Current Affairs (6th February 2021)
Tax interest incomes
CONTEXT:
- In the Union Budget 2021, Finance Minister announced a decision to tax interest incomes at current income tax rates on annual Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) and Voluntary Provident Fund (VPF) contributions by employees of over Rs 2.5 lakh a year.
REASONS:
- Many people put huge sums of money annually towards EPF and earned interest income from it without having to pay any tax.
IMPACT:
- Help restore equality and discourage high-income earners or high net-worth individuals (HNIs) who make large voluntary contributions to provident fund annually from making high annual contributions towards provident fund.
|
EPF |
VPF |
| Mandatory for any company with 20+ employees.
Both employer and employee are required to contribute some part of the monthly salary of the employee (generally 12%) into the EPF investment account. |
It is a voluntary scheme which allows employees to voluntarily contribute to their PF account after contributing 12% as per the EPF guideline.
The interest rate with VPF is similar to EPF and employees can contribute up to 100% of their salary. |
Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana
CONTEXT:
- Till 2020 financial year (FY), this scheme has crossed 75 crore eligible women.
- A total sum of Rs. 5,931.95 crore was paid to 1.75 crore eligible beneficiaries between financial year 2018 and 2020.
ABOUT:
- Maternity Benefit Programme
- Implemented in all the districts of the country
- Announced on December 31, 2016.
- Centrally sponsored scheme
- Executed by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- In accordance with the provision of the National Food Security Act, 2013.
- Beneficiaries: Pregnant women and lactating mothers (PW&LM) excluding who are in regular employment with the Central
- Government or the State Governments or PSUs or those who are in receipt of similar benefits under any law for the time being in force.
- All eligible PW&LM who have their pregnancy on or after 1st January 2017 for the first child in the family.
- Receive ₹ 5,000 on the birth of their first child in three instalments, after fulfilling certain conditionalities like early registration of pregnancy, ante-natal check-up and registration of the birth of the child and completion of first cycle of vaccination for the first living child of the family.
- The eligible beneficiaries also receive cash incentive under Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY). Thus, on an average, a woman gets ₹ 6,000.
- Objective : To help expectant mothers meet enhanced nutritional requirements as well as to partially compensate them for wage loss during their pregnancy.

Farm exports
Context:
- Farm exports have registered 9.8% growth for the period of April-December 2020, according to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
ABOUT:
- Overall merchandise exports include all the goods manufactured in India registered 15.5% fall while Farm exports include only the agricultural products registered 9.8% growth.
- Earlier, the government of India replaced Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) with Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Product (RoDTEP) scheme to further enhance exports.
- Reasons For Growth in Farm Exports:
- Rising International Prices – According to Food Price Index, released by FAO UN, FPI has increased from a 48-month-low to a 78-month-high. Restoration of supply chains post-Covid has made exports of non-basmati rice, sugar, oilseed meals, cotton and even wheat and other cereals (mainly maize) products from India competitive.
- Agriculture Exempted from Lockdown – Farmers harvested a bumper rabi crop during April-June.
- Chinese Stockpiling – China had increased imports of maize, wheat, soyabean and barely, sugar and milk powder to build strategic food reserves amid geopolitical tensions.
- India’s Surplus Monsoon – No serious weather issues; both 2019 and 2020 recorded surplus monsoon rainfall along with timely onset of winter.
- Dry Weather of Different Countries like Argentina, Brazil, Ukraine, Thailand and Vietnam.
WAY AHEAD:
- It can help increase crop prices when the next rabi harvest is due from March 2021. This may be politically useful in a context of farm unrest.
- It will help in achieving the USD 5-trillion economy goal.
- It will help achieve an ambitious target of doubling farmers’ income by 2022.
Transgender community
CONTEXT:
- The government is working on an umbrella scheme to address issues of access to health, education, welfare, skill upgradation, shelter, and economic support and livelihood for the transgender community.
- Government had enacted the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 for the welfare of the community.
