Current Affairs (3rd March 2021)
India-Japan-Sri Lanka
Context
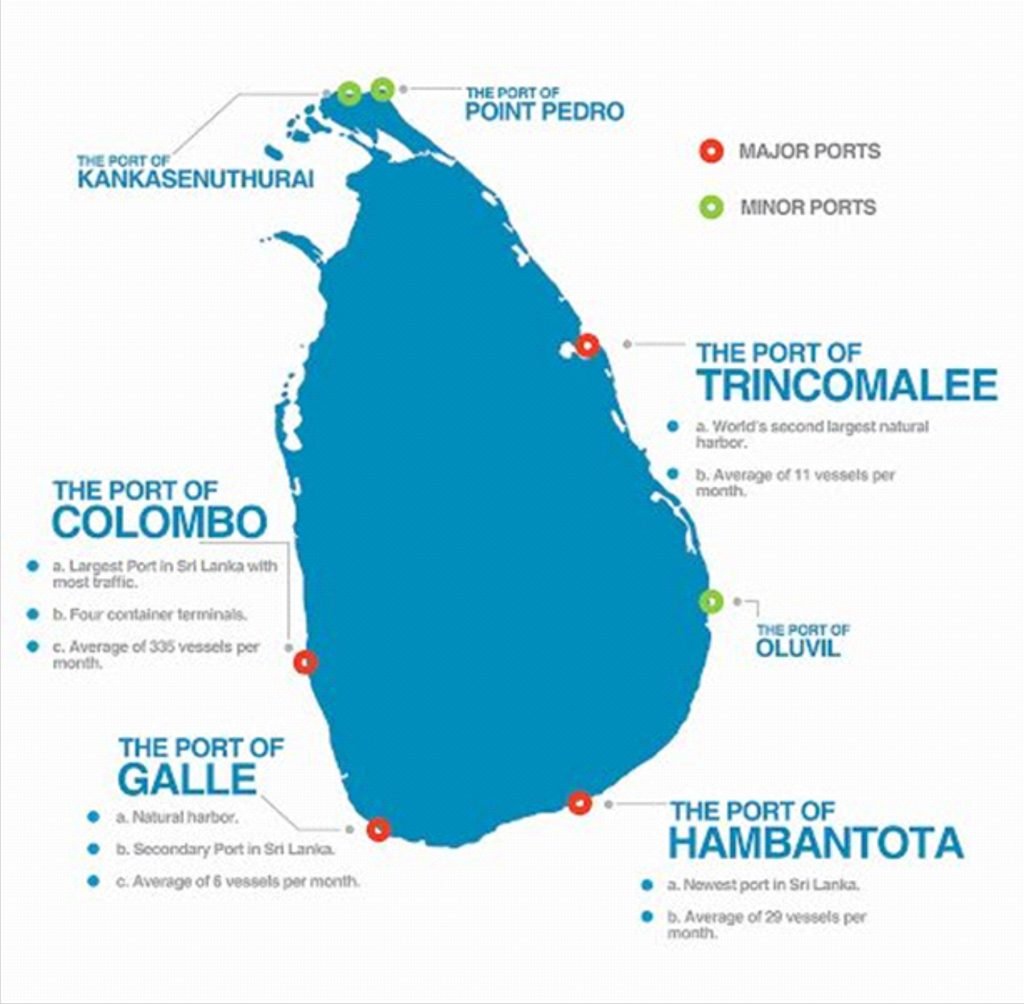
Recently, Sri Lankan government announced that it will develop the West Container Terminal (WCT) at the Colombo Port along with India and Japan.
Background
- Earlier the Sri Lankan government had ejected the two partners from a 2019 tripartite agreement to jointly develop the East Container Terminal (ECT), citing resistance to “foreign involvement”.
Significance
- The ECT already has a 600-metre quay wall, and is adjacent to a shallow terminal, allowing swift cargo transfers.
- The terminal’s further development, which is now to be undertaken by the Sri Lanka Port Authority (SLPA), is aimed at augmenting operations at an estimated cost of upto $700 million.
