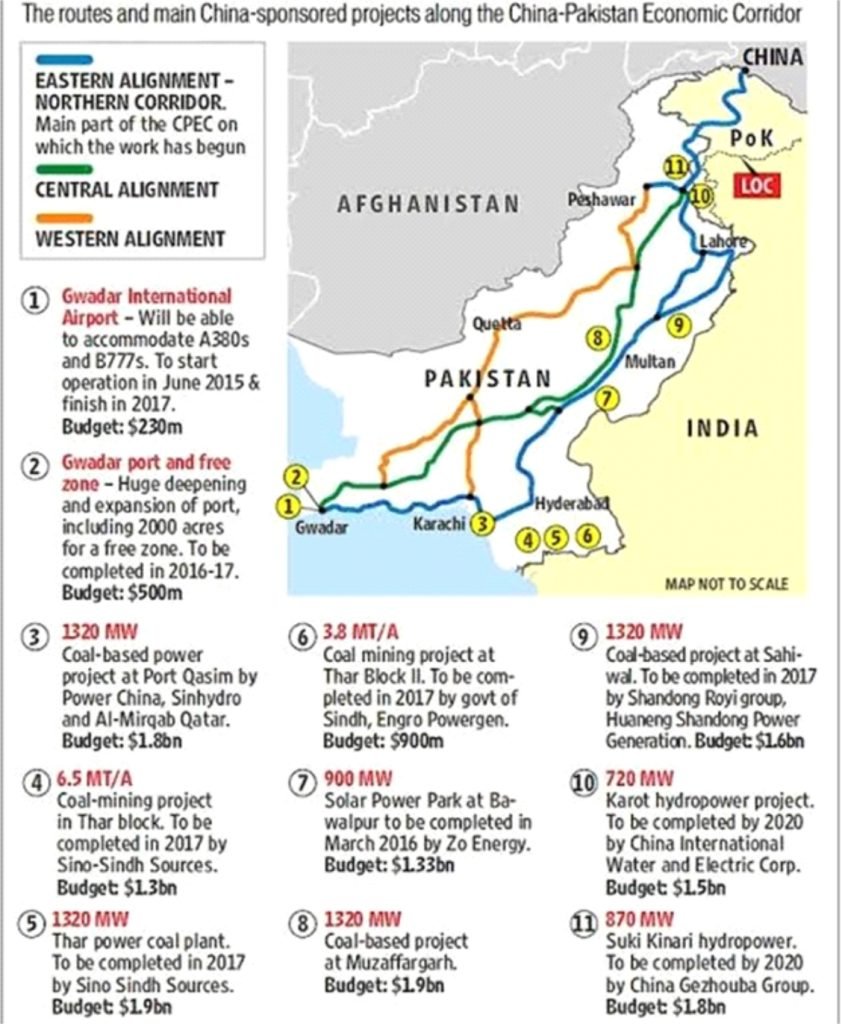
Concerns of India:
- India has been concerned that Gwadar, which gives China strategic access to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean, is not just being developed as a trade entrepot but as a dual-purpose port for use by the Chinese Navy.
- It is intended to expand Chinese presence in the Indian Ocean Region alongside Kyaukpyu in Myanmar and Hambantota in Sri Lanka.
- India has protested to China over the CPEC as it traverses through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- The recent discovery of a secret Chinese military base in the UAE can only heighten the concerns.

