Sinking Joshimath due to land subsidence
Why in news:
- Various houses and buildings, roads have developed cracks in the Joshimath town, Uttarakhand.
- Residents of Joshimath, the Himalayan pilgrim town that appears to be sinking, are blaming major power and road infrastructure projects for their plight.
- They are demanding that the government resettle and give new homes for all those who have lost their properties in the town.
- The residents of Joshimath, also known as the gateway town to the Badrinath temple, said they had been complaining to the government about cracks in their houses for over a year now.
- However, the administration became active only after its own building started developing cracks.
- In fact, now even roads and rocks on trekking routes have visible fractures.
More about the news:
- Members of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) are set to visit the town on Monday to assess the situation and advise the Uttarakhand government.
Reasons for the land subsidence:
- Residents are blaming the TapovanVishnugad power project of the National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) for the irreversible” damage to the sacred town.
- The blame is also on the construction of the HelangMarwari bypass by the Border Roads Organisation.
Land subsidence:
- Subsidenceis a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth’s surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities.
- Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope movement.
Land subsidence
Causes of land subsidence:
- Dissolution of limestone
- Mining
- Extraction of petroleum and natural gas
- Earthquake
- Groundwater-related subsidence
- Faulting induced
- Isostatic subsidence
- Seasonal effects
Effects of land subsidence:
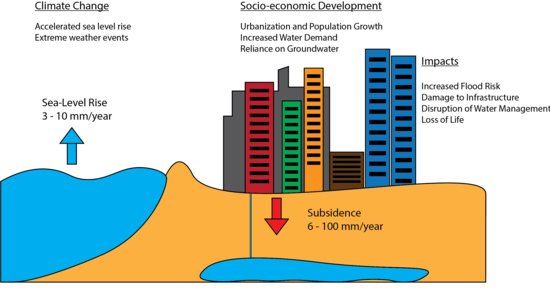
Sinking cities:
Drivers, processes, and impacts of sinking cities
- Sinking cities are urban environments that are in danger of disappearing due to their rapidly changing landscapes.
- The largest contributors to these cities becoming unlivable are the combined effects of climate change (manifested through sea level rise, intensifying storms, and storm surge), land subsidence, and accelerated urbanization.
- Many of the world’s largest and most rapidly growing cities are located along rivers and coasts, exposing them to natural disasters.
- As countries continue to invest people, assets, and infrastructure into these cities, the loss potential in these areas also increases.
- Sinking cities must overcome substantial barriers to properly prepare for today’s dynamic environmental climate.
Syllabus: Prelims + Mains; GS3 – Disaster management