US-Canada Great Lakes turning acidic: study seeks to establish details
Context- Scientists are building a sensor network to detect the trends in the water chemistry of Lake Huron, one of the five Great Lakes of North America.
It is known that the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide has caused the world’s oceans to turn more acidic. Recently, it has been observed that by 2100, even the Great Lakes — Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario — might approach acidity at around the same rate as the oceans.
The Great Lakes, five interconnected bodies of water straddling the US-Canada border that drain into the Gulf of St Lawrence in the North Atlantic through the St Lawrence River, are the largest group of freshwater lakes in the world.

(Credits- Geology.com)
What is Acidification of water bodies?
Acidification of oceans or freshwater bodies takes place when excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere gets rapidly absorbed into them. it has been established that absorption of carbon dioxide leads to a lowering of the pH, which makes the water bodies more acidic. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) of the US government, oceans have in 200 years alone, ocean water has become 30 percent more acidic.
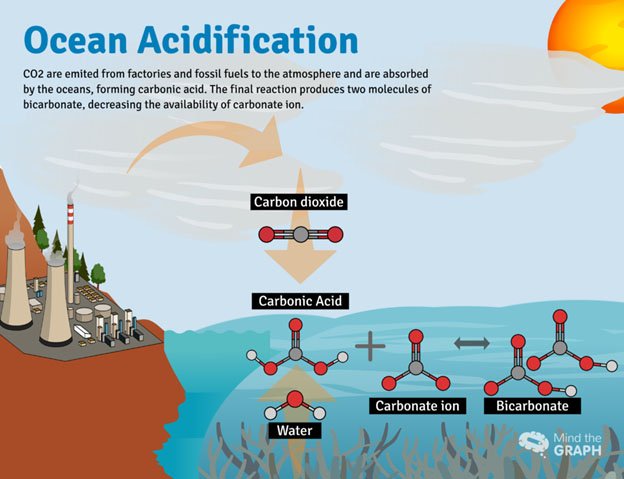
(Credits- Medium.com)
What are the Consequences of acidification?
- Acidification may lead to a decrease in native biodiversity, create physiological challenges for organisms, and permanently alter the structure of the ecosystem, scientists say.
- The oceans are a significant CO2 reservoir, absorbing a significant amount of it (one-third) produced by anthropogenic activities and effectively mitigating climate change.
- In some organisms, increasing acidity reduces metabolic rates and immune responses.
- Carbonic acid, bicarbonate, and carbonate ions are formed when sea water absorbs CO2.
- Increased CO2 levels in the atmosphere cause a decrease in pH, an increase in the concentration of carbonic acid and bicarbonate ions, and a decrease in the concentration of carbonate ions.
- The reduced availability of carbonate ions makes it more difficult for marine calcifying organisms like coral and some plankton to form biogenic calcium carbonate.
- Commercial fisheries are under threat as a result of acidification, which harms calcifying organisms, which form the foundation of Arctic food webs.
- Coral bleaching is exacerbated by rising acidity because corals are extremely sensitive to changes in water composition.
Way Forward- Scientists have said that without a collective global effort to reduce concentrated atmospheric carbon dioxide, not much can be done to stop the acidification of the Great Lakes. Even if all countries were to take action to arrest the increase in carbon emissions, the lakes would continue to acidify due to the carbon dioxide that is already present in the atmosphere, along with carbon-laden water runoffs from land.
NEWS- US-Canada Great Lakes turning acidic: study seeks to establish details
Syllabus- Mains; GS-1; GS-3; World Geography; Climate Change


