SAMVAD Programme 2.0
PIB
GS 2: Government Policies and Interventions
Context:
- The 2nd phase of the SAMVAD programme was recently launched on the completion of one year of the programme by the Union Minister of Women and Child Development.
About:
- The initiative aimed at mental health and psychosocial care of children in difficult circumstances encompass a specialized training curriculum on
- Childhood trauma
- Interventions for children in conflict with the law
- Forensics in child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health
- Education and mental health support to children with special needs
- Protection and care in the context of adoption and foster care
- Integration of child protection and mental health in the Panchayati Raj systems.
- For the first time in independent India, SAMVAD will engage with functionaries in Panchayats for addressing psychosocial challenges amongst vulnerable children.
Refuge in Tajikistan
Indian Express
GS 2: International Relations
Context:
- Taliban forces have swept across Afghanistan, finally capturing the capital city of Kabul. As people are desperately trying to leave Afghanistan, many will likely seek refuge in neighbouring Tajikistan.
Concerns for Tajikistan:
- First, Tajikistan will have to consider the sentiments of Afghan Tajiks, some who have been welcomed in the Taliban’s ranks but the majority of whom passionately reject the group.
- Second, Dushanbe will be cognisant of the rise in extremism caused by the dominance of the Taliban, and the impact it will have on radical factions within Tajikistan who aim to establish an Emirate of their own.
- Thirdly, Tajikistan will have to find ways to police its porous border with Afghanistan to prevent illicit drugs and refugees from overflowing into the country.
History of relations:
- Tajikistan lies on Afghanistan’s northeastern border, adjacent to the Afghan provinces of Badakhshan, Takhar, Kunduz and Balkh.
- The 1200-km border is also home to the junction between the Hindu Kush and Karakoram Mountains, and is characterised by its rocky, inhospitable terrain.
- For a long time, Tajikistan was under the influence of the Persians, and many ethnic Tajiks residing in Afghanistan retain similar cultural values.
- Today, Tajikistan, a small landlocked Central Asian nation, has a predominantly Muslim population and is largely considered to be undemocratic, volatile, and economically unstable.
- Until 1991, Tajikistan was a part of the Soviet Union.
- When Moscow invaded Afghanistan in 1979, Tajikistan, along with the other Soviet Socialist Republics in Central Asia, supported the takeover.
- Tajikistan’s support for the Soviets made them a target of the Afghan Mujahadeen who launched attacks against the country in 1987.
- Due to the close cultural and kinship ties between Afghanistan and Tajikistan, many Tajiks secretly joined the Afghan jihad, fighting alongside the Mujahadeen.
Earthquakes in Haiti
Indian Express
GS 1: Geography
Context:
- Earthquakes have been wreaking havoc in Haiti since at least the 18th century, when the city of Port-au-Prince was destroyed twice in 19 years. Recent powerful quake killed hundreds and injured thousands more.
Where is Haiti?
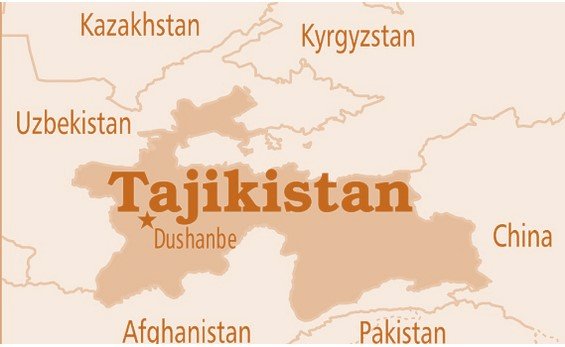
- An island country located in the Caribbean Sea, on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago.
- Bordered in land by the Dominican Republic in east.
- Maritime borders with the Bahamas, Colombia, Cuba, and Jamaica.
What causes frequent quakes in Haiti?
- Its unique geology makes it seismically active and prone to devastating earthquakes.
- Located near the intersection of two tectonic plates–the North American plate and the Caribbean plate.
- Multiple fault lines between those plates cut through or near the island of Hispaniola.
- Not all of those fault lines behave the same way; here, plates transition from smashing together to sliding past one another.
- The recent earthquake likely occurred along the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault zone.
What are the challenges?
