Climate Action and Finance Mobilization Dialogue (CAFMD)
PIB
GS 2: International Relations
GS 3: Environment and Conservation
Context:
- India and the United States of America (USA) launched the “Climate Action and Finance Mobilization Dialogue (CAFMD)”.
About:
- The CAFMD is one of the two tracks of the India-USA Climate and Clean Energy Agenda 2030 partnership launched at the Leaders’ Summit on Climate in April 2021, by Indian Prime Minister and US President.
- The launch was preceded by a bilateral meet where both sides discussed at length a wide range of climate issues relating to COP26, Climate Ambition, Climate Finance, Global Climate Initiatives including International Solar Alliance (ISA), Agriculture Innovation Mission for Climate (AIM4C).
- Significance : This will not only strengthen India-US bilateral cooperation on climate and environment but will also help to demonstrate how the world can align swift climate action with inclusive and resilient economic development, taking into account national circumstances and sustainable development priorities.
Rural Connectivity in Maharashtra
News on Air
GS 2: Government Policies and Interventions
GS 3: Economy
Context:
- Indian government and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) have signed a 300-million-dollar loan as additional financing to scale up improvement of rural connectivity to help boost rural economy in Maharashtra.

About:
- The additional financing for the ongoing Maharashtra Rural Connectivity Improvement Project will help improve an additional 1,100 rural roads and 230 bridges for a total length of 2,900 km in 34 districts.
- The ongoing project with 200 million dollar financing, approved in August 2019, is already improving and maintaining the condition and safety of 2,100 km of rural roads.
- With the additional financing, the overall project will improve the condition and safety of five thousand kilometer of rural roads and over 200 bridges connecting rural communities.
- The new project is expected to generate about 3.1 million person-days of employment for local communities, of which at least 25% will be for women, over the construction and maintenance periods.
- A gender action plan has also been prepared to focus on capacity development of women workers so that they can benefit from the semiskilled and unskilled labor opportunities.
Migration Due to Climate Change
Down to Earth
GS 3: Environment and Conservation
Context:
- The World Bank’s updated Groundswell report noted that climate change can force some 216 million people in six world regions to move within their own countries by 2050.
- Hotspots of internal climate migration can emerge as early as 2030 and continue to spread and intensify by 2050.
About:
- Climate change is a powerful driver of internal migration because of its impacts on people’s livelihoods and loss of livability in highly exposed locations.
- By 2050, sub-Saharan Africa could see as many as 86 million internal climate migrants; east Asia and the Pacific, 49 million; south Asia, 40 million; north Africa, 19 million; Latin America, 17 million and eastern Europe and Central Asia, five million.
- This report is a stark reminder of the human toll of climate change, particularly on the world’s poorest — those who are contributing the least to its causes.
- It also clearly lays out a path for countries to address some of the key factors that are causing climate-driven migration.
Way Ahead:
- All these issues are fundamentally connected which is why humans support to countries is positioned to deliver on climate and development objectives together while building a more sustainable, safe and resilient future.
- Immediate and concerted action to reduce global emissions and support green, inclusive and resilient development, could reduce the scale of climate migration by as much as 80%.
Thawing Permafrost Cause Another Pandemic
The Indian Express
GS 1: Geography
Context:
- According to the latest IPCC report, increasing global warming will result in reductions in Arctic permafrost and the thawing of the ground is expected to release greenhouse gases like methane and carbon dioxide.
