Current Affairs (4th June 2021)
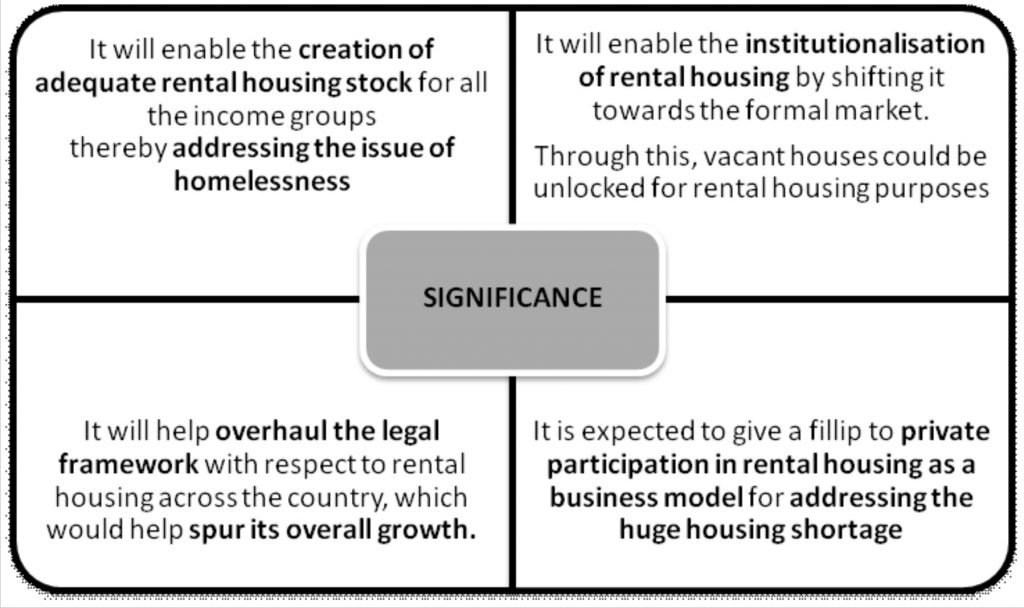
Model Tenancy Act
Context:
- After releasing the draft in 2019, the Centre recently formally approved the Model Tenancy Act (MTA) to streamline the process of renting property in India.
About:
- States and Union Territories can adopt the Model Tenancy Act by enacting fresh legislation or they can amend their existing rental laws.
- The model Act, if passed by the States and UTs, would prescribe the norms for lease agreements, deposits, dispute handling and other aspects of rental properties.
- Separate rent authorities, courts and tribunals will be set up in districts to protect the interests of both the owner and the tenant.
Koklass pheasant
Context:
- The rare subspecies of the male Koklass pheasant called the Pucrasia macrolopha meyerihas been photographed for the first time in India.
About:
- Koklass pheasant is described as a resident bird of the Western Himalayas.
- They are not known for migration and are essentially residential birds of mid-altitude dense forests in the Himalayas.
- Of the nine subspecies identified across the world, four are found in the Uttarakhand, Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh.
- The male subspecies — meyeri — had not been recorded outside China and Tibet.
- The bird has a distinctive golden ring and its emerald, green head distinguishes it from the female.
- The bird has been declared extinct in Tibet.
- The golden collar is not seen in the other subspecies found in India.