ACT, 2019:
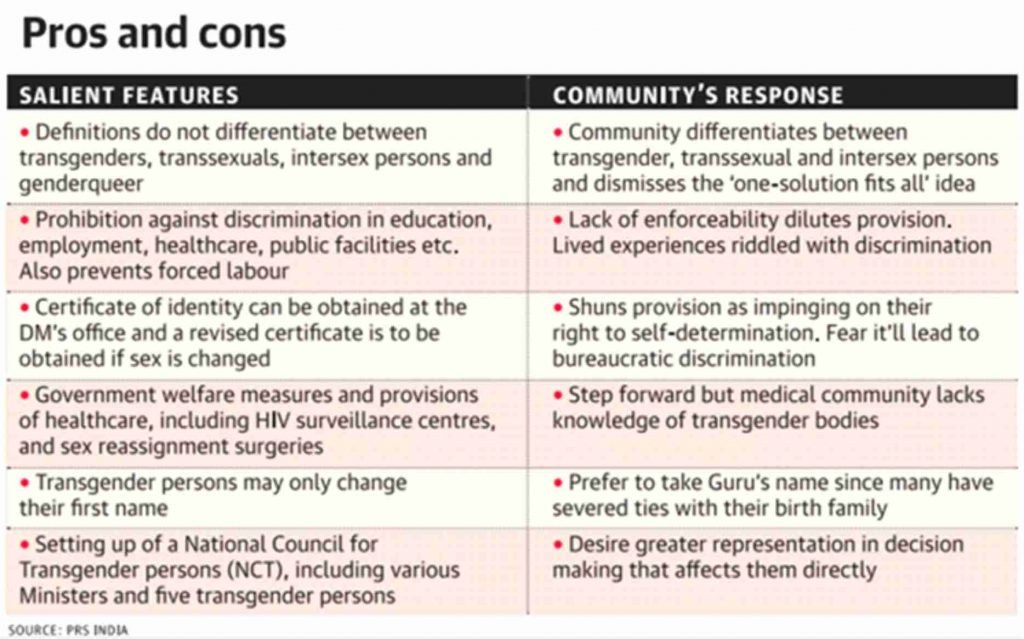
- The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 is an act of the Parliament of India with the objective to provide for protection of rights of transgender people, their welfare, and other related matters.
- The Bill defines a transperson as someone whose gender does not match the one assigned at birth.
- It prohibits discrimination against them in employment, education, housing, healthcare and other services.
- The Bill allows self-perception of gender identity. But it mandates that each person would have to be recognised as ‘transgender’ on the basis of a certificate of identity issued by a district magistrate.
MORE FACTS:
- Act deals with the issue of grant of identity certificates and lays down a streamlined procedure for it, besides making provisions for non-discrimination, equal opportunities in employment, schemes on education, social security and accessible healthcare for the community.
- National portal enabled the transgender community to apply for identity certificates from the District Magistrate concerned, and the portal has received 259 applications so far.
- Government has constituted a National Council for Transgender Persons – a platform for the representatives of the community — to act as an apex body to address the community’s concerns.
- The Council is headed by the Minister of Social justice and Empowerment and draws participation from the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Home Affairs, Housing and Urban Affairs, Education, Rural Development, Labour and Employment, Legal Affairs, Niti Aayog, etc.
- Government has provided for one-time assistance of Rs 1,500 for each member of the community through the NCBCFDC during the pandemic, and 5,711 people have benefited from direct transfers.
- Ration kits were distributed through the district administration and medical camps were also organised in eight states which were attended by 1,005 people.
CADRE MERGE
CONTEXT:
- THE GOVERNMENT introduced a Bill in the Rajya Sabha to merge the IAS, IPS and IFS cadre of Jammu and Kashmir with that of Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Mizoram and Union Territories (AGMUT) cadre.
- The cadres had been merged last month through an Ordinance.
- The move has allowed officers posted in these states and union territories to work in Jammu and Kashmir and vice versa.
