US WITHDRAWS SANCTIONS WAIVER ON CHABAHAR
Why in News
- On September 19, 2025, the United States announced the withdrawal of thesanctions waiver granted in 2018 to India for its involvement in the development of Iran’s Chabahar Port.
- The waiver, issued under the Iran Freedom and Counter-Proliferation Act (IFCA), had allowed India to operate at the Chabahar port without facing US sanctions.
- The waiver will be revoked effective September 29, 2025, significantly impacting India’s strategic and economic interests in the region.
- The decision follows US military strikes on three Iranian nuclear facilities on June 22, 2025, escalating tensions between Washington and Tehran.
- Location: Southeastern Iran, along the Gulf of Oman, near the border with Pakistan.
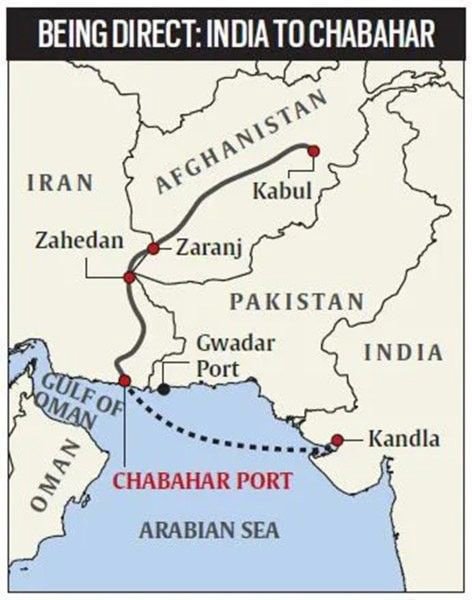
- Strategic Position: Provides direct access to the Arabian Sea and bypasses Pakistan for trade with Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- Components:
- Shahid Beheshti Terminal – being developed by India.
- Shahid Kalantari Terminal – developed by Iran.
- Importance: First deepwater port in Iran, capable of handling large cargo vessels, enhancing Iran’s role in global trade.
TIMELINE

INDIA’S INVESTMENTS & OPERATIONS
- India’s involvement is focused on the Shahid Beheshti terminal.
- Operated by India Ports Global Ltd (IPGL) since December 2018.
- Aimed at enhancing trade with Afghanistan and Central Asia by bypassing Pakistan.
- India’s investment so far includes:
- ₹100 crore (2023–24 budget) for Chabahar port development.
- Additional ₹200 crore in aid to Afghanistan (2022 onwards).
INFRASTRUCTURE STATUS OF THE PORT
- The Shahid Beheshti terminal is being developed in four phases.
- Upon completion:
- Total capacity: 82 million tonnes per year.
- Infrastructure: 32 jetties – including 16 multipurpose, 10 container, 3 oil, and 3 dry bulk jetties.
- As of 2019, port capacity had reached 5.8 million tonnes per year.
- A cruise terminal was also built to increase cargo handling.
STRATEGIC IMPORTANCE
For India
- Bypasses Pakistan: Vital trade route for connecting with Afghanistan, Central Asia, and Europe.
- Connectivity to INSTC: Integral to the International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC), linking India to Russia and Europe via Iran and the Caspian Sea.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) announced during the G20 Summit 2023
- IMEC connects India → UAE → Saudi Arabia → Jordan → Israel → Europe
- Chabahar was meant to serve as an eastern complement for land access to Central Asia and Russia
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) announced during the G20 Summit 2023
- Counterbalance to Gwadar: India’s answer to China’s development of the Gwadar Port in Pakistan under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
For Iran
- Facilitates economic development and international trade amid Western sanctions.
- Strengthens strategic partnerships with India and potentially Central Asian countries.
For Afghanistan
- Offers regional connectivity independent of Pakistan.
- Facilitates Indian humanitarian and trade assistance.
BACKGROUND
- The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) or Iran nuclear deal was signed in 2015 between Iran and P5+1 countries (US, UK, France, China, Russia + Germany).
- In 2018, the Trump administration unilaterally withdrew from JCPOA and imposed sanctions on Iran under the “maximum pressure” campaign
- An exception (waiver) was granted to India for Chabahar port under Section 1244(h) of the Iran Freedom and Counter-Proliferation Act (IFCA):
- Justification: The port’s use in Afghanistan’s reconstruction and humanitarian needs.
- In September 2025, the US revoked this waiver, stating that continued operations at the port would now be considered sanctionable.