About:
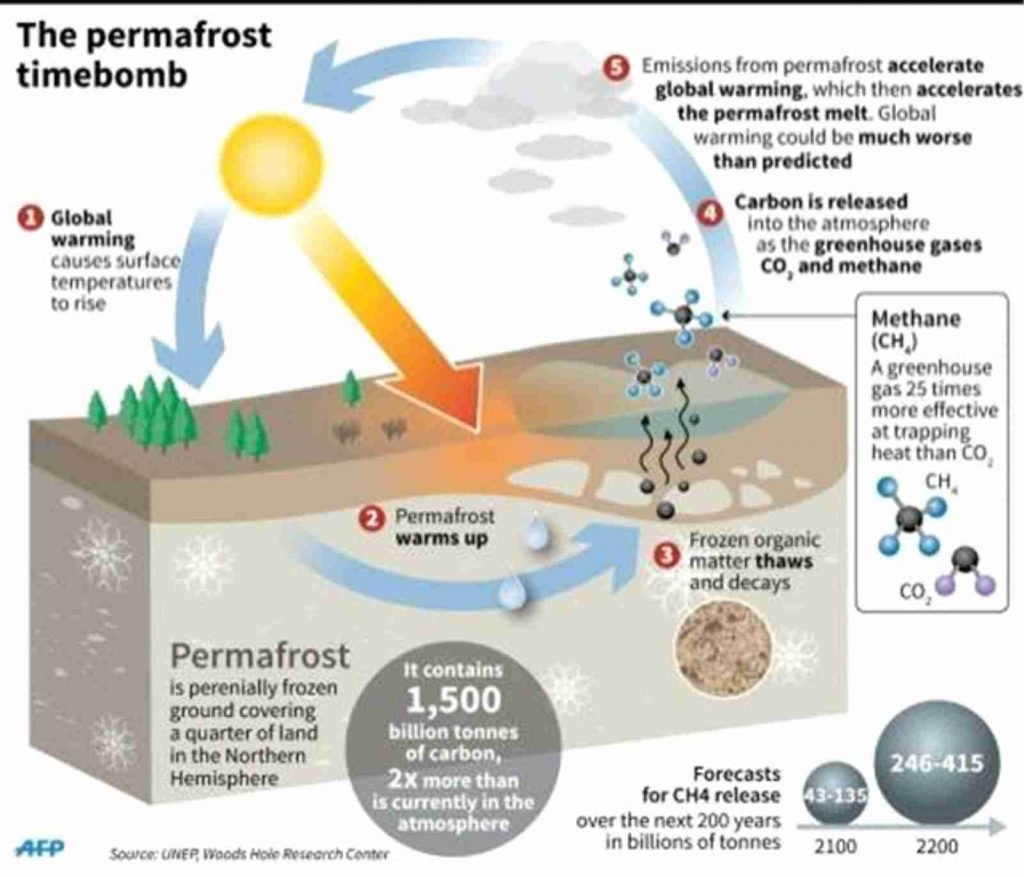
- Permafrost is defined as ground (soil, rock and any included ice or organic material) that remains at or below zero degree Celsius for at least two consecutive years.
- It is spread across an area of over 23 million square kilometers, covering about 15% of the land area of the globe.
Immediate effects as permafrost melts due to increasing global temperatures:
- The first impacts that are very rapid will affect countries where roads or buildings were constructed on permafrost, for e.g., the Russian railways.
- Another biggest international problem is to do with the potential for organic material, which is now entombed and frozen in the ground.
- If the ground begins to thaw, this material will become available for microbiota to break down.
- In some environments, the biota will release carbon dioxide, and in others release methane which is about 25 to 30 times more potent as a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide.
- The total quantity of carbon that is now buried in the permafrost is estimated at about 1500 billion tonnes and the top three meters of the ground has about 1000 billion tonnes.
- The world currently emits into the atmosphere, approximately 10 billion tonnes of carbon a year. So, if the permafrost thaws and releases even only 1% of the frozen carbon in any one year, it can nullify anything that humans do about industrial emissions.
- The number of diseases that humans can find in India is much greater than the number of diseases find in Greenland.
- The environment now is so much more suitable than during the Ice Age for not just human life, but also the evolution or development of viruses and bacteria.
LCA-Mk2
The Hindu
GS 3: Defence and Security
Context:
- LCA-Mk2 to roll out next year, first flight in 2023, says scientist.
About:
- The configuration for the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA)-Mk2 has been frozen and steel cutting is expected to begin soon while configuration for the fifth-generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) has been frozen and preliminary design completed.
- Roll-out of the aircraft (Mk2) is planned next year and the first flight in early 2023.
- The aircraft features enhanced range and endurance including an onboard oxygen generation system, which is being integrated for the first time.
- Heavy weapons of the class of Scalp, Crystal Maze and Spice-2000 will also be integrated on the Mk2. The LCA-Mk2 will be a heavier and much more capable aircraft than the current LCA variants.
- The Mk2 is 1,350 mm longer featuring canards and can carry a payload of 6,500 kg compared to 3,500 kg the LCA can carry.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) has one squadron of the LCA in initial operational clearance and deliveries of the second squadron in final operational clearance configuration are under way.
