Current Affairs (15th June 2021)
Tulu Language
Context:
- Various organisations initiated a Twitter campaign demanding official language status to Tulu in Karnataka and Kerala.
About:
- Tulu is a Dravidian language spoken mainly in two coastal districts Dakshina Kannada and Udupi of Karnataka and Kasaragod district of Kerala.
- As per the 2011 Census report, there are 18,46,427 Tulu-speaking people in India. Some scholars suggest Tulu is among the earliest Dravidian languages with a history of 200 years.
Demand by Tulu speakers:
- The Tulu speakers, mainly in Karnataka and Kerala, have been requesting the governments to give it official language status and include it in the eighth schedule to the Constitution. Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, Bodo, Santhali, Maithili and Dogri are the 22 languages presently in the eighth schedule to the Constitution.
Present status of Tulu:
- People who speak Tulu are confined to the above-mentioned regions of Karnataka and Kerala, informally known as Tulu Nadu.
- At present, Tulu is not an official language in the country. Efforts are being made to include Tulu in the eighth schedule. If included in the eighth schedule, Tulu would get recognition from the Sahitya Akademi.
Tulu in Education:
- The Karnataka government introduced Tulu as a language in schools a few years ago.
- Last year, ‘Jai Tulunad’ conducted an online campaign demanding to include Tulu in the new National Education Policy (NEP).
- The organization started a ‘Tweet Tulunad’ campaign with the hashtag #EducationInTulu.
Separate statehood for Tulu Nadu:
- The political party ‘Tuluvere Paksha’, which got recognition from the Election Commission of India in February 2021 under section 29A of Representation of the People Act 1951, has given wings to the political aspirations of the Tulu-speaking people.
Tulu art, culture, and cinema
- Tulu has a rich oral literature tradition with folk-song forms like paddana, and traditional folk theatre yakshagana.
- Tulu also has an active tradition of cinema with around 5 to 7 Tulu language movies produced a year. Tulu films are being screened every day in Mangaluru and Udupi in at least one theatre.
PENCIL Portal
Context:
- The instances of Child Labour can be reported by citizens on PENCIL Portal or by calling on Childline-1098.
About:
- The Platform for Effective Enforcement for No Child Labour (PENCIL) portal was launched by the Ministry of Labour and Employment to rehabilitate child labour in the country.
- This portal is an online platform that aims at engaging the Central and State Governments, District, civil society, and the public in eradicating child labour to achieve the target of child labour free society.
- It aims to mainstream into legal schools of all children who have been withdrawn from child labour and rehabilitated through the National Child Labour Project (NCLP) Scheme.
- It aims to build a strong authentication mechanism for implementing and monitoring both the enforcement of the legislative provisions and effective implementation of the NCLP Scheme.
Components of PENCIL Portal –
- Child Tracking System,
- Complaint Corner,
- State Government,
- National Child Labour Project,
- Convergence.
Implementation Process –
- All complaints filed will be received by the District Nodal Officers (DNOs) who are nominated by the districts.
- After receiving the complaints, the rescue measures will be taken within the 48 hours in coordination with the police department only if the complaint filed is found to be genuine.
Global Liveability Index 2021
Context:
- The Global Liveability Index for 2021 of 140 cities around the world was released by the Economist Intelligence Unit.
About:
- Handling of the Covid-19 crisis seems to be one of the most important factors that dominated the formulation of the Index for 2021.
- The index considers more than 30 qualitative and quantitative factors spanning five categories – stability (25%), healthcare (20%), culture and environment (25%), education (10%), infrastructure (20%).
Findings:
- New Zealand’s Auckland is named the world’s most liveable city for 2021, due to its successful approach in containing the pandemic.
- Austria’s Vienna (Topped in 2018 and 2019) has completely dropped out of the top 10 after being heavily affected by Covid and ranks 12.
Blue-finned Mahseer
Context:
- On the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) red list, the Blue-finned Mahseer (Tor Khudree) has been moved from the ‘endangered’ status to the ‘least concern’ status.
- However, the golden mahseer is still in danger of going extinct.
- The IUCN group is involved in conservation of the blue finned and golden Mahseer for 50 years in Lonavala, Maharashtra.
Characteristics –
- They inhabit both rivers and lakes. Most of species ascend into rapid streams with rocky bottoms for breeding.
- They are omnivorous. They eat algae, crustaceans, frogs, insects and other fish. They also eat fruits that fall from trees overhead.
Habitat –
- This species is found in River Mota Mola east of Pune and other rivers of the Deccan Plateau.
- The species is migratory, moving upstream during rains. It prefers clean, fast flowing and well oxygenated waters.
Threats –
- Over harvesting, habitat manipulation and competition from other fish species.
