Current Affairs (24th April 2021)
Crew-2 mission
Context:
- Four astronauts were launched to the International Space Station (ISS) from Florida as part of a collaboration between NASA and SpaceX under the Commercial Crew Program.
- The mission is called Crew-2 and is the second crew rotation of the SpaceX Crew Dragon and the first with international partners.
About:
- Out of the four astronauts, two are from NASA and two are from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the European Space Agency (ESA).
- The aim of this test flight was to see if SpaceX capsules could be used on a regular basis to ferry astronauts to and from the ISS.
What will Crew-2 do at the ISS?
- Starting mid-November 2020, Crew-1 team members joined members of Expedition 64 and conducted microgravity studies at the ISS.
- Now, Crew-2 astronauts will join the members of Expedition 65, NASA astronaut Mark VandeHei and cosmonauts Oleg Novitskiy and PyotrDubrov of Roscosmos. They will stay aboard the ISS for six months during which time they will conduct science experiments in low-Earth orbit.
- Their central focus during this time will be to continue a series of Tissue Chips in Space studies. Tissue Chips are small models of human organs that contain multiple cell types that behave similarly to the human body. According to NASA, these chips can potentially speed up the process of identifying safe and effective drugs and vaccines.
- Therefore, scientists can use these tissue chips in space to study diseases that affect specific human organs, which would take months or years to develop on Earth.
What is the Commercial Crew Program?
- The main objective of this program is to make access to space easier in terms of its cost, so that cargo and crew can be easily transported to and from the ISS, enabling greater scientific research. Through this program, NASA plans to lower its costs by sharing them with commercial partners such as Boeing and SpaceX, and also give the companies incentive to design and build the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS).
- Secondly, by encouraging private companies such as Boeing and SpaceX to provide crew transportation services to and from low-Earth orbit, NASA can focus on building spacecraft and rockets meant for deep space exploration missions.

National Panchayati Raj Day
Context:
- 12th National Panchayati Raj Day to be commemorated on 24 April 2021.
- Prime Minister will dedicate the Scheme of SVAMITVA to the entire nation on 24th April 2021. He will also launch distribution of e-property cards to 4.09 lakh property owners on this occasion.

About:
- 24th April, 1993 marks a defining moment in the history of decentralization of power to the grassroots, with the institutionalization of Panchayati Raj, through the Constitution (73rd Amendment) Act, 1992 which came into force with effect from that day.
- Ministry of Panchayati Raj commemorates 24th April of every year as the National Panchayati Raj Day (NPRD), as the 73rd Constitutional Amendment came into force on this date.
- This occasion provides an opportunity for direct dialogue with Panchayat representatives from all over the country as well as recognizing their achievements to empower and motivate them further.
- Every year, on this occasion, Ministry of Panchayati Raj has been awarding the best performing Panchayats/States/UTs across the country under the Incentivization of Panchayats in recognition of their good work for improving delivery of services and public goods.
SVAMITVA
- Towards the objectives of socio-economic empowerment of the rural mass and making them self-reliant, a Central Sector Scheme of Ministry of Panchayati Raj, “Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas’ (SVAMITVA) was launched by the Prime Minister on 24thApril 2020.
- The pilot phase of the Scheme was implemented during 2020–2021 in States of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Madhya Pradesh and few border villages of Punjab & Rajasthan.
- The scheme aims to provide the ‘record of rights’ to village household owners in rural abadi areas and issuance of Property cards.
- The Scheme has been approved for implementation at an outlay of Rs 566.23 cr across the country in phased manner over a period of five years (2020-2025) and would eventually cover approx. 6.62 lakh villages of the entire country.
- Nearly in 40,000 thousand villages in the States of Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand and few border villages of Punjab & Rajasthan drone flying have been completed, along with establishment of Continuous Operating System (CORS) stations’ network across Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab & Rajasthan in the Pilot phase during 2020-21.
- The Scheme has the potential to transform rural India. It will pave the way for using property as a financial asset by villagers for taking loans and other financial benefits, as in the case in towns and cities.
- Further, this is the first time ever that such a large-scale exercise involving most modern technology is being carried out to benefit millions of rural property owners.

