INDIA’S SPACE POLICY
India’s Space journey starts with the establishment of ISRO (INDIAN SPACE RESEARCH ORGANISATION).
ABOUT ISRO :

- ISRO was established in 1969 from the INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research) program under the leadership of Dr. Sarabhai and Dr. Ramanathan.
- It later became the part of the DOS (Department of Space) and the Space Commission, which was created in 1972.
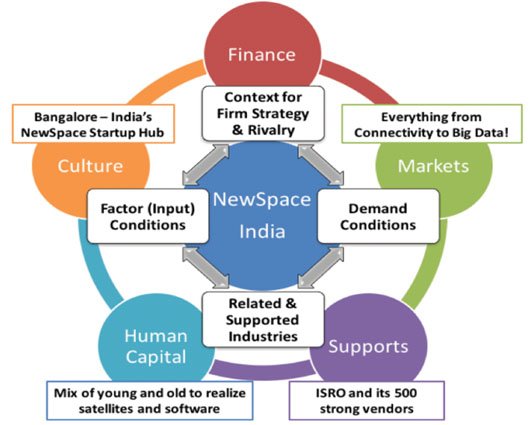
- It is the premier space research body of India and playing a huge role in the development of the country through educational, agricultural, communication, and defence sector projects.
- It is headquartered in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- ISRO has launched from Aryabhata, India’s first satellite in 1975 to the successful Mars Orbiter Mission named Mangalyaan in 2013, which made India the first country to reach Mars on its first attempt, with the cost of only $76 million.
RECENT SHIFT IN INDIA’S SPACE POLICY :
- The Indian Government is eyeing its interest in expanding the boundaries of the Indian space arena.
- Government has also proposed that private companies be allowed to take a more active role in the space industry.
- ISRO has been switching from “Supply-Based Model” to a “Demand-Based Model”.
- It has employed New Space India Limited (NSIL) as an intermediary for customer requirements and commitments.
- NSIL will also acquire control of DOS operational launch vehicles and market launches, satellites, and other services.
Indian Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) :
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently inaugurated the Indian Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe), a government agency aimed at promoting private investment and innovation in the space sector.
- IN-SPACe will support the private sector and help it participate in building satellites, launching vehicles, carrying out launches, and providing space-based services.
- It will also hand-hold, promote and guide the private industries in space activities through encouraging policies and a friendly regulatory environment.
NEW NATIONAL SPACE POLICY :
- The Indian government’s new space policy is assumed to come into effect by early 2023 as the draft is already released.
- It is expected to lead to the development of a vibrant and innovative space ecosystem in the country.
- With the new policy, the government agency intends to play the role of a mentor through technology transfers and allowing the private players to enter into every segment of space economy.
- The new space policy will outline how non-government entities can work in the space sector and provide support for the private sector through the IN-SPACe.
- Policy will allow non-government entities to come into this domain and operate in India.
FOCUS AREAS OF NEW SPACE POLICY :
- The policy will focus on the use of low earth orbit (LEO) satellites, which are cheaper than traditional satellites.
- It will encourage the private sector to manufacture satellites for various applications such as agriculture, healthcare, urban development, disaster management, etc.
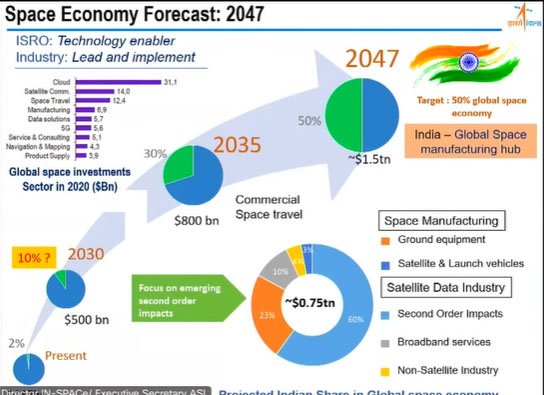
- The global space economy is estimated to be worth $423 billion dollars, with India constituting 23 per cent of that market.
- Thus the government hopes to tap into the full potential of the sector and expects to have its own SpaceX-like start-ups within the next two years.
- India’s policy has already attracted the start-ups, as with their number in the space sector increasing from just four in 2018 to over 250 in 2022.
NOTABLE START-UPS IN SPACE SECTOR :
- SKYROOT AEROSPACE : On November 18, 2022, ISRO has launched India’s first privately built rocket, called Vikram-S, from the Sriharikota launchpad.
- The rocket was developed by Skyroot Aerospace (which became the first Indian private company to reach outer space when its rocket reached an apogee of 89.5 km).
- AGNIKUL : It is developing a small satellite launch vehicle and has already secured funding of $96 million. The company plans to launch its first rocket by 2024 and has set a goal of launching 100 small satellites per year.
- SATSURE : Satsure is another Indian start-up that is focused on developing small satellite platforms and has raised $1.5 million in seed funding.
- The PSLV-C54 mission carried nano satellites built by Indian start-ups PIXXEL and DHRUVA Space into space.
- The mission was a major milestone for both companies and has raised hopes that they will be able to make significant contributions to the development of the space industry in India.
WAY FORWARD :
- The global space industry is currently valued at more than $400 billion and has the potential to become a $1 trillion industry by 2040.
- Space sector can play a major catalytic role in the technological advancement and expansion of our Industrial base. Thus India may have a robust space infrastructure, including multiple launch sites, a range of advanced rockets and satellites, and a skilled and experienced workforce by 2040.
As India is all set to reclaim its lost glory, which smiles in the adulation of Pushpak-Vimanas dating 7000 years ago. The current space policy shall be a catalyst on this path to glory.
Syllabus : GS3, SPACE SECTORS, S&T