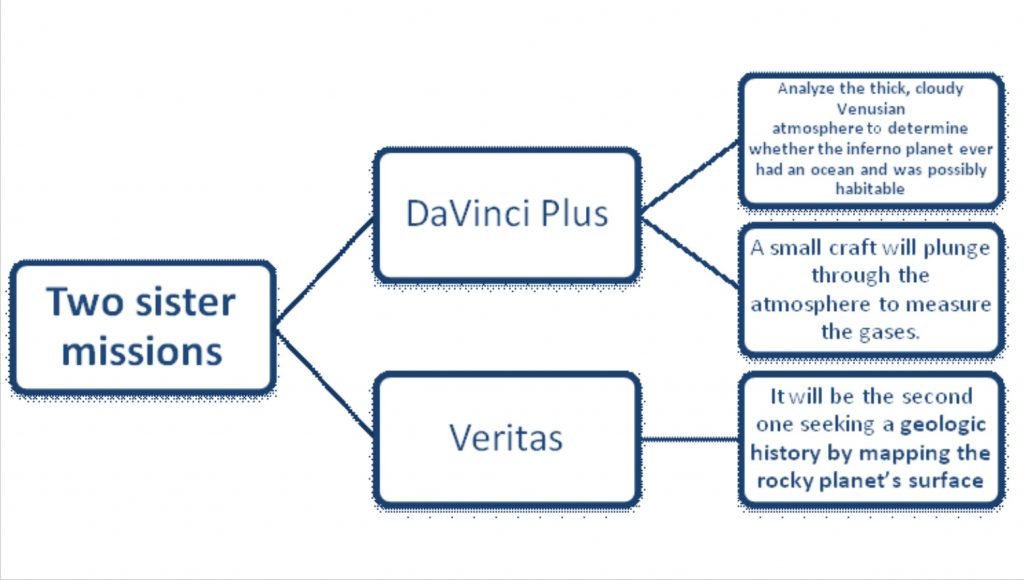
Two new robotic missions to Venus
Context:
- Recently, the NASA announced two new robotic missions to Venus. Earlier, scientists obtained new data about Venus by bouncing radio waves off the planet.
Aim:
- The two sister missions aim to understand how Venus became an inferno-like world capable of melting lead at the surface.
Significance:
- The new missions will give fresh views of the planet’s atmosphere, made up mostly of carbon dioxide, down to the core.
Previous Missions:
- Indian Initiative: India plans to launch a new orbiter named Shukrayaan to Venus in 2024.
- US:Mariner series 1962-1974, Pioneer Venus 1 and Pioneer Venus 2 in 1978, Magellan in 1989.
- Russia:Venera series of space craft’s 1967-1983, Vegas 1 and 2 in 1985.
- Japan:Akatsuki in 2015.
- Europe:Venus Express in 2005.
Sedition Case
Context:
- The Supreme Court quashed the sedition case registered against journalist Vinod Dua in Shimla, Himachal Pradesh, more than a year after an FIR was filed against him by a local BJP leader over comments Dua made on his YouTube show criticising the Central government.
Issue:
- The complainant had alleged that Dua had accused Prime Minister Narendra Modi of using “deaths and terror attacks” to get votes, and the journalist was charged under sections 124A (sedition), 268 (public nuisance), 501 (printing matter known to be defamatory) and 505 (statements conducive to public mischief).
Stand of SC:
- On the issue of protection of freedom of speech and expression of media personnel, it said, “Every journalist is entitled to protection under the Kedar Nath Singh judgment (the famous verdict of 1962 on the scope and ambit of offence of sedition in the IPC).”
Kedar Nath Singh v State of Bihar (1962):
- In 1953, Kedar Nath Singh, a member of the Forward Communist Party from Bihar, took on the ruling Congress during a rally at Begusarai, where he said,
“Today, the dogs of CBI are loitering around Barauni [in Begusarai]. Many official dogs are sitting even in this meeting. The people of India drove out the British from the country and elected these Congress goondas to the gaddi.
As we drove out the British, we shall strike and drive out these Congress goondas as well. They have today established a rule of lathis, bullets in the country.
We believe in revolution which will come, and in the flame of which, capitalists, zamindars and Congress leaders will be reduced to ashes, and on their ashes will be established a government of the poor and the downtrodden people of India.”
- The fiery speech led to his conviction and imprisonment by a first-class magistrate on sedition charges, and an appeal to the Patna High Court was struck down.
- Then 1962, an appeal by Singh came before the Supreme Court, in which he questioned the constitutional validity of Section 124A, contending it stifled his right to free speech under Article 19 of the Constitution.
