Role of Governor in State and Central Universities
Indian Express
GS 2: Indian Constitution
Context:
- Recently, Gopinath Ravindran as the Vice-Chancellor of Kannur University was reappointed by the Governor of the state, which created a controversy.
- The disputes are, quite naturally, more common in states run by political rivals of the party running the Union government, which appoints the Governors through the President of India.
About:
| STATE UNIVERSITIES | CENTRAL UNIVERSITIES |
| Governor of the state is the ex-officio chancellor. | Under the Central Universities Act, 2009, and other statutes, the President of India shall be the Visitor of a central university. |
| Governor’s powers and functions as the Chancellor are laid out in the statutes that govern the universities under a particular state government. | Chancellors are appointed by the President in his capacity as Visitor. |
| Disputes: In Kerala’s case, the Governor’s official portal asserts that “while as Governor he functions with the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers, as Chancellor he acts independently of the Council of Ministers and takes his own decisions on all University matters”.
In marked contrast, the website of Rajasthan’s Raj Bhawan states that the “Governor appoints the Vice-Chancellor on the advice/ in consultation with the State Government”. |
They are titular heads with their role limited to presiding over convocations.
The VCs too are appointed by the Visitor from panels of names picked by search and selection committees formed by the Union government.
|

Wildlife Conservation in India
The Hindu
GS 3: Conservation
Context:
- According to the recent data by the Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) and State Forest and Police Authorities, in the past three years (2018-2020), about 2054 cases were registered for killing or illegal trafficking of wild animals in India.
- To control this, the WCCB has conducted a number of species-specific enforcement operations with coordination of State Enforcement Agencies.
- WCCB is a statutory multi-disciplinary body established by the Government of India under the Ministry of Environment and Forests, to combat organized wildlife crime in the country. It has its headquarter in New Delhi.
Impact of Illegal Wildlife Trade:
- Illegal wildlife trade as part of the illegal trade syndicates undermines the economy of the country and thereby creates social insecurity.
- Species face extinction because of demands arising out of illegal wildlife trade.
- Wild plants that provide genetic variation for crops (natural source for many medicines) are threatened by the illegal trade.
- Overexploitation of the wildlife resources due to its illegal trade creates imbalances in the ecosystem.

Species-Specific Enforcement Operations:
- Operation Save Kurma: WCCB had launched Operation “Save Kurma”from 15th December 2016 to 30th January 2017. It focuses on poaching, transportation and illegal trade of live turtles and tortoises.
- Operation Turtshield: Illegal trade of live turtles.
- Operation Lesknow: To gain attention of enforcement agencies towards the illegal wildlife trade in lesser-known species of wildlife.
- Operation Clean Art: To drag attention of enforcement agencies towards illegal wildlife trade in Mongoose hair brushes.
- Operation Softgold: To tackle Shahtoosh Shawl (made from Chiru wool) illegal trade and to spread awareness among the weavers and traders engaged in this trade.
- Operation Birbil: To curb illegal trade in wild cat and wild bird species.
- Operation Wildnet: It was aimed to draw the attention of the enforcement agencies within the country to focus their attention on the ever increasing illegal wildlife trade over the internet using social media platforms.
- Operation Freefly: To check illegal trade of live birds.
- Operation Wetmark: To ensure prohibition of sale of meat of wild animals in wet markets across the country.
Steps Taken:
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Protected Areas like National Parks, Biodiversity Reserves, etc. were created
- Project Tiger: Initiated in 1972. It helped in the conservation of both tigers and the entire ecosystem.
- Project Elephant: Initiated in 1992 with the aim of conserving elephants and their habitat and of migratory routes by developing scientific and planned management measures.
- Crocodile Conservation Project: The main objectives of the crocodile project is to protect the remaining population of crocodiles and their natural habitat by establishing sanctuaries.
- UNDP Sea Turtle Project: To conserve the Olive Ridley Turtles. Initiated by Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun as the Implementing Agency in 1999.
- Cheetah Reintroduction Programme in Kuno Palpur sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh from Namibia.
- Vulture Conservation: National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) has cleared a plan for conserving vultures.
- India Rhino Vision (IRV) 2020: It aims to increase the rhino population in Assam to 3,000 by establishing populations in new areas.
- Wetland (Conservation and Management) Rules 2010 have been drafted to protect wetlands in India.
- Related Organisations: Wildlife Crime Control Bureau, Central Zoo Authority, National Tiger Conservation Authority, Wildlife SOS, Wildlife Trust of India, Wildlife Institute of India, Aaranyak, Nature Conservation Foundation, etc.
- Citizens’ participation: The Prime Minister called for active participation of people in conservation efforts.
- Article 51 A (g) states that it shall be the fundamental duty of every citizen to protect and improve the natural environment including forests and Wildlife.
- Article 48 A in the Directive Principles of State policy, mandates that the State shall endeavor to protect and improve the environment and to safeguard the forests and wildlife of the country.
National Helpline Against Atrocities (NHAA)
PIB
GS 1: Social Issues
Context:
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment is launched a National Helpline Against Atrocities (NHAA).
About:
- Aim is to ensure proper implementation of the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities){PoA} Act, 1989 which was enacted with a view to, inter-alia, preventing atrocities on members of Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs).
- The NHAA will be available round the clock on toll-free number 14566 across the country.
- It can be accessed by making a voice call /VOIP either from a mobile or land line number of any Telecom Operator across the country.
- This service will be available in Hindi, English, and regional language of the State/UTs. Its Mobile application will also be available.
- Available as a web-based self-service portal also, the NHAA will generate awareness about the Protection of Civil Right (PCR) Act, 1955 and its rules as well.
- A Docket number shall be given for each complaint received from Victim/Complainant/NGOs regarding non-compliance of the POA Act, 1989 and the PCR Act, 1955. The status of the grievance can be tracked by complainant/NGOs online.
- Any inquiry shall be replied by IVR or operators in Hindi, English, and Regional languages.