- The WCT is adjacent to the China-run CICT and just a couple of kilometres away from the China-backed Port City being built on reclaimed land, making it a strategically desirable spot for India, whose concerns over China’s presence in Sri Lanka are well known.
- Colombo’s alternative offer also comes at a time when Sri Lanka is seeking support at the ongoing UN Human Right Council session, where a resolution on the country’s rights record will soon be put to vote.
Ex Desert Flag VI
Context
The Indian Air Force is participating for the first time in Exercise Desert Flag-VI which is going to be held at Al-Dhafra airbase, UAE.
About
- It is an annual multi-national large force employment warfare exercise
- Hosted by the United Arab Emirates Air Force.
- Apart from Indian Air Force, the Air Forces of United Arab Emirates, United States of America, France, Saudi Arabia, South Korea and Bahrain will also participate.
- The aim of the exercise is to provide operational exposure to the participating forces while training them to undertake simulated air combat operations in a controlled environment.
- The participating forces will get an opportunity to enhance their operational capabilities along with mutual exchange of best practices.

Himalayan serow spotted in Assam
Context
Recently, a Himalayan serow, a goat-antelope, has been confirmed as the newest creature to be spotted in Manas National Park, Assam.
About Manas Tiger Reserve
- The Reserve is contiguous with the 1,057-sq. km. Royal Manas National Park in Bhutan.
- It is also a UNESCO Natural World Heritage site, a Project Tiger reserve, an elephant reserve and a biosphere reserve.
- Manas is famous for its population of the wild water buffalo.
- Major river- Manas river (tributary of Brahmaputra river)
Other species
- A medium-sized mammal with a large head, long and coarse hair and mule-like ears, the black-necked crane.
- A colourful Mandarin duck
- A critically endangered white-bellied hero

Revival of Indian Economy
Context
After two quarters of a sharp contraction, now India’s GDP is rising by 0.4% and GVA by 1%.
More on news
- Now, most of the economy sectors like manufacturing, construction is showing growth trend.
- The spending on public administration, defence and other services is getting decreased.
- Also, other sectors like retail, trade, hotels, transport and communication contracted by 7.7%.
Concerns
- Growth numbers alone may still not be capturing the tumult faced by swathes of informal and micro-enterprises, nor do they reflect a recovery in the job market.
- The second wave of infections in industrial hotspots such as Maharashtra, and the risk of infections rising in poll-bound States, do not bode well either for services or the fragile recovery in manufacturing.
Way Forward
- The continuing stress in employment- and contact-intensive services sectors is a worry, and the government must consider support measures.
- A smooth and expeditious roll-out of the vaccine, with the private sector drafted in to achieve scale, is an imperative to help India navigate the bumps ahead more deftly.
India- EU Relations
Context
Recently, the Atmanirbhar Bharat programme and the Budget 2021-22 focused upon increasing investments and phase-wise reduction of import tariffs with strategic partners such as the European Union (EU).
Significance
- This will help in realising the vision of a self-reliant India would entail localising an increasing share of value added along supply chains.
- India has an untapped export potential of $39.9 billion in the EU and Western Europe.
- The top products with export potential include apparel, gems and jewellery, chemicals, machinery, automobile, pharmaceuticals and plastic.
- India benefits from tariff preferences under the EU’s Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) for several of these products.
- However, there are several products where India has export potential in the EU, but these have “graduated” or are at the brink of “graduation” under EU GSP.
- Product graduation applies when average imports of a product from a beneficiary country exceed 17.5% of EU-GSP imports of the same product from all beneficiary countries over three years.
- India’s exports of products such as textiles, inorganic and organic chemicals, gems and jewellery, iron, steel and their articles, base metals and automotives are already out of the ambit of EU-GSP benefits.
Concerns
- There is also a likelihood of losing EU-GSP benefits in other categories such as apparel, rubber, electronic items, sports goods and toys due to product graduation.
- India’s competitors in apparel exports such as Bangladesh would continue to receive tariff benefits in the EU under Everything but Arms Initiative.
