Current Affairs (13th August 2021)
Sovereign right to taxation
Indian Express
GS 2 : Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein
Context:
- Recently, the central government has decided to withdraw the retrospective taxation amendment in the I-T Act introduced in March 2012.
- While scrapping the retrospective levy is believed to provide clarity to investors by removing a major source of ambiguity on taxation laws, the government has stressed the need to establish its “sovereign right to taxation”.
About:
- Constitution gives the government the right to levy taxes on individuals and organisations but makes it clear that no one has the right to levy or charge taxes except by the authority of law. Any tax being charged has to be backed by a law passed by the legislature or Parliament.
- According to the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, the definition of tax as a “pecuniary burden laid upon individuals or property owners to support the government, a payment exacted by legislative authority”, and that a tax “is not a voluntary payment or donation, but an enforced contribution, exacted pursuant to legislative authority”.
- Taxes in India come under a three-tier system based on the Central, State and local governments, and the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution puts separate heads of taxation under the Union and State list.
- There is no separate head under the Concurrent list, meaning Union and the States have no concurrent power of taxation, as per the document.

Private players in Indian Railways
Indian Express
GS : Indian Economy
Context:
- Last year, the Indian Railways launched the formal process of inviting private parties to run trains on the Indian railway system. Bids were finally opened last month.
- But the poor responses call for assessing the real needs of and necessary changes to the system.
About:
- There were no bids for nine clusters and only two bids for three clusters.
- Even for these three clusters, the only serious bid was by Indian Railways’ (IR) own company IRCTC, which in effect negated the basic objectives of bringing in private capital.
- This, in effect, negated the basic objectives of bringing in private capital.
Reasons for their failure:
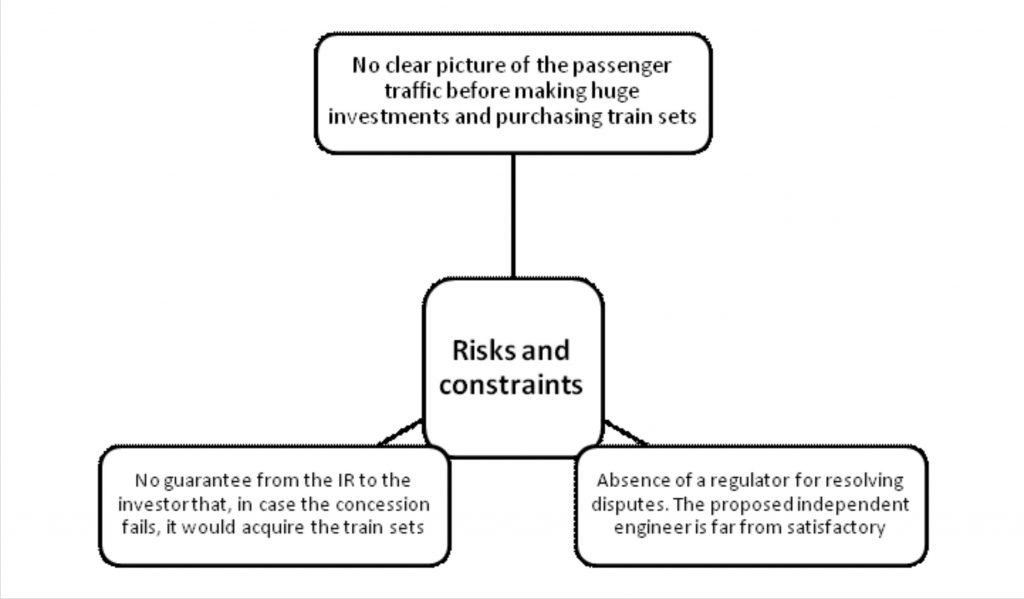
- It is an outcome of the lack of alignment of the interests of IR and the concessioners.
- IR wants the capital and technology without giving up control, while the concessioner wants a far more equal relationship to be moderated by a regulator.
