NATO @ 75 YEARS
At an event marking 75 years of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) on April 4, Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg said “NATO is bigger, stronger, and more united than ever.”
With 32 member-states – the most it has ever had – that may be true in one regard. However, the grouping also faces significant challenges. Its expansion is believed to be a key factor behind Russia’s 2022 invasion of Ukraine and the continued conflict.
On the anniversary, Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov spoke to reporters about Russia’s ties with NATO, saying relations have now “slipped to the level of direct confrontation.”
WHY WAS NATO ESTABLISHED?
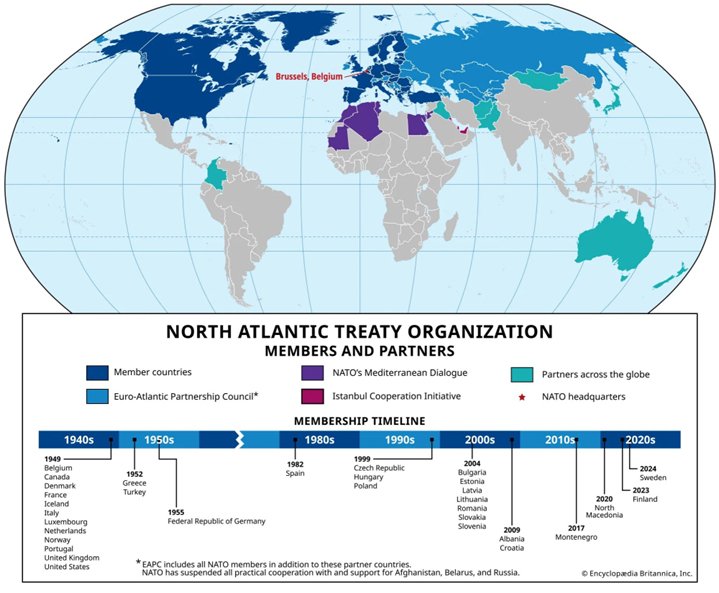
NATO is a Western security alliance founded on April 4, 1949, with 12 founding members – Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom and the United States.
THE UN NATO CONNECTION:
They signed the Washington Treaty, which gets its power from Article 51 of the United Nations Charter, “which reaffirms the inherent right of independent states to individual or collective defence.”
WHAT IS COLLECTIVE DEFENCE?
At the very heart of the alliance is the concept of “collective security” – an attack on any of the members is seen as an attack on all of them and demands collective action.
WHAT WAS THE NEED FOR SUCH A TREATY TO BE ADOPTED?
This was deemed necessary in 1949 amid the Cold War rivalry between the then USSR and the US, over ideological and economic superiority.
WHICH PROVISION OF WASHINGTON TREATY ENTAILS COLLECTIVE DEFENCE?
Article 5 of the Washington Treaty, on collective security, was added “to counter the risk that the Soviet Union would seek to extend its control of Eastern Europe to other parts of the continent.”
DOES IT NECESSITATE DIRECT MILITARY INTERVENTION BY ALL THE MEMBERS?
It doesn’t necessitate direct military intervention constituting all members. The scale of action is dependent on each member country “as it deems necessary”.
HAS ARTICLE 5 BEEN INVOKED TILL NOW?
The only time the article has been invoked so far was following the September 11, 2001 attacks on the US.
NATO forces were sent to Afghanistan and deployed for nearly 20 years.
CHALLENGES FACED BY NATO
- Unequal military spending by the members:
- In 2014, NATO members pledged to spend at least 2% of their GDP on defence after Russia annexed Crimea.
- In 2019, there were clear tensions between members. US President Donald Trump argued that countries needed to raise their military spending.
- Trump criticised this, saying it was unfair to countries like the US, who doing the requisite spending.
- As of 2023, of the 30 countries member countries then, 11 spent more than the limit.
- Differences between the member countries:
- While NATO has a liberal “open door” policy for membership, all members need to ratify the entry of a new applicant for it to become a member. Turkey held off against Sweden and Finland for long, as the two countries’ politicians had criticised Turkey in the past over human rights violations. Turkey also claimed the countries gave refuge to “terrorists”.
- In 2019, French President Emmanuel Macron said there was “a lack of strategic coordination between European allies on the one hand and the United States and Turkey, on the other”.
- Funding the Russia-Ukraine war has again become a source of disagreements among members, much to Ukraine’s displeasure.
- The secretary General of NATO suggested creating a five-year, $107 billion fund for Ukraine, but the suggestion drew mixed reactions from members.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.