- Another competitor, Vietnam, concluded a free trade agreement (FTA) with the EU in 2019.
- India’s negotiation for a Broad-based Trade and Investment Agreement, which commenced in 2007, is yet to materialise due to lack of concurrence in areas like automotives and dairy and marine products.
- India’s cautious approach to FTAs derives from its past experience of an unequal exchange of benefits in several FTAs signed by the country.
Way Forward
- In light of the declining preferential access and the plausible erosion of competitiveness in the EU market, there is clearly a need to deepen trade and investment ties with the region.
- Therefore, a thorough assessment of the benefits from FTA for domestic producers is warranted, with due consideration to the impact on sensitive sectors, and possibility of inclusion of safeguards such as sunset clause on concessions for some items.
- Further, there should also be provisions for aspects such as investment and non-tariff measures (NTMs).
- China has already negotiated a comprehensive agreement on investment. India also needs to negotiate on investment-related aspects with the EU to enhance bilateral investments and foster stronger value chains, especially in technology-intensive sectors in which the EU has a comparative advantage.
- FTAs have some institutional arrangements for NTMs. India should critically review the availability of such arrangements in its negotiations, as also their operationalisation and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Post-Brexit EU finds itself in the midst of a growing need for recalibrating ties with its partner countries. Forging stronger ties with the region through a mutually beneficial agreement could help strengthen Indian manufacturing and revitalise the flailing exports.
LinkedIn Opportunity Index 2021
CONTEXT:
- Recently, the Opportunity Index 2021 has been released by LinkedIn.
Findings:
- As many as 85 per cent of working women in India have said they missed out on a raise, promotion or work offer because of their gender compared to the average of 60 per cent in the Asia-Pacific region.
- More women in India have experienced the impact of gender on career development when compared to the APAC region.
- In India, more than 4 in 5 working women (85 per cent) claim to have missed out on a raise, promotion, or work offer because of their gender, compared to the regional average of 60 per cent.
- Even though 66 per cent of people in India feel that gender equality has improved compared to their parents’ age, more than 7 in 10 working women and working mothers feel that managing familial responsibilities often come in their way of career development.
- About two-thirds of working women or 63 per cent and working mothers or 69 per cent said they have faced discrimination at work because of familial and household responsibilities.
- One in five or 22 per cent working women in India said their companies show a ‘favourable bias’ towards men at work when compared to the regional average of 16 per cent.
- The LinkedIn Opportunity Index 2021 shows that 37 per cent of India’s working women say they get fewer opportunities than men and that only 25 per cent of men agree with this.
- And 37 per cent of the women said they are paid less than men while only 21 per cent of the men shared this sentiment.
US Trade Agenda and 2020 Annual Report
Context:
- The Office of the United States Trade Representative delivered President Biden’s 2021 Trade Agenda and 2020 Annual Report , detailing a comprehensive trade policy in support of the Administration’s effort to help the U.S. recover from the COVID-19 pandemic and build back better.
Key observations
- While India’s large market, economic growth, and progress towards development make it an essential market for many U.S. exporters, a general and consistent trend of trade-restrictive policies have inhibited the potential of the bilateral trade relationship.
- Recent Indian emphasis on import substitution through a “Make in India” campaign has epitomised the challenges facing the bilateral trade relationship.
- The report describes the Trump administration’s revocation of India’s preferential trading status under the Generalised System of Preferences (GSP) program in June 2019 and the ensuing discussion to achieve a mini trade deal (“package”) throughout 2020.
Make in India campaign:
- Launched by Prime Minister Modi in 2014 to incentivise production in India.
- It seeks to encourage manufacturing in India and galvanize the economy with dedicated investments in manufacturing and services.
TARGETS:
- To increase the manufacturing sector’s growth rate to 12-14% per annum in order to increase the sector’s share in the economy.
- To create 100 million additional manufacturing jobs in the economy by 2022.
- To ensure that the manufacturing sector’s contribution to GDP is increased to 25% by 2022 (revised to 2025) from the current 15-16%.