Banking Reforms
The Hindu
GS 3: Economy
Context:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor Shaktikanta Das indicated that the banking regulator will ring in sweeping regulatory changes to reform urban cooperative banks that have been plagued by a spate of failures, and warned people against parking their savings in banks offering high returns.
About:
- While describing the Government’s decision to raise the insured limit for bank deposits to ₹5 lakh from ₹1 lakh with a 90-day time limit to pay out such deposits as ‘landmark’ developments, Mr. Das stressed that the payment of deposit insurance should be seen as a “measure of last resort”.
- There are institutions that are offering higher interest rates which are viable, but depositors should always be very careful,” he reiterated at an event to mark the payment of nearly ₹1,300 crore to over 1 lakh depositors whose funds were stuck in distressed banks for years.
- Prime Minister addressed a function on “Depositors First: Guaranteed Time-bound Deposit Insurance Payment up to Rs. 5 Lakh” in New Delhi.
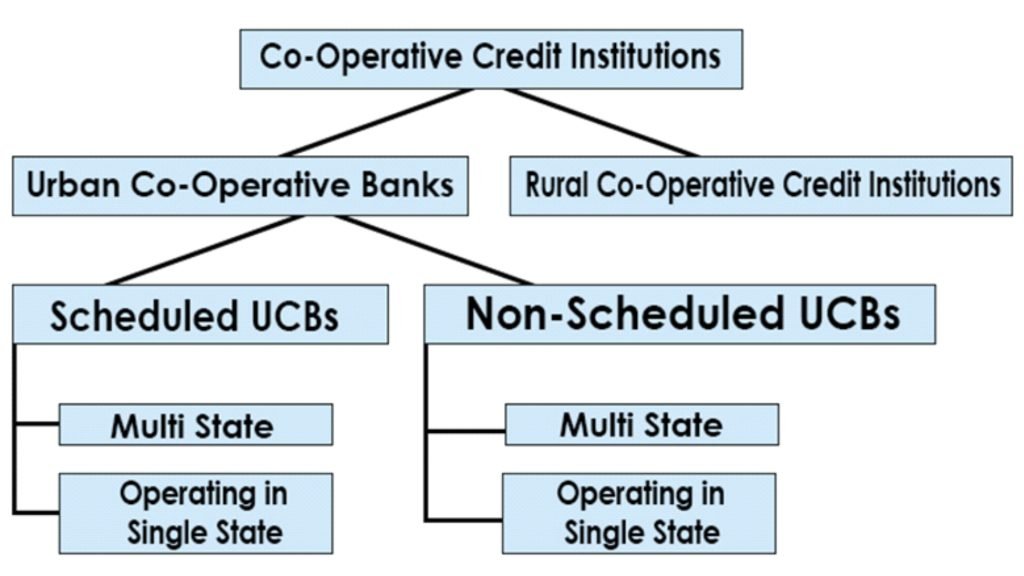
Urban Co-operative Bank
- The term “Urban Cooperatives Banks” (UCB) refers to main cooperative banks based in cities and towns.
- Traditionally, these banks concentrated on communities, towns, and workplace organizations.
- They mostly lend to small borrowers and enterprises. Its operational environment has grown significantly in recent years.
Significance of Urban Co-operative Bank
- Urban cooperative banks (UCBs) have been around for over a century and provide mostly regional financial services.
- Their specialty is catering to the lower middle class and persons with little resources, as well as self-employed and micro-enterprises.
- UCBs are most at ease working with these consumers.
Concerns Associated with Urban Co-operative Bank
- The uncovering of large-scale financial irregularities has taken urban cooperative banks off guard.
- Low capital basis, weak corporate governance, inability to detect fraud, delayed adoption of new technologies, and insufficient system of checks and balances are difficulties confronting urban cooperative banks (UCBs).
- The latest Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act 2020 empowers the RBI with all powers, including those formerly reserved for the registrar of cooperative organizations.
- The RBI’s control was limited, and it shared it with the registrar of cooperative societies of states, resulting in the much-discussed dual control and the issues it posed to the central bank.
- The cooperative sector has two challenges:
- first, increased competition from not just Scheduled Commercial Banks, but also from minor financing banks and payments banks;
- second, vulnerability caused by internal shortcomings, such as the inability to detect and prevent fraud.
Conclusion: –
- The construction of a standard regulatory and supervisory framework, as well as an umbrella organization, should be given top importance in the architecture.
- The RBI is also anticipated to interpret the Act’s provisions such that they do not disrupt UCBs. It remains to be seen how the RBI will put them into effect.
- The establishment of our country’s dedicated Ministry of Cooperation is a watershed moment in the history of our country’s cooperative movement.

