Durga Puja Festival
Indian Express
GS 1: Indian Culture
Context:
- UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage put “Durga Puja in Kolkata” on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.

Puja in Kolkata:
- It is celebrated across the country — notably in Tripura, Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, Assam, Maharashtra, Delhi, and Uttar Pradesh — and in neighbouring Bangladesh, the heart of the 10-day annual Sharodotsav festival is in Kolkata.
- It is one of the largest cultural carnivals and street art festivals of the country.
- During this time, intricately-designed clay models of the Goddess are worshiped in ‘pandals’ and pavilions where people get together.
- Folk music, culinary, craft, and performing arts traditions are a part of the celebration.
Intangible Heritage:
- According to UNESCO, “cultural heritage does not end at monuments and collections of objects”, but “also includes traditions or living expressions inherited from our ancestors and passed on to our descendants, such as oral traditions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, knowledge and practices concerning nature and the universe or the knowledge and skills to produce traditional crafts”.
- Intangible cultural heritage, according to UNESCO, is “traditional, contemporary and living at the same time”, “inclusive”, “representative”, and “community-based”.
- It is “an important factor in maintaining cultural diversity in the face of growing globalisation” — and “an understanding of the intangible cultural heritage of different communities helps with intercultural dialogue, and encourages mutual respect for other ways of life”.
- The Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity currently has 492 elements.
- The list of Intangible Cultural Heritage elements on the UNESCO website includes 13 entries from India.
- Durga Puja in Kolkata (2021),
- Kumbh Mela (2017);
- Nowruz (2016);
- Traditional brass and copper utensil-making among the Thatheras of Jandiala Guru, Punjab (2014);
- Sankirtana of Manipur (2013);
- Buddhist chanting of Ladakh (2012);
- Chhau dance, Kalbelia dance of Rajasthan, and Mudiyettu of Kerala (2010);
- Ramman festival of Garhwal (2009); and
- Kutiyattam Sanskrit theatre, Ramlila, and Vedic chanting (2008).
Significance:
- This step will offer encouragement to the local communities that celebrate Durga Puja, including all the traditional craftspeople, designers, artists, and organisers of large-scale cultural events, as well as tourists and visitors.
- Earlier this year (2021), the British Council in India had mapped the creative economy of Durga Puja to over Rs. 32,000 crore for the year 2019 and added that the festival contributes 2.58% of West Bengal’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Rustom-2 Indigenous UAV
The Hindu
GS 3: Defence and Security
Context:
- India’s indigenous Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) programme Rustom-II achieved an important milestone in its development cycle and has moved a step forward towards production stage.

About:
- The indigenous Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) development programme by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has crossed a milestone by reaching an altitude of 25,000 feet and an endurance of 10 hours.
- Rustom-2 has been designed and developed by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE), Bengaluru with production partners being Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd and Bharat Electronics Limited.
- It is being developed to carry out surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) roles and is capable of carrying different combinations of advanced payload and capable of auto-landing among others.
- It is being designed to acquire real-time, high-quality pictures and signal intelligence from fields of concern at medium to long ranges.
- It technologically matches contemporary UAVs available and will also be cheaper than the imported ones.
- It is also known as Tapas-BH (Tactical Airborne Platform for Aerial Surveillance-Beyond Horizon 201).
-
- The UAV is actually named after Rustom Damania, a former professor at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru.
- In the 1980s, he led the National Aeronautical Laboratories’ light canard research aircraft (LCRA) program.
- The LCRA platform and R&D provide the preliminary drive for DRDO ADE’s eventual Rustom-II design.
- The UAV is actually named after Rustom Damania, a former professor at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru.
50th Vijay Diwas
The Hindu
GS 2: India and foreign relations
Context:
- The Prime Minister of India led the nation in paying tribute to the martyrs of the 1971 war on the 50th Vijay Diwas.