- IR has imposed constraints that prevent efficient decisions and adopted an organisational design that does not consider the characteristics and associated risks that will determine outcomes and investment decisions.
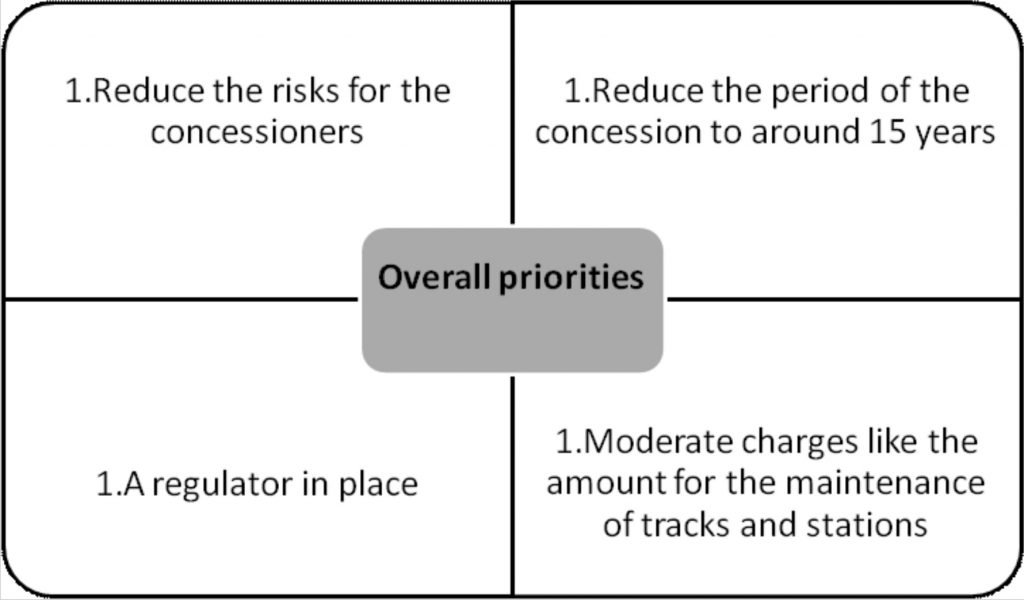
Way Forward:
- Designing and manufacturing state-of-the-art rolling stock
- Establishing a company that leases rolling stock (train sets) not only to concessioners but also to IR.
- This will reduce the investment risks and enable reducing the concession period from 35 years to a more reasonable 10-15 years, bringing in competition.
- For starters, IRFC (Indian Railway Finance Corporation), which is already into leasing rolling stock, can be that company.
- The rolling stock company can also be used for bringing in new technology : Moving the rolling stock industry up the industrial value chain and bringing about a structural change of the Indian economy.
- Encouraging long-term arrangements with rolling stock suppliers.
- Giving access to IR’s rolling stock market – an effective way to compel global players to share technology and form joint ventures with Indian companies.
- Huge investments and the involvement of universities, research institutes and national laboratories – to understand the critical elements of the technology and absorb them into the design-production process.
GSLV-F10/EOS-03
Indian Express
GS 3 : Science and Technology
Context:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation’s second mission of the year — to place an earth observation satellite by a GSLV rocket — faced a setback as it could not be accomplished fully due to performance anomaly in the cryogenic stage of the rocket.
About:
- The GSLV-F10/EOS-03 rocket successfully lifted off from the second launch pad at the spaceport. However, minutes later, they announced that the “mission could not be accomplished fully due to performance anomaly”.
- EOS-03 is a state-of-the-art agile Earth observation satellite which will be placed in a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit by GSLV-F10. Subsequently, the satellite will reach the final geostationary orbit using its onboard propulsion system.
- EOS-03 was launched ahead of EOS-02, which has been delayed. EOS-02 is now scheduled for a launch in September-October.
- That launch will try out a new rocket — SSLV, or small satellite launch vehicle. Though India has developed four rockets till now — SLV, ASLV, and different versions of PSLV and GSLV — only two are currently operational.
