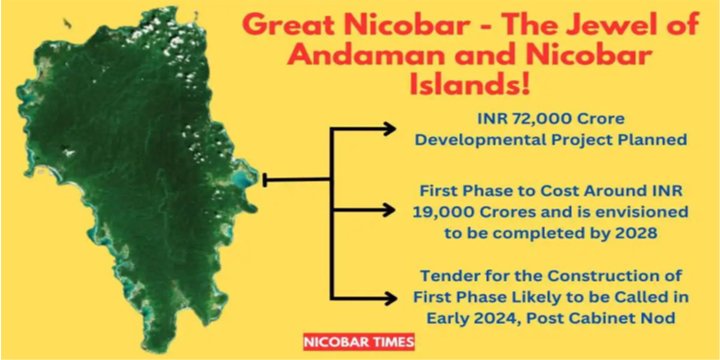
GREAT NICOBAR INFRA PROJECT
The Central government’s Rs 72,000 cr-Great Nicobar Island (GNI) infrastructure project has also faced legal challenges in the National Green Tribunal (NGT) and the Calcutta High Court, which has jurisdiction over the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
ABOUT GREAT NICOBAR ISLAND
- Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands, a sparsely inhabited 910-sq-km patch of mainly tropical rainforest in southeastern Bay of Bengal.
- Indira Point on the island, India’s southernmost point, is only 90 nautical miles (less than 170 km) from Sabang at the northern tip of Sumatra, the largest island of the Indonesian archipelago.
- Great Nicobar has two national parks (Galathea Bay National Park and Campbell Bay National Park, a biosphere reserve (Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve.), small populations of the Shompen and Nicobarese tribal peoples, and a few thousand non-tribal settlers.
ABOUT THE PROJECT
- NITI Aayog has come up with a plan for the Holistic Development of Great Nicobar Island.
- Project implementation agency is the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- Mega project includes:
- international container transshipment terminal (ICTT),
- a military-civil dual use airport,
- a solar power plant and
- an integrated township.
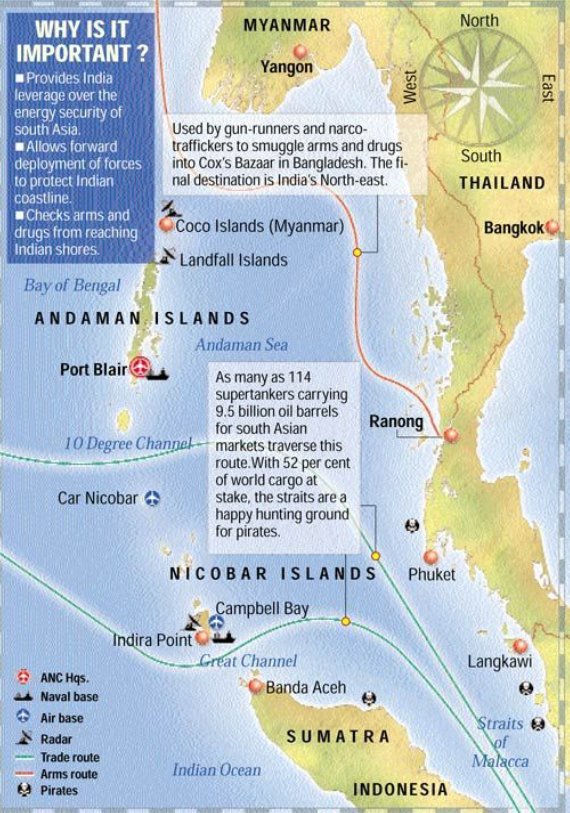
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE PROJECT
- Strategic Importance as it is in close proximity with South East Asia as well as SL. It will give a push to our Act East Policy.
- Enhanced Security as it will give us a base deep down the IOR. Maritime Piracy, terrorism, illegal trade & undue dominance of China can be tackled.
- It can create an economic trade hub in Andaman & Nicobar Island.
- It may promote tourism.
- It will also increase employment.
THE ENVIRONMENTAL CONCERNS
- The proposed infra upgrade has been opposed on grounds of the threat it poses to the ecology of the islands.
- The opposition — by wildlife conservation researchers, anthropologists, scholars, and civil society— has focused on the potentially devastating impact on the Shompen, a particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG) of hunter-gatherers with an estimated population of a few hundred individuals who live in a tribal reserve on the island.
- It is feared that the port project will destroy coral reefs with spinoff effects on the local marine ecosystem, and pose a threat to the terrestrial Nicobar Megapode bird and leatherback turtles who nest in the Galathea Bay area.
- The proposed port is in a seismically volatile zone that saw permanent subsidence of about 15 ft during the 2004 tsunami.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.