About:
- Vijay Diwas is observed to commemorate India’s victory in the 1971 war and the Liberation of Bangladesh.
- The year 2021 is being observed as Swarnim Vijay Varsh to commemorate 50 years of India’s victory over Pakistan in the 1971 war.
- The Government of India decided on 3rd December 1971, that India would go for war with Pakistan to save Bengali Muslims and Hindus.
- This war was fought between India and Pakistan for 13 days.
- On 16th December 1971, the chief of the Pakistani forces with 93,000 soldiers had surrendered unconditionally to the allied forces consisting of Indian Army and Mukti Bahini in Dhaka.
- Mukti Bahini refers to the armed organizations that fought against the Pakistan Army during the Bangladesh Liberation War. It was a guerrilla resistance movement.
- Bangladesh was born on this day. Hence, Bangladesh celebrates its independence day (Bijoy Dibos) on 16th December every year.
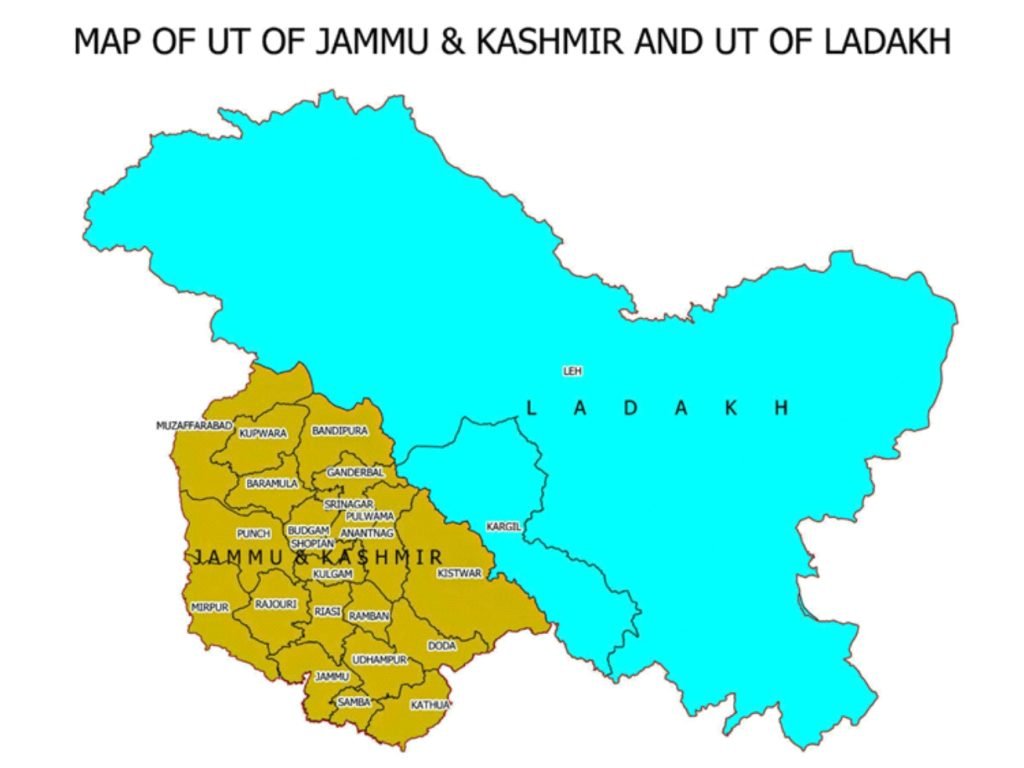
Ladakh under Sixth Schedule
Indian Express
GS 2: Indian Constitution
Context:
- Recently, a demand has been raised in Parliament to include the Union Territory (UT) of Ladakh in the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution to safeguard land, employment, and cultural identity of the local population.
- On August 5, 2019, when the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir was stripped of its special status and bifurcated into two Union Territories, the representatives of Ladakh.

Need of it:
- The administration of the UT of Ladakh region is now completely in the hands of bureaucrats. The government now looks even more distant than Srinagar.
- The changed domicile policy in Jammu and Kashmir has raised fears in the region about its own land, employment, demography, and cultural identity.
- The UT has two Hill councils in Leh and Kargil, but neither is under the Sixth Schedule.
- Their powers are limited to collection of some local taxes such as parking fees and allotment and use of land vested by the Centre.
- Buddhist-dominated Leh district had long demanded UT status because it felt neglected by the erstwhile state government.
- The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST) has recommended that the Union Territory (UT) of Ladakh be included in the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution.
- It was predominantly tribal (more than 97%), people from other parts of the country had been restricted from purchasing or acquiring land there, and its distinct cultural heritage needed preservation.
Legal hurdles
- The Constitution is very clear, Sixth Schedule is for the Northeast. For tribal areas in the rest of the country, there is the Fifth Schedule. No region outside the Northeast has been included in the Sixth Schedule.
- It remains the prerogative of the government. For this, a constitutional amendment is required.

Sixth Schedule of the Constitution:
- Articles 244(2) and 275(1) has provisions for the administration of tribal areas in the border states of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- Autonomous districts and councils, administered by elected representatives, have a varying degree of autonomy to frame laws to protect the interests of tribal people.
Atmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana Beneficiaries
Business Standard
GS 2: Government Policies & Interventions
Context:
- Maharashtra has topped the list of states with maximum number of beneficiaries under the Atmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY), followed by Tamil Nadu and Gujarat.
About:
- As on December 4, 2021, as many as 6,49,560 beneficiaries were recorded in Maharashtra, followed by Tamil Nadu (5,35,615), Gujarat (4,44,741) and Karnataka (3,07,164).
- In Maharashtra, the beneficiaries have been provided a total of Rs 409.72 crore under the scheme to new employees of 17,524 establishments.
- In Tamil Nadu, the beneficiaries were provided Rs 300.46 crore under the scheme to new employees of 12,803 establishments.
- In Gujarat, funds to the tune of Rs 278.63 crore have been provided to the new employees of 12,379 establishments and in Karnataka, the beneficiaries were provided a total of Rs 221.63 crore under the scheme to the new employees of 8,024 establishments.
- The government had launched ABRY to incentivize employment generation in Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) registered establishments during COVID-19 for a period from October 1, 2020 to March 31, 2022.
- Under the ABRY, the government is paying both employees’ and employers’ contributions of 24 per cent of wages (12 per cent of wages for each) in respect of establishments having 1,000 employees and employees’ contribution of 12 of wages to establishments employing more than 1,000 employees.
Eligibility Criteria for Establishments:
- Establishments registered with EPFO will be eligible for the benefits if they add new employees compared to the reference base of employees as in September 2020.
- Establishments, with up to 50 employees, would have to add a minimum of two new employees.
- The organizations, with more than 50 employees, would have to add at least five employees.