#FOSS4GOV INNOVATION CHALLENGE
Context:
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MEITY) has announced #FOSS4GOV Innovation Challenge to accelerate adoption of Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) In Government.
About:
- The #FOSS4GOV Innovation Challenge calls upon FOSS innovators, technology entrepreneurs and Indian Startups to submit implementable open source product innovations in CRM and ERP with possible applications for Govtech in Health, Education, Agriculture, Urban Governance etc.
- India is well positioned to become a vibrant hub for Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) innovations, due to the large number of 4G data subscribers in India, 96% of whom access the digital world via open-source based mobile operating systems (primarily Android).
- Some of India’s largest-government projects (including Aadhaar) and many technology start-ups have also been built using FOSS.
- Acknowledging the huge potential of FOSS, the Government of India had issued a Policy on Adoption of Open Source Software in 2015.
Crude Oil and Natural Gas Production
Context:
- India’s crude oil production and natural gas output declined in 2020-21, according to the latest government data.
About:
- Crude Oil Production declined by 5.2% as private and public firms produced 30.5 million tonnes in 2020-21 compared to 32.17 million tonnes produced during the same period in 2019-2020.
- Natural Gas Production declined by 8.1% and in 2020-21 only 28.67 billion cubic meters was produced compared to 31.18 billion cubic meters in 2019-20.
Why decline?
- No more easy oil and gas available in India and that producers would have to invest in extracting oil and gas using technologically intensive means from more difficult fields such as ultra deepwater fields.
- Low Interest of Foreign Companies
- Domination of State Owned Companies like Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited (ONGC) and Oil India.
- Mounting pressure due to climate change is prompting oil and gas players to diversify into clean energy.
- Ageing wells that have become less productive over time.
Impact:
- Dependence on Imports
- This does not favours India’s vision of Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiative
Way ahead:
- A variety of new technologies can prolong the life of ageing oil fields
- Fiscal framework must ensure adequate returns for producers to deploy Enhanced Oil Recovery mechanisms.
- The current approval processes must be simplified with stipulated timelines for each sign-off, thereby avoiding cost escalations due to delays.
- Potential of Unconventional Hydrocarbons (UHC) such as Shale Oil and gas, tight oil/gas and gas hydrates must be opened now for commercial exploitation.
Centre cracks down on curbs to oxygen movement
Context:
- The Centre invoked the Disaster Management Act, making the District Magistrates and Senior Superintendents of Police personally liable to ensure unhindered inter-State movement of vehicles carrying medical oxygen and to not restrict the supply to a particular State where the oxygen plant is located.
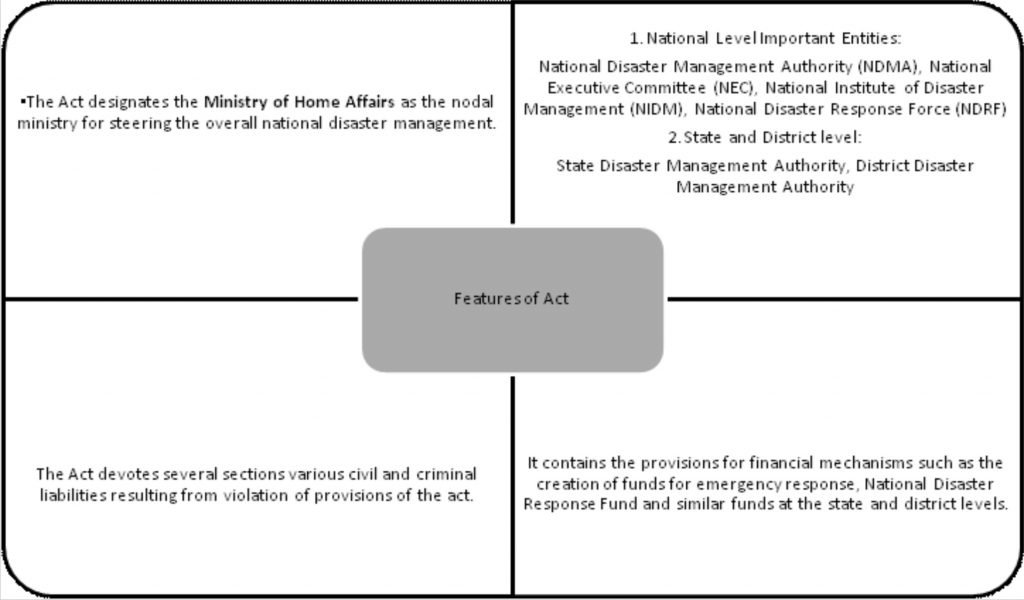
Disaster Management Act of 2005 (DMA 2005):
- It was passed by the government of India in 2005 for the ‘efficient management of disasters and other matters connected to it. However, it came into force in January 2006.
- It is an act passed by the government of India for the efficient management of disasters and other matters connected to it.
- The stated object and purpose of the DM Act is to manage disasters, including preparation of mitigation strategies, capacity-building and more.
Draft Standards for Road-Trains
Context:
- Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has published Draft Standards for Road-Trains.
About:
- To revolutionize the transport of goods and reduce the overall logistic costs, the Automotive Industry Standards Committee has amended its AIS-113 Standard to include the safety requirements of Road-Trains and has hosted the draft on Ministry of Road Transport & Highway’s website.

- The amended standard AIS-113 (Code of Practice for Type Approval of Trailers / Semi-trailers of categories T2, T3 and T4 being towed by Motor Vehicles of categories N2 and N3) has been published for invitation of public comments, after which it shall be notified in due course.
- The standards have been prepared after examining European benchmarks, keeping in mind Indian operating conditions.