REASONS:
- Paucity of officers in the newly created UT of Jammu and Kashmir. There is a huge deficiency of officers of All India Services in the J&K.
- The J&K Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, 2021 seeks to amend the J&K Reorganisation Act, 2019 which had then made provision for retention of the J&K cadre for existing officers and stated that new officers posted there would henceforth come from the UT cadre.
- The developmental schemes, centrally sponsored schemes and other allied activities suffer due to non-availability of All India Officers in the existing cadres of J&K.
- There is a requirement of merging AGMUT cadre so that the officers in this cadre can be posted in the J&K to meet out any deficiency to some extent.
- Bill is being brought “in order to provide uniformity in the governance of all the union territories and to further enhance efficiency in their administration.
e-NAM platform
CONTEXT:
- More than 69 crore Farmers & 1.55 Lakh traders are registered on e-NAM platform so far.
e-NAM (Electronic National Agriculture Market)
- Online trading platform for agriculture produce
- Aims to help farmers, traders, and buyers with online trading and getting a better price by smooth marketing.
- Implemented by: Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC) under the aegis of Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare.

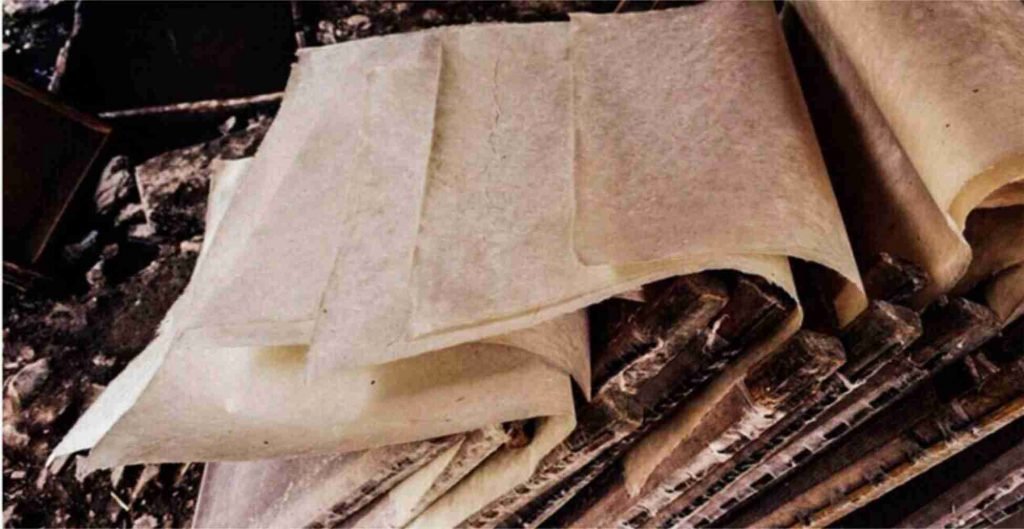
Monpa handmade paper
CONTEXT:
- Gradually this art became an integral part of local custom and culture of Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh.
ABOUT:
- 1000-year-old heritage art of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Art of making handmade paper originated among the Monpas over 1000 years ago.
- The fine-textured handmade paper, which is called ‘Mon Shugu’ in the local dialect, is integral to the vibrant culture of the local tribes in Tawang.
- The Monpa handmade paper is made from the bark of a local tree called ‘Shugu Sheng’, which has medicinal values
Monpa:
- The Monpa are a major tribe of Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India. The Monpa are believed to be the only nomadic tribe in Northeast India – they were totally dependent on animals like sheep, cow, yak, goats and horses.
- The Monpa share very close affinity with the Sharchops of Bhutan. Apart from paper making, the Monpa are also known for wood carving, Thangka painting, carpet making and weaving.
- The Monpa are generally adherents of the Gelug sect of Tibetan Buddhism, which they adopted in the 17th century as a result of the influence of the Bhutanese-educated Merag Lama.