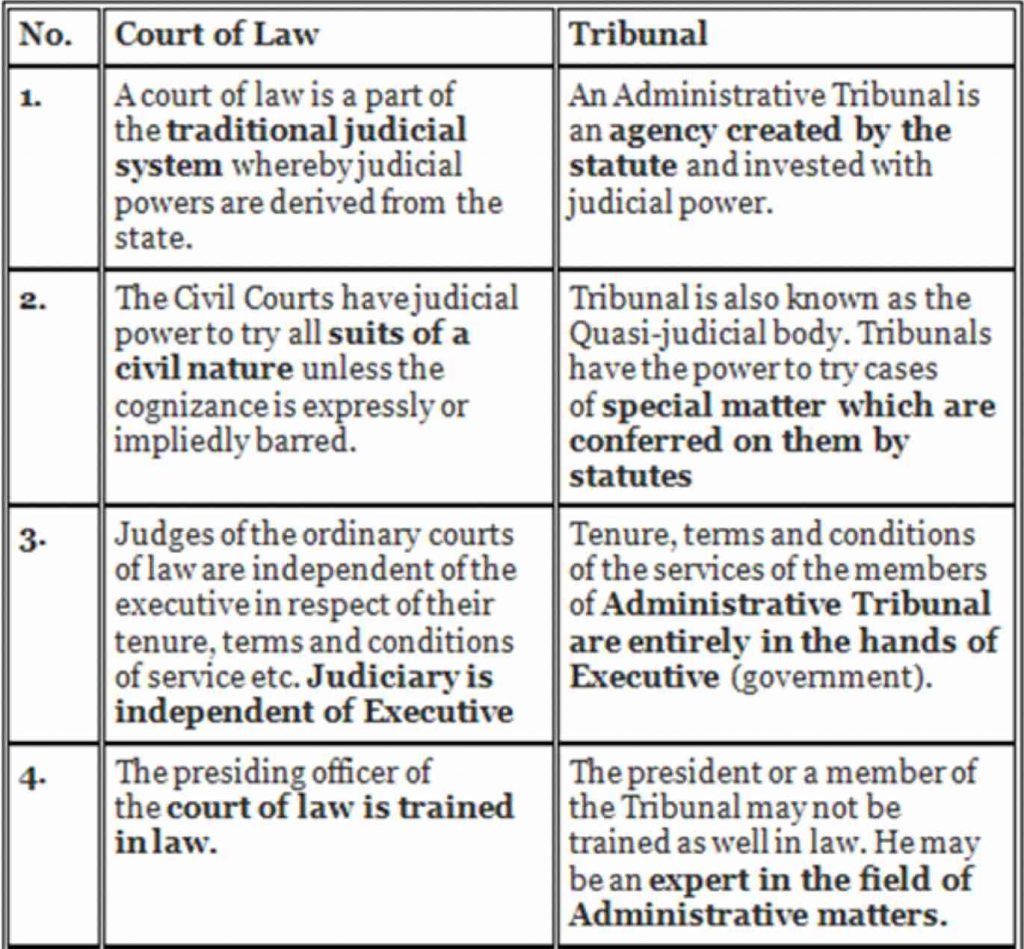
Tribunals
The Hindu
GS 2: Polity and Governance
Context:
- The government has appointed 31 people as judicial, technical and accountant members at the NCLT and the ITAT, amid the Supreme Court flagging concerns about vacancies in various tribunals.
About:
- The National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) deals with matters mainly related to companies law and the insolvency law, while the Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) deals with income tax matters.
- The appointments also come at a time when the Supreme Court has flagged concerns, saying the Centre was “emasculating” tribunals by not appointing officials to the quasi-judicial bodies that are facing a staff crunch.
- The appointments will be for five years from the date of assumption of charge or till attaining the age of 65 or until further orders.
- There are around 250 posts lying vacant at various key tribunals and appellate tribunals such as the NCLT, the DRT, the TDSAT and the SAT.
N-DEAR
All India Radio
GS : Education
Context:
- Recognizing the transitions happening in the Education sector, where Digital Technology has come to dominate the face of most remote learnings, the Government of India has announced a National Digital Educational Architecture, or in short, N-DEAR.
What NDEAR is?
- An architectural blueprint for the education ecosystem and not a system.
- That defines a set of
- Principles – e.g. technology and ecosystem
- Standards and Specifications – e.g. technology and data
- Guidelines – e.g. data process, ecosystem engagement
- Policies – e.g. data, openness, inclusion, accessibility
- And identifies the key building blocks needed to make the architecture blueprint a reality
- For an ecosystem of
- Actors to build, develop, innovate – interoperable building blocks
- Applications/Innovations in the form of Solutions, platforms, tools, assets to be developed and used
- To enable the achievement of policy goals through programmes such as – SSA, FLN Mission – etc
Ranikhet Fernery
The Hindu
GS 3: Environment and Conservation
Context:
- India’s Largest open air fernery was inaugurated in Uttarakhand’s Ranikhet.
About:
- The fernery is home to a large number of fern species, some of which are endemic to the state, some hold medicinal value while some are threatened species that demand care and conservation.
- The newly inaugurated fernery is one of the biggest ferneries in India. The fernery has the largest collection of fern species, second to only Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanical Garden and Research Institute (TBGRI), Thiruvananthapuram.
- However, it is the country’s first open-air fernery in natural surroundings which is not under any poly-house/shade house.
- It has been developed by the Research Wing of Uttarakhand Forest Department over a period of three years, under Central Government’s CAMPA scheme.
- The CAMPA or Compensatory Afforestation Management Funds Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) by the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF) was introduced in 2004 to accelerate activities for the preservation of natural forests, management of wildlife, infrastructure development in forests, and other allied works.