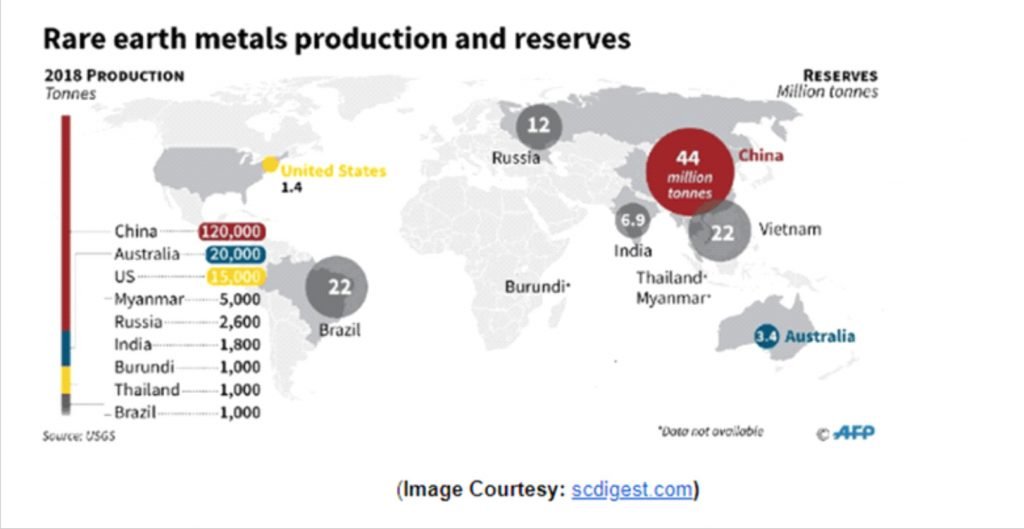
Rare earth metals at the heart of China-U.S. rivalry
Context:
- China’s dominance in the rare Earth Metals, key to the future of manufacturing, is a cause for concern for the West.
- Recently, the U.S. Senate passed the U.S. Innovation and Competition Act, aimed at countering China’s technological ambitions.
-
- Among many other interventions, the bill also aimed at improving American competitiveness in the rare earth metals market.
- The bill includes several provisions to help improve critical minerals supply chains.
Rare earth metals:
- Rare earth metals are a group of 17 elements – lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, scandium, yttrium.
- They are lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals.
- These metals have unusual fluorescent, conductive, and magnetic properties, which make them very useful when alloyed, or mixed, in small quantities with more common metals such as iron.
- However, except for the highly unstable prometheum, rare earth elements are found in relatively high concentrations in the earth’s crust.
- The rare earths occur in many other minerals and are recoverable as by-products from phosphate rock and from spent uranium leaching.
- Although they are more abundant than their name implies, they are difficult and costly to mine and process cleanly.
Use of rare earth metals:
- Rare earths find application in a wide range of products including rechargeable batteries for electric and hybrid cars, advanced ceramics, computers, DVD players, wind turbines, catalysts in cars and oil refineries, monitors, televisions, lighting, lasers, fiber optics, superconductors, mobiles, and glass polishing as well as military jet engines, satellites, and lasers.
- Lanthanum is needed to manufacture night vision devices.
- These rare minerals are essential to the manufacture of electric vehicles, wind turbines and drones considered very important sectors in the coming future.
-
- Rare earth minerals like neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium, are crucial to the manufacture of magnets used in wind turbines and electric cars.
- Hence the transition to green energy is dependent on the availability of these critical rare earth metals.

China’s dominance in rare earth metals:
- The rare earth metals are largely extracted and refined in China.
-
- Most of the rare earth metal reserves are located within China. After China, the major rare earth countries based on reserve volume are Vietnam, Brazil, and Russia.
- China hosts most of the world’s processing capacity and in 2017, China accounted for 81% of the world’s rare earth production.
- In 2019, the USA imported 80% of its rare earth minerals from China, while the EU gets 98% of its supply from China.
Issues:
- Rising tensions between the United States and China have sparked concerns over China’s dominant position as a supplier of rare earths.
- Most of the reserves being present in few nations causes problems for most of the world because of the concentration of reserves in the hands of few countries.
- China could use its dominance in the sector to cut off supplies to the west in case of a geopolitical friction.
-
- Example – Japan accused China of halting rare earth supplies for political reasons (in the aftermath of a diplomatic dispute between China and Japan in 2010), sparking recognition worldwide of the risks of dependence on one supplier.
- The chief concern is that the rare earth elements are bound up in mineral deposits with the low-level radioactive element thorium, exposure to which has been linked to an increased risk of developing lung, pancreatic, and other cancers.
- Recognizing the fact that the failure to expand its semiconductor production, or reroute rare earths supply chains, could leave the USA at a strategic disadvantage in the years ahead, the act makes several recommendations in this regard.
- The USA aims to boost domestic production and processing of rare earths and lithium, another key mineral component, while working with allies to increase sustainable global supply and reduce reliance on competitors like China.
- Recycling has also emerged as a potential source for rare earth minerals. Scaling up recycling could help meet a substantial proportion of the demand for rare earth metals.
Efforts of the USA:
- The U.S. aims to boost production and processing of rare earths and lithium, another key mineral component, while working with allies to increase sustainable global supply and reduce reliance on competitors.
- The best hope for boosting American production can be found at the Mountain Pass mine in California.
- The US Senate passed a law aimed at improving American competitiveness that includes provisions to improve critical minerals supply chains.

