Telecom Sector Reforms
Indian Express
GS 3: Growth and Development
Context:
- Recently, the Union Cabinet approved a relief package for the telecom sector.
About:
- Relief package includes a four-year moratorium on payment of statutory dues by telecom companies, both AGR and spectrum charges.
- Definition of AGR has been rationalised by excluding non-telecom revenue of telecom companies.
- 100% FDI in telecom via the automatic route has been approved.
- The regime of heavy interest, penalty, and interest on penalty on payment of licence fees, spectrum charges and all kinds of charges has been rationalised.
- The relief package for the telecom sector has offered the prospect of an annual cash flow breather of an estimated Rs 45,000 crore to the fund-starved industry.
Structural Reforms:
- Huge reduction in Bank Guarantees (BGs) requirements (80%) against License Fee (LF) and other similar Levies.
- No requirements for multiple BGs in different Licenced Service Areas (LSAs) regions in the country. Instead, one BG will be enough.
- From 1st October, 2021, delayed payments of LF/Spectrum Usage Charge (SUC) will attract interest rate of SBI’s MCLR plus 2% instead of MCLR plus 4%; interest compounded annually instead of monthly; penalty and interest on penalty removed.
- For Auctions held henceforth, no BGs will be required to secure instalment payments. Industry has matured and the past practice of BG is no longer required.
- In future Auctions, tenure of spectrum increased from 20 to 30 years.
- Surrender of spectrum will be permitted after 10 years for spectrum acquired in the future auctions.
- No SUC for spectrum acquired in future spectrum auctions.
- Additional SUC of 0.5% for spectrum sharing removed.
Procedural Reforms:
- Spectrum auctions to be normally held in the last quarter of every financial year.
- The cumbersome requirement of licenses under 1953 Customs Notification for wireless equipment removed. Replaced with self-declaration.
- Self-KYC (App based) permitted. E-KYC rate revised to only One Rupee. Shifting from Prepaid to Postpaid and vice-versa will not require fresh KYC.
Significance of Reforms:
- This will lead to the way for large-scale investments in the telecom sector. Investment means employment – more the investment, more the employment.
- It is a welcome step towards strengthening the industry and ensuring survival of players to maintain healthy competition for the benefit of the customers.
- These measures are expected to ease the cash flow issues being faced by some players in the industry and provide relief to companies such as Vodafone Idea that have to pay thousands of crores of rupees in unprovisioned past statutory dues.
- The telecom package comes as a relief to the banks as it mitigates the imminent possibility of default by vulnerable operators. This would help in stabilising and reducing the non-performing assets in the sector.
- The steps announced by the government will help the companies conserve cash and it will significantly improve the probability of repayment at least for the next 3-4 years.
Way Ahead:
- The removal of non-telecom revenues from the definition of AGR and the removal of penalty is a much needed change that has been brought in.
- There is a need for the government’s intervention in setting sustainable telecom floor tariffs, as it has done in the civil aviation sector to protect competition.
- More efforts are needed to address the significant losses in the balance sheets of a majority of the stakeholders.

PROF. S.K. JOSHI LABORATORY EXCELLENCE AWARD
PIB
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Context:
- Quality Council of India (QCI) launched the S.K. Joshi Laboratory Excellence Award.
About:
- This is country’s first-of-its- kind Laboratory Excellence Award.
- This Award has been instituted to promote Laboratory Quality and performance improvement in the country.
- The award has been incepted to ensure the laboratory’s commitment to achieve excellence in providing high precision testing and calibration services in line with the prevalent national/international quality systems legislations, including Health, Safety & Environment.
- This award will be open to all currently operational Laboratories pertaining to Testing, Calibration & Medical including their Proficiency Testing Providers & Reference Material Producers located in India.
Prof. S.K. Joshi:
- He was a luminary in the field of Science and Academica.
- Joshi made a significant contribution in improving scientific research in India by serving as President-INSA, DG-CSIR, Director-NPL and Chairman-NABL.
- Joshi was felicitated with Padma Bhushan, Padma Shri, CV Raman Medal of INSA and several other prestigious awards.