TRUMP’S PUSH TO RECLAIM BAGRAM AIR BASE
Recent Developments
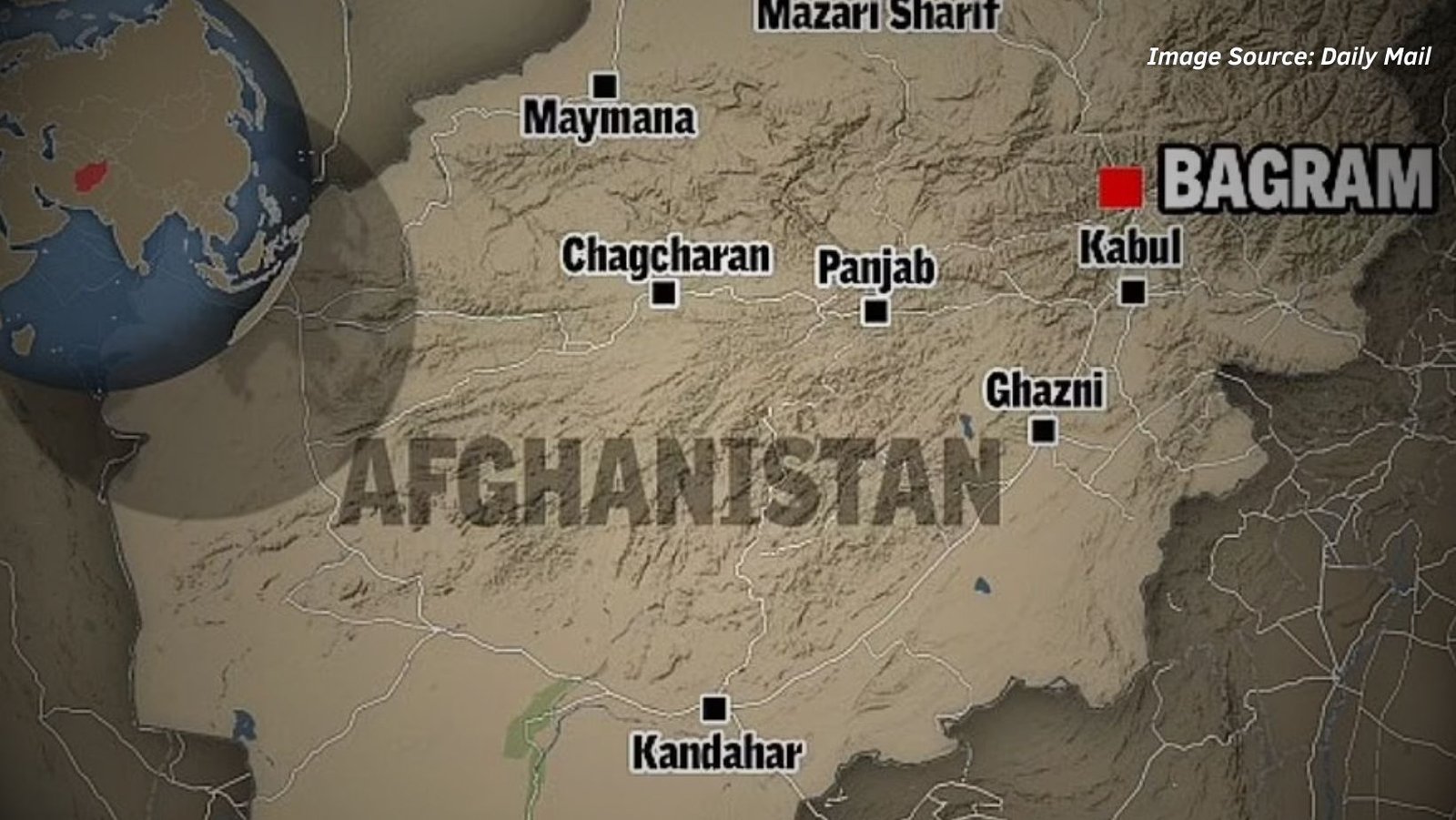
- Trump, during a UK visit in September 2025, announced his intention to “take back Bagram”.
- He claimed:
- “We want it back, and we want it back right away.”
- Suggested that the base is key due to its proximity to China’s nuclear facilities.
TALIBAN’S REACTION
- Taliban rejected the demand outright.
- Supreme leader Hibatullah Akhundzada and Afghan Defence Chief Fasihuddin Fitrat both declared that foreign reoccupation is unacceptable.
US Motivation
- Bagram is 2,000 km from China’s Lop Nur nuclear site, much closer than US bases in:
- Philippines (~3,000 miles from Xinjiang)
- A 2024 Defense Intelligence Agency report indicated:
- China is undertaking the fastest nuclear modernization in its history
WHY DID USA WITHDRAW WAIVERS?
- Part of renewed geopolitical tension following US airstrikes on Iranian nuclear facilities on June 22, 2025.
- Reflects a hardline stance towards Iran under the Trump-era policy of maximum pressure.
- Aimed at isolating Iran economically and diplomatically, even at the cost of disrupting India’s strategic projects.
IMPLICATIONS OF WAIVER WITHDRAWAL
For India
- Strategic Setback:
- Disruption in access to Afghanistan and Central Asia via Iran.
- Weakens India’s efforts to counter China–Pakistan–Iran strategic alignment.
- Economic Impact:
- India’s investments in Chabahar risk becoming non-operational or sanctioned.
- IPGL and contractors may face secondary sanctions.
- Diplomatic Dilemma:
- India needs to balance ties with the US and Iran.
- May need to lobby for reinstatement of waiver or carve out a humanitarian exemption.
For Afghanistan
- Loss of a neutral trade corridor for humanitarian aid and exports.
- Increases reliance on Pakistan-based routes.
For Iran
- Intensifies economic isolation amid renewed US pressure.
- May accelerate closer ties with China and Russia as alternatives to Western alignment.
ALTERNATIVES & POLICY WITHDRAWAL
- Diplomatic Engagement:
- Open discussions with the US to restore a limited waiver.
- Emphasize the port’s use for humanitarian and non-strategic purposes.
- Multilateral Partnerships:
- Involve Central Asian nations or Russia in Chabahar to dilute US pressure.
- Diversify Connectivity:
- Accelerate alternative routes through Russia, Central Asia, or via the North-South Corridor through Azerbaijan.
CONCLUSION
The withdrawal of the Chabahar waiver marks a major turning point in India’s regional connectivity strategy and poses challenges to its influence in Afghanistan and Central Asia. India must now reassess its options, step up diplomatic engagement, and explore alternative connectivity routes while maintaining a fine balance in its geopolitical relations with both the US and Iran.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.