- The top court had to lay down the law in the face of two directly conflicting interpretations of Section 124A by British era courts.
- The two previous judgments, one from 1942 and the other from 1947, expressed contradictory views on whether the incitement to violence or a tendency to disturb public order was a necessary ingredient of the offence under Section 124A.
What did the Supreme Court rule?
- In a landmark verdict, a Constitution Bench (five-judge) of the top court upheld the validity of section 124A (sedition) of the IPC, but also attempted to restrict the colonial-era law’s scope for misuse by trying to demarcate the difference between which acts amounted to sedition and which ones did not.
- It said that any act that had the “effect of subverting the Government” by violent means or creating public disorder would come within the definition of sedition.
- It also upheld Section 505 (statements conducive to public mischief) as constitutionally valid.
- However, the court ruled that disapproval of the measures of government with a view to their improvement or alteration by lawful means is not sedition.
- It held that “comments, however strongly worded, expressing disapprobation of actions of the Government, without exciting those feelings which generate the inclination to cause public disorder by acts of violence” would not attract the penal offence.
- A citizen has a right to say or write whatever he likes about the Government, or its measures, by way of criticism or comment, so long as he does not incite people to violence against the Government established by law or with the intention of creating public disorder.
Relaxation Two Child Policy by China
Context:
- Recently, China relaxed its two-child policy and announced it will now allow three children per married couple.
- It would increase the retirement age by a few months every year. For the past four decades, the retirement age in China has been 60 for men and 55 for women.

Decreasing Population:
- A problem unique to China, though, is that unlike the other developed countries part of this trend, it is still a middle-income society, despite being the world’s second-largest economy.
- Prosperous countries like Japan and Germany, which face similar demographic challenges, can depend on investments in factories, technology, and foreign assets.
- China, however, still depends on labour-intensive manufacturing and farming.
- A drop in demographic dividend could thus hurt China and other developing nations like India more than those in the rich world.
- When the young population in a country declines, it creates labour shortages, which have a major detrimental impact on the economy.
- More older people also means that demands for healthcare and pensions can soar, burdening the country’s social spending system further when fewer people are working and contributing to it.
Memorandum of Understanding Between India and Maldives
Context:
- Recently, the Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister was apprised of the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between India and Maldives on cooperation in the field of Sustainable Urban Development.
About:
- The MoU comes into effect on the date of signing by the two contracting parties i.e. 20th February, 2021 and will remain in force for indefinite period.
- A Joint Working Group (JWG) will be constituted to strategize and implement programmes on cooperation under the framework of the MoU.
- The Joint Working Group will meet once in a year, alternately in Maldives and in India.
- Objectives: To facilitate and strengthen India-Maldives technical cooperation in the field of sustainable urban development including Urban Planning, Smart Cities Development, Solid waste management, Affordable housing, Urban Green Mobility, Urban Mass Rapid Transport, smart cities development and any other related area mutually agreed by contracting parties.
- To promote strong, deep, and long-term bilateral cooperation in the field of Sustainable Urban Development between the two countries.
- The MoU is expected to create employment in the areas of sustainable urban development.
Bal Swaraj
Context:
- According to Bal Swaraj Portal, as of May 29, 2021, nearly 10,000 children in the country are in immediate need of care and protection. They include children aged between zero and 17 orphaned or abandoned during the COVID-19 pandemic since March 2020.
About:
- The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has created an online tracking portal “Bal Swaraj (COVID-Care)”.
- NCPCR has developed it in furtherance to its function as a monitoring authority under section 109 of the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015 and in view of the growing problem related to children affected by COVID-19.
- This portal will do online tracking and real-time monitoring of Childrens who have lost both its parents or either of the parent during COVID-19 and need care and protection under Section 2(14) of the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015.
- It will track children affected by COVID-19 right from the production of children before the Child Welfare Committee (CWC) to the restoration of the children to their parent/guardian/relative and its subsequent follow-up.
- The data will be filled in the portal by the district officers and State officers for each child.

