LIPULEKH PASS DISPUTE
- On 20 August 2025, India rejected Nepal’s objections to the resumption of border trade between India and China through the Lipulekh Pass, located in Uttarakhand.
- Nepal had raised formal objections after China’s Foreign Minister Wang Yi visited India on 19 August 2025, during which both countries announced reopening of key Himalayan trade routes:
- Lipulekh Pass – Uttarakhand
- Shipki La Pass – Himachal Pradesh
- Nathu La Pass – Sikkim
- India stated that Nepal’s territorial claims are not supported by historical facts or evidence.
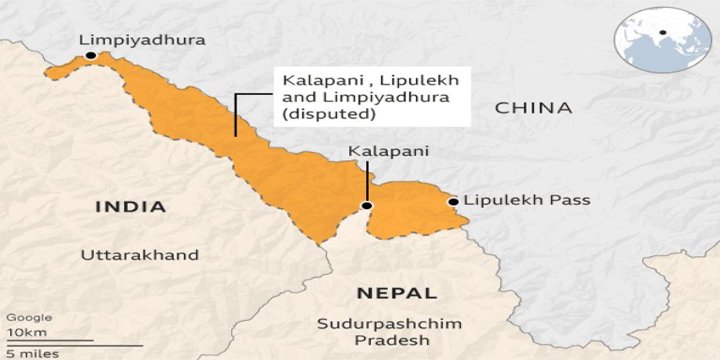
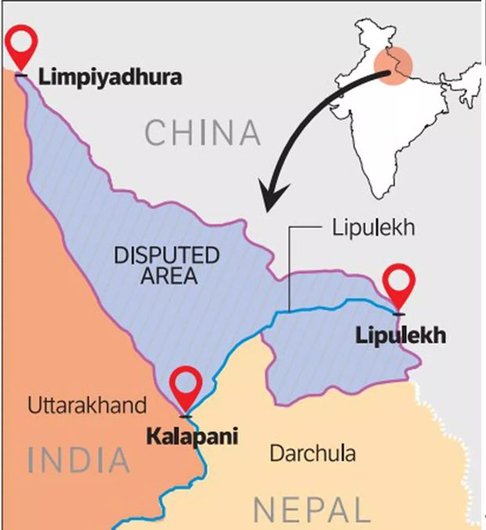
- Nepal reaffirmed its position, citing its official map enshrined in the Constitution, which claims Limpiyadhura, Lipulekh, and Kalapani as its territory.
| Feature |
Details |
| Geographical Location | In the Kumaon region of Uttarakhand, near the India-Nepal-China trijunction |
| Altitude | Approximately 5,334 meters or 17,500 feet above sea level |
| Connectivity | Connects Uttarakhand (India) with Tibet Autonomous Region (China) |
| District | Located in Pithoragarh district, Uttarakhand |
| Strategic Use | Important trade route and access point for Kailash Mansarovar Yatra pilgrimage |
| Historical Trade Use | Trade through this pass began in 1954; formally reopened in 1992 as India’s first trade post with China |
INDIA CHINA TRADE THROUGH HIMALAYAN PASSES
| Border Pass | State | Year Opened for Trade | Significance |
| Lipulekh Pass | Uttarakhand | 1992 | First border trade post with China; religious and strategic |
| Shipki La Pass | Himachal Pradesh | 1994 | Connects Kinnaur district with Tibet; trade in wool, salt |
| Nathu La Pass | Sikkim | 2006 | High-volume trade; links Gangtok to Lhasa |
GEOPOLITICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF LIPULEKH PASS
- Trijunction Point: Close to where India, Nepal, and China meet.
- Strategic Height: Provides surveillance advantage and access to the higher Himalayas.
- Pilgrimage Route: Part of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra, attracting religious pilgrims from India.
- Border Infrastructure: Presence of military roads, border outposts, and ongoing infrastructure development by India.
INDIA’S OFFICIAL POSITION
- Trade History:
- India-China border trade through Lipulekh has been ongoing since 1954.
- Recent disruptions were due to COVID-19 and other developments, not related to territorial disputes.
- Territorial Claims:
- Nepal’s claim over Lipulekh, Limpiyadhura, and Kalapani is not based on historical facts or legal treaties.
- India rejects unilateral and artificial expansion of territorial claims.
- Diplomatic Stance:
- India remains open to constructive dialogue with Nepal on agreed outstanding boundary issues, through bilateral mechanisms.
NEPAL’S OBJECTIONS & CLAIMS
- Nepal’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs objected to the resumption of trade through Lipulekh.
- Cited the official map of Nepal, adopted in 2020, which shows:
- Limpiyadhura
- Kalapani
- Lipulekh
…as lying east of the Mahakali River, thereby claimed as part of Nepali territory.
- The Nepalese Constitution has been amended to include this revised map.
HISTORICAL BACKGROUND
- Treaty of Sugauli (1815–1816):
- Signed between British India and the Kingdom of Nepal.
- Mahakali River (called Kali River) was designated as the western boundary of Nepal.
- Interpretational Dispute:
- India claims that the origin of the Mahakali River lies east of Kalapani, placing the area within Indian territory.
- Nepal claims the river originates near Limpiyadhura, placing Kalapani, Lipulekh, and Limpiyadhura within Nepal.
- Status of Dispute:
- Boundary disputes have remained unresolved, but were previously handled through bilateral dialogue.
RELIGIOUS & CULTURAL IMPORTANCE
- Lipulekh is part of the route for Kailash Mansarovar Yatra, undertaken by Hindu pilgrims to Mount Kailash and Lake Mansarovar in Tibet.
- The Vyas Valley, where the pass is located, is associated with ancient Indian texts and mythology.
WAY FORWARD
- Bilateral Dialogue:
- Revive India-Nepal Boundary Working Group to resolve issues through facts and evidence.
- Cartographic Restraint:
- Avoid unilateral actions such as map revisions without mutual agreement.
- Public Diplomacy:
- Educate citizens in both countries about historical treaties and maps to avoid misinformation.
- Strategic Clarity:
- Maintain open channels with both Nepal and China, balancing sovereignty and diplomacy.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Continue border infrastructure upgrades to improve logistics and monitoring without escalating tensions.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.