Extinct Shark Species
Indian Express
GS 3: Science and Technology
Context:
- Researchers from the Geological Survey of India and the Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee have discovered a new extinct species of hybodont shark from the Jaisalmer Basin of Rajasthan.
About:
- Hybodonts dominated both marine and freshwater environments during the Triassic and early Jurassic periods.
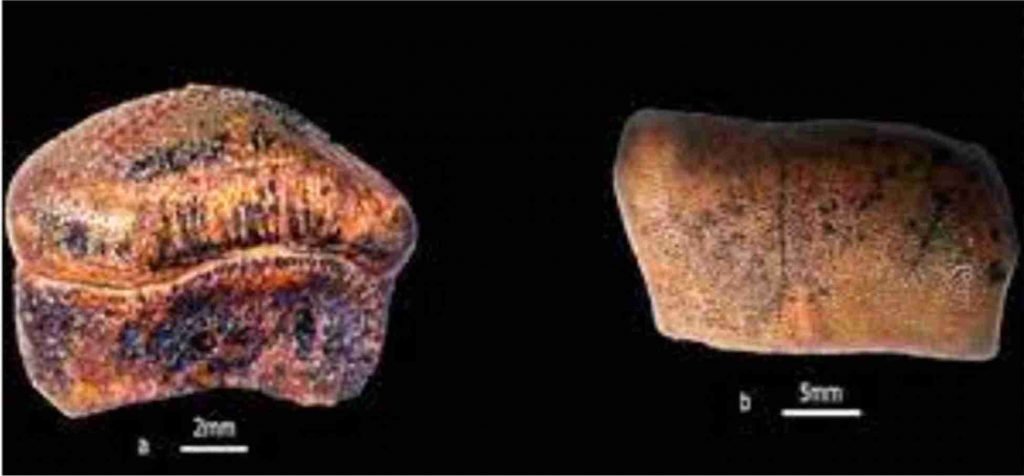
- Over 30 teeth specimens collected from the region showed that the species lived about 160 and 168 million years ago.
- It was named Strophodus jaisalmerensis.
- The discovery is significant as this is the first record of Strophodus genus from the Indian subcontinent.
- It is speculated that hybodont sharks could have grown about 2-3 metres long.
- They became extinct about 65 million years ago, probably due to competition from other fishes including sharks.
- Dinosaurs also went extinct 65 million years ago. It is not clear if these two extinctions are related.

Govt. Sets up ‘Bad Bank’ to Clear the NPA Mess
The Hindu
GS 3: Economy
Context:
- The Cabinet has cleared a Rs. 30,600 crore guarantee programme for securities to be issued by the National Asset Reconstruction Company Limited (NARCL).
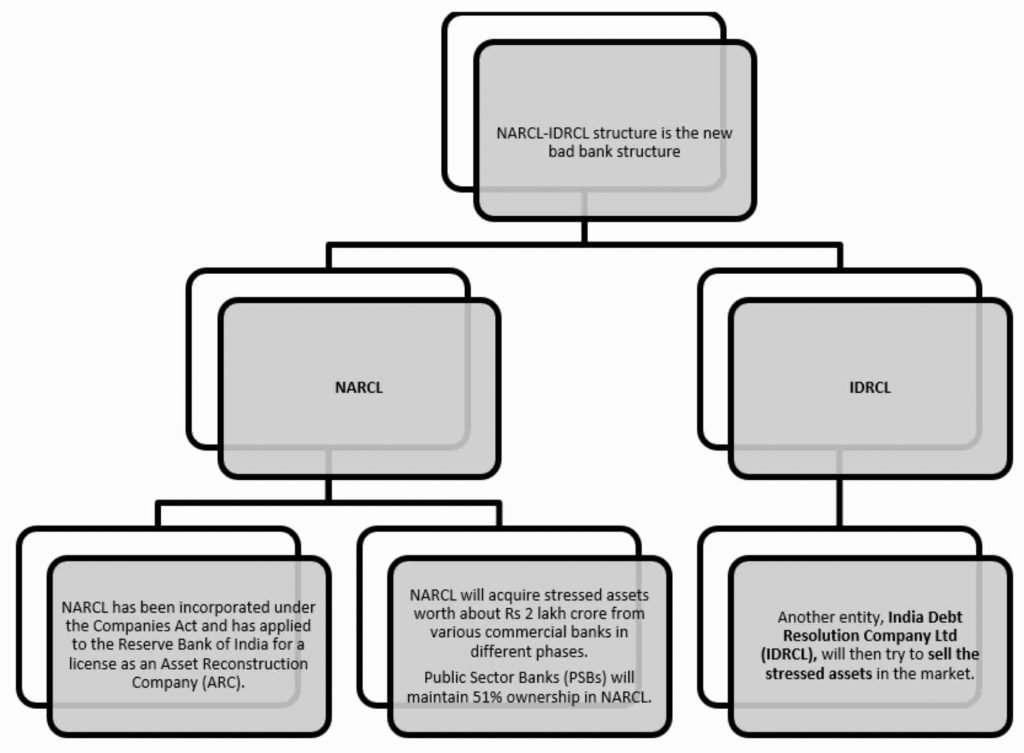
NPA stress in the Indian financial system:
- The Indian banking system has been reeling under the pressure of non-performing assets (NPAs) since 2015.
