FIN-TECH COMPANIES
WHY IN NEWS?
- Recently, Reserve Bank of India published a draft framework which lays down the broad functions, eligibility criteria and governance standards for setting up a self-regulatory organization (SRO) for fintech Companies.
WHAT ARE FINTECH COMPANIES?
- Financial technology is used to describe financial technology that seeks to improve and automate the delivery and use of financial services.
- It is utilized to help companies, business owners, and consumers better manage their financial operations, processes, and lives.
- Finetch is composed of specialized software and algorithms that are used on computers and smartphones.
- Fintech also includes hardware, too like internet-connected piggy banks.
- The platforms enable run-of-the-mill financial tasks like depositing checks, moving money between accounts, paying bills or applying for financial aid.
- Fintech also facilitate technically intricate concepts, including peer-to-peer lending and crypto exchanges.
STATUS OF INDIA’S FINTECH INDUSTRY:
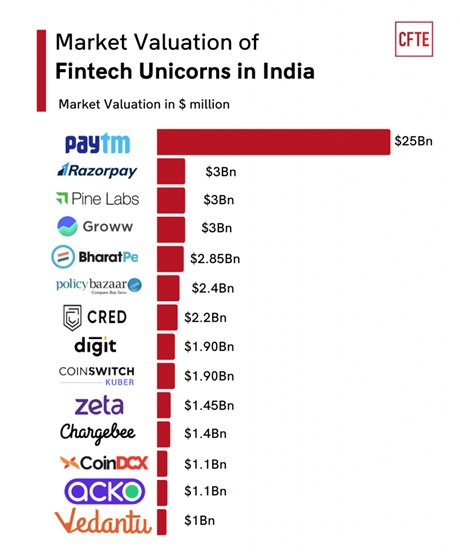
- As per RBI, India has the largest fintech ecosystem in terms of the number of entities.
- India’s fintech ecosystem is projected to hit $150 billion by 2025, from $50 billion in 2021.
- According to RBI, “The projection indicates that by 2030, the sector could potentially contribute to approximately 13% of the global fintech industry’s total revenue.”
HOW DOES FINTECH WORK?
- Fintech provides people & businesses the access to traditional financial services in innovative ways that previously were not available.
- Nowadays many conventional banks’ mobile apps now offer customers on-the-go access to bank services, including the ability to view your balance, transfer funds or deposit a check.
- They also automates many services businesses use, such as loan underwriting and real estate appraisals.
- I combined with large troves of consumer data helps fintech businesses understand their customers and powers their marketing campaigns, product development and underwriting.
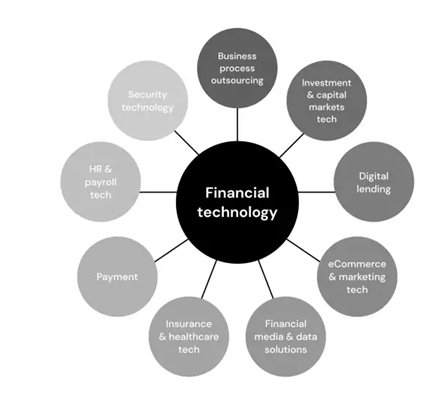
TYPES OF FINTECH STARTUPS AND COMPANIES
- Consumer banking and investing
- Mobile payments
- Insurance tech
- Digital lending and leasing
- Budgeting apps
RBI’S CONCERNS REGARDING FINTECHS:
- Fintechs play a pivotal role in India’s financial system by enhancing access, lowering costs and saving time.\
- But there are few concerns also.
- India’s fintech industry is largely unregulated and from time to time several issues crop up on data privacy, cyber security, grievance handling and internal governance.
- The impact that fintechs could have on financial stability due to poor lending standards can be huge.
- The rise in fraudulent loan apps, on the back of rapid growth in digital lending, has added to concerns.
- Also, a rush to roll out products and services could undermine market integrity and customer protection.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES OF SELF-REGULATORY ORGANISATION (SRO):
- In 2020, RBI released guidelines for a payments SRO.
- This time, the SRO is expected to cover the entire fintech industry.
- According to the draft norms, the SRO should be a NGO that is expected to identify a path to a phased regulatory compliance.
- SRO should engage with the central bank on industry developments, and in developing and updating the taxonomy for fintechs.
- The SRO is also expected to put in place a code of conduct to fair competition foster transparency and consumer protection.
CHALLENGES OF SELF-REGULATORY ORGANISATION (SRO):
- RBI concerns include the question of how an SRO will create incentives for membership.
- RBI also ponders whether SRO should only have unregulated members or there also be regulated fintechs.
- The RBI has also left it to the industry to decide on the number of SRO fintechs that would require recognition.
- RBI said, “Given the diverse nature of the fintechs, restricting to one SRO could dilute some industry concerns, while having multiple SROs could undermine the representative character of self-regulation.”
WAY FORWARD:
- Nowadays, Fintech is so pervasive in financial services that it’s all but ubiquitous.
- Consolidation, partnerships and continued collaborations between banks and financial technolgy seem imminent now.
- As Consumers, businesses and all sorts of financial services firms are increasingly, thus turning to imaginative combinations of software, hardware and data to create and deliver both new and traditional financial products and services.