- The SSLV is designed to cater to the increasing demand for launch of small satellites, mainly from businesses and universities; it costs much less and consumes less energy.

Quality of Life for Elderly Index
PIB
GS 2 : Management of Social Sector Services
Context:
- Recently, Quality of Life for Elderly Index has been released by the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM).
Highlights:
- Rajasthan and Himachal Pradesh are top-scoring regions in Aged and Relatively Aged States, respectively.
- Chandigarh and Mizoram are top-scoring regions in Union Territory and North-East States category.
- The share of elders, as a percentage of the total population in the country, is expected to increase from around 7.5% in 2001 to almost 12.5% by 2026, and surpass 19.5% by 2050.
- The Health System pillar observes the highest national average, 66.97 at an all-India level, followed by 34 in Social Well-being.
- Financial Well-being observes a score of 7, which is lowered by the low performance of 21 States across the Education Attainment & Employment pillar, which showcases scope for improvement.
- States have performed particularly worse in the Income Security pillar because over half of the States have a score below the national average in Income Security, which is the lowest across all pillars.
About:
- The Index has been created by the Institute for Competitiveness at the request of EAC-PM and it sheds light on an issue often not mentioned- problems faced by the elderly.
- It identifies the regional patterns of ageing across Indian States and assesses the overall ageing situation in India.

Medicine and Homeopathy Bills, 2021
All India Radio
GS 3 : Health
Context:
- Parliament has passed the National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (Amendment) Bill, 2021 and National Commission for Homeopathy (Amendment) Bill, 2021 with the Rajya Sabah approving it. The Lok Sabha had passed it earlier.
National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (Amendment) Bill, 2021:
- It proposes to amend the National Commission for Indian System of Medicine Act, 2020.
- The 2020 Act replaced the Indian Medicine Central Council Act, 1970. The 1970 Act set up the Central Council of Indian Medicine to regulate the education and practice of the Indian Medicine system which includes Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy.
- The 2020 Act replaced the Council with a National Commission for regulating education and practice of the Indian medicine system.
- The National Commission was constituted on June 11, 2021 to supersede the Central Council and on the same date the 1970 Act was repealed.
- The 2021 Bill specifies that all powers and functions of the Board of Governors (as under the 1970 Act) will be deemed to have been done under the 2020 Act and will continue to remain in force.
National Commission for Homeopathy (Amendment) Bill:
- It proposes to amend the National Commission for Homeopathy Act, 2020 to provide a medical education system that improves access to quality and affordable medical education.
- The 2020 Act replaced the Homeopathy Central Council Act, 1973, which set up the Central Council of Homeopathy for regulating homeopathic education and practice.
- The 2020 Act replaced the Council with a national commission for regulating homeopathic education and practice.
- The National Commission was constituted on July 5, 2021 to supersede the Central Council and on the same date the 1973 Act was repealed.
- The 2021 Bill specifies that all powers exercised and functions performed by the Board of Governors (as under the 1973 Act) will be deemed to have been done under the 2020 Act and will continue to remain in force.
DAY-NRLM
PIB
GS 3 : Economy
Context:
- Indian PM participated in ‘Atmanirbhar Narishakti se Samvad’ and interact with women Self Help Group (SHG) members/community resource persons promoted under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM).
About:
- DAY-NRLM aims at mobilizing rural poor households into SHGs in a phased manner and provide them long-term support to diversify their livelihoods, improve their incomes and quality of life.
- Most of Mission’s interventions are being implemented and scaled up by the SHG women themselves who are trained as community resource persons (CRPs) – Krishi Sakhis, Pashu Sakhis, Bank Sakhis, Bima Sakhis, Banking Correspondent Sakhis etc.
- The Mission is also working on empowering the SHG women through awareness generation and behaviour change communication on issues like domestic violence, women’s education and other gender related concerns, nutrition, sanitation, health etc.

