IMF ASSISTANCE TO NATIONS

WHY IN NEWS?
- Recently International Monetary Fund (IMF) confirmed a $3 billion bailout plan for Sri Lanka’s struggling economy.
- IMF officials are also in negotiations with Pakistan for a $1.1 billion bailout plan.
ABOUT IMF :
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) was established on 27th December 1945 with 29 member countries with the objectives of boosting economic growth and eradicating poverty across the world.
- Eventually, the IMF evolved to be a lender of last resort to governments of countries that had to deal with severe currency crises.
Some of the major objectives of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) are discussed below :
- Global Monetary Cooperation : One of the major objectives of the IMF is to promote international monetary cooperation with the support of its members.
- Financial Stability : IMF aims to ensure economic stability by removing or mitigating the risks engaged in exchange rate fluctuations.
- Employment : The objective of the IMF is to promote employment generation through economic assistance and sustainable growth.
- International trade : The foremost aim is to furnish a balanced international trade.
- Poverty : Eradication of poverty across the world is one of the primary objectives of the IMF.
WHY DO COUNTRIES SEEK AN IMF BAILOUT?
- Countries seek help from the IMF usually when their economies face a major macroeconomic risk, mostly in the form of a currency crisis.
- In the case of Sri Lanka and Pakistan, both countries have witnessed domestic prices rise rapidly and the sharp drop in exchange value of their currencies against the U.S. dollar.
- Such currency crises are generally the result of gross mismanagement of the nation’s currency by its central bank. It is often seen under the covert influence of the ruling government.
- Central banks may be forced by governments to create fresh money to fund populist spending of government.
- Such spending eventually results in a rapid rise of the overall money supply, which in turn causes prices to rise across the economy and the exchange value of the currency to drop.
- Foreigners may also be unwilling to invest in an economy where the value of its currency gyrates in an unpredictable manner.
- In such a scenario, many countries are forced to seek help from the IMF to meet their external debt and other obligations.
HOW DOES IMF HELP THE NATIONS?
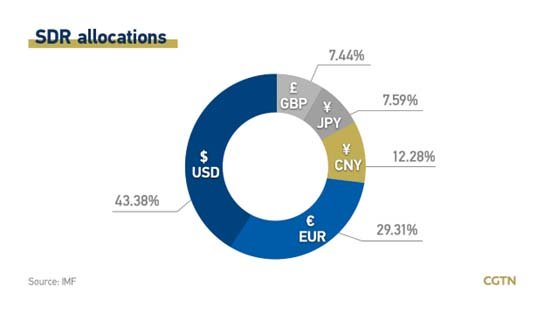
- The IMF basically lends money, often in the form of special drawing rights (SDRs).

- SDRs simply represent a basket of five currencies, namely the U.S. dollar, the euro, the Chinese yuan, the Japanese yen, and the British pound.
- The IMF carries out its lending to troubled economies through a number of lending programs such as the extended credit facility, the flexible credit line, the standby agreement, etc.
- Countries receiving the bailout can use the SDRs for various purposes depending on their individual circumstances.
- Currently, both Sri Lanka and Pakistan are in urgent need for U.S. dollars to import essential items and also to pay their foreign debt.
- So any money that they receive from the IMF is likely to go towards addressing these urgent issues.
CHALLENGES ASSOCIATED WITH IMF BAILOUTS
- The IMF usually imposes conditions on countries before it lends any money to them.
- For example, a country may have to agree to implement certain structural reforms as a condition to receive IMF loans.
- The IMF’s conditional lending has been controversial as many believe that these reforms are too tough on the public.
- IMF’s lending decisions are influenced by International politics.
- Thus, IMF’s bailouts are also known as conditional lending.
WAY FORWARD
- IMF may demand a country affected by high price inflation to ensure the independence of its central bank. As it does not make sense for the IMF to throw money at a country when the policies that caused its crisis remain untouched.
- The institutions should also be asked to stay accountable, responsible and free from corruption. As it may turn out to be a wasted effort because these economies have poor institutions and suffer from high corruption.
SOURCE : THE HINDU
SYLLABUS : MAINS, GS-2, INTERNATIONAL ORGANISATIONS