- The twin balance sheet problem which caused a lot of stress amounted to a huge challenge for the Indian economy.
-
- Twin balance sheet problem is a scenario where the balance sheets of both public sector banks (PSBs) and some corporate houses are in bad shape.
- It is known as the twin balance sheet problem as the challenges faced by the banks are linked to that of the corporate sector.
- The corporates are unable to repay their loans to banks which in turn affect the capacity of the banks to lend.
- The enhanced stresses experienced by both lenders and borrowers had the potential to lead to financial instability and also undermine the growth potential of the Indian economy.
Attempts at resolution of NPAs:
- Various resolution measures like Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), strengthening of Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Securities Interest and Debt Recovery Tribunals, as well as setting up of dedicated Stressed Asset Management Verticals (SAMVs) in banks for large-value NPA accounts were undertaken to bring down NPAs.
- In spite of these efforts, a substantial amount of NPAs continues on the balance sheets of banks primarily because the stock of bad loans as revealed by the Asset Quality Review is not only large but fragmented across various lenders.
Concept of bad bank:
- A bad bank is a bank set up to buy the bad loans and other illiquid holdings of another financial institution.
- The entity holding significant nonperforming assets will sell these holdings to the bad bank at market price.
- It will then manage and dispose of the assets to potential investors for eventual value realization.
- In other words, it will hold problem loans for public sector banks which can then be sold on to investors at a reduced price. This will ultimately help clean up the balance sheets of banks.
- The Union Finance Minister in the budget speech had announced the setting up of an Asset Reconstruction Company Limited and Asset Management Company.
Report on Reforms in Urban Planning Capacity in India
PIB
GS 2: Polity and Governance
Context:
- NITI Aayog today launched a report titled ‘Reforms in Urban Planning Capacity in India’, on measures to ramp up urban planning capacity in India.
About:
- The report makes several recommendations that can unblock bottlenecks in the value chain of urban planning capacity in India.
- Every city must aspire to become a ‘Healthy City for All’ by 2030. The report recommends a Central Sector Scheme ‘500 Healthy Cities Programme’, for a period of 5 years, wherein priority cities and towns would be selected jointly by the states and local bodies.
- Formation of an apex committee at the state level is recommended to undertake a regular review of planning legislations (including town and country planning or urban and regional development acts or other relevant acts).
- It recommends a ‘Citizen Outreach Campaign’ for demystifying urban planning.
- The Central universities and technical institutions in all the other States/UTs are encouraged to offer postgraduate degree programmes (MTech Planning) to cater to the requirement of planners in the country in a phased manner.
- The report recommends the constitution of a ‘National Council of Town and Country Planners’ as a statutory body of the Government of India.
- Also, a ‘National Digital Platform of Town and Country Planners’ is suggested to be created within the National Urban Innovation Stack of MoHUA. This portal will enable self-registration of all planners and evolve as a marketplace for potential employers and urban planners.

