Nagorno-Karabakh dispute
Context:
- Recently, the leader of Armenian said that his previous decree which was issued to order the dissolution of separatist institutions was not valid.
Quick Recap of the decree:
- Azerbaijan sent troops to Karabakhon September 19 and after just one day of fighting the Armenian separatist forces surrendered.
- Armenian separatist forces that had controlled the disputed region for three decades agreed to reintegrate with Baku.
- After a week, separatist president Samvel Shahramanyan issued a decree ordering the dissolution of the separatist institutions by January 1, 2024.
- But in a sudden move recently Shahramanyan taken back on the announcement given in Yerevan, the capital of Armenia.
About the region:
- The conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh is generally called as the one of the “frozen conflicts” of the world.
- The region is landlocked and mountainous which has been subjected to the long standing territorial dispute between Armenia and Azerbaijan.
Main Source of dispute:
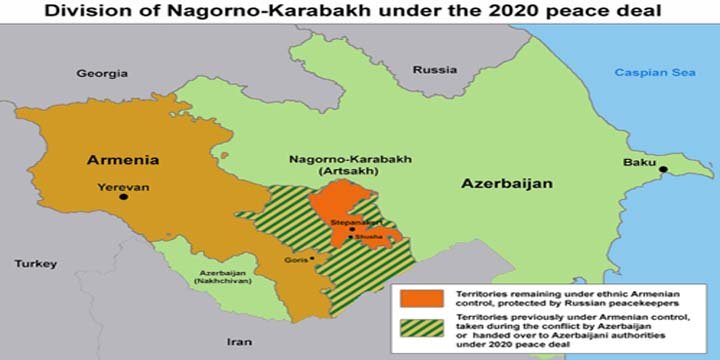
- The conflicted region Nagorno-Karabakh is a mountainous region officially recognised as part of Azerbaijan.
- But the majority nearly 1.2 lakh population is predominantly ethnic Armenian, having close cultural, social, and historical ties with Armenia.
- So, in general Nagorno-Karabakh is an ethnic Armenian enclave in Azerbaijan.
- The Armenians are basically Christians, while Azeris are Muslims.
- The disputed conclave is connected to Armenia through the 5-km Lachin Corridor.
Background to the Conflict:
- Since the medieval period, the region has been the source of conflicts between regional powers such as imperial Russia, Ottoman Empire (modern-day Turkey) and the Persian empire (Iran).
- Nagorno-Karabakh was part of the Azerbaijan SSR (Soviet Socialist Republic), when Czarist Russia gave way to the Soviet Union in 1921.
- When the Soviet Union collapsed, the first round of disputes over Nagorno-Karabakh began in 1988.
- The regional legislature of Nagorno- Karabakh passed a resolution declaring its intention to join Armenia, even though it is being geographically located within Azerbaijan.
- After the dissolution of Soviet Union in 1991, both Armenia and Azerbaijan achieved statehood and Nagorno-Karabakh officially declared independence.
- By the year 1993, Armenia had captured the Nagorno-Karabakh region, and also occupied 20 per cent of Azerbaijan’s geographic area.
- In 1994, Russia brokered a ceasefire between the two nations which is known as the Bishkek Protocol.
- This protocol made the Nagorno-Karabakh region de facto independent with a self-proclaimed government, however it was still heavily dependent on close economic, political, and military ties with Armenia.
- Nearly, after 16 years, in September 2020, Azerbaijan and Armenia went to war again.
- Azerbaijan managed to gain control of the territory around Nagorno-Karabakh.
- After 2 years that is in 2022, the Lachin Corridor was blockaded by Azerbaijan, which caused severe shortages of essential goods including food, fuel and water in Nagorno-Karabakh.
- On September 19, Azerbaijan launched an “anti-terrorist” offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh and claimed to have regained full control over the region.
India’s position:
- On the conflict, India has always didn’t believe in taking sides.
- In 2020, after the conflict broke out India told that, any lasting resolution of the conflict can only be achieved peacefully through diplomatic negotiations.
- In this regard, India support OSCE Minsk Group’s continued efforts for a peaceful resolution of the conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan.
About Minsk Group:
- The Minsk Group was primarily set up by the Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (which had not yet become the OSCE) in March 1992.

- In March 1995, the OSCE established a co-chairmanship between Russia and the United States.
- France was added to the grouping in 1997, making it tripartite.
- It is usually less known fact that the Minsk Group also had eight other members in addition to the co-chairs.
- The reason behind this is the co-chairs rarely, if ever, consulted with other members of the group.
- These members include Armenia and Azerbaijan, Belarus, Finland, Germany, Italy, Sweden, and Turkey.
- The Minsk Group and the Minsk Process, promotes the OSCE’s efforts to find a peaceful solution to the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict.
About OSCE:
- The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe(OSCE) is a regional security oriented intergovernmental organization.
- It comprises of member states in Europe, North America, and Asia.
- Its mandate includes issues which include arms control, the promotion of human rights, freedom of the press, and free and fair elections.
- The OSCE has its roots initially in the 1975 Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe (CSCE).