- Financial challengesin constructing more earthquake-resistant buildings. Haiti is the poorest nation in the Western Hemisphere. It is still recovering from the 2010 earthquake and Hurricane Matthew in 2016.
- Lack of political will, centralized effort, and funding to build earthquake-resistant structures, despite the availability of technical knowledge, trained architects, and city planners.
- Political instability following recent assassination of Haiti’s President Jovenel Moïse.
- NGOs focus on their own compartmentalized projects; no coordination.
- More quakes may be ahead as 2010 earthquake was said to mark the beginning of a new cycle of large earthquakes on the Enriquillo fault system after 240 years of seismic dormancy.
Two Child Policy
The Hindu
GS 1: Population and Associated Issues
Context:
- The Uttar Pradesh Government is striving hard towards bringing a two-child Policy in the State.
About:
- After reviewing over 8,000 suggestions from the public, the Uttar Pradesh State Law Commission has submitted a report and draft Bill of a new population control law (The Uttar Pradesh Population (Control, Stabilisation and Welfare) Bill, 2021) proposing two-child policy to the State government.
- The Commission adopted the suggestion that special facilities extended to BPL families who have only one child and undertake voluntary sterilisation would be extended to all couples irrespective of the BPL category.
- It, however, rejected suggestions that the right to vote of persons having more than two children be curtailed and that they also are barred from the benefit of reservation.
- The right to vote is a constitutional and Fundamental Right. Therefore, the State government has no competence to make such a law.
Background:
- On World Population Day (11th July), the Uttar Pradesh government announced a new population policy for 2021-2030.
- The new policy has provisions to give incentives to those who help in population control.
Focus areas:
- To increase the accessibility of contraceptive measures issued under the Family Planning Programme and provide a proper system for safe abortion.
- To reduce the new borns’ and maternal mortality rate.
- To provide for care of the elderly, and better management of education, health, and nutrition of adolescents between 11 to 19 years.
Provisions in the Policy:
- Debarment from benefits of welfare schemes
- Barred from contesting elections at local level
- Ineligible to apply for state Government jobs
- Barred from promotion
- One Child Reward
- Rebates for People not in Government Jobs
- Reducing Gross Fertility Rate

Applicability:
- The provision of this legislation shall apply to a married couple where the boy is not less than 21 years of age and the girl is not less than 18.
- The policy will be voluntary – it will not be enforced upon anyone.
Challenges with policy:
- The international experience shows that any coercion to have a certain number of children is counter-productive and leads to demographic distortions.
- India is committed to its obligations under international law, including the principles contained in the International Conference on Population and Development Programme of Action, 1994.
- In Suchita Srivastava & Anr vs Chandigarh Administration (2009), the Court found that a woman’s freedom to make reproductive decisions is an integral facet of the right to personal liberty guaranteed by Article 21.
- It would lead to increased gender inequality. Any coercive measure is likely to worsen the discrimination against girls.
- In India, the number of missing girls at birth has increased from 35 lakhs in 1987-96 to 55 lakhs in 2007-16. Bringing any such population control bill will worsen the situation.
- In the patriarchal dominant society, when people can have only 2 children, pressure on women to give birth to male children will increase. Thereby leading to unsafe abortions and skewed sex ratio also.
Way Ahead:
- Given UP’s large population and geography, family planning and fertility should be targeted.
- Bringing educational reforms and giving choices for family planning would work more appropriately.
- This would lead to an overall improvement in the fertility outcome of the state as well as at the national level.
Tomato Leaf Curl New Delhi Virus (ToLCNDV)
PIB
GS 3: Science and Technology
Context:
- Effective defense strategy deployed by a resistant tomato cultivar against Tomato leaf curl New Delhi virus has been unravelled by scientists of National Institute of Plant Genome Research.
About:
- ToLCNDV infection causes severe losses in tomato yield worldwide.
- Lack of information on resistance (R) genes against ToLCNDV has considerably retarded the pace of crop improvement against this rapidly spreading pathogen. Several attempts have been made to identify antiviral genes against ToLCNDV and related viruses.
- Scientists from DBT Autonomous Institution, National Institute of Plant Genomics Research (NIPGR) report an effective defense strategy deployed by a resistant tomato cultivar against ToLCNDV.
- It employs Sw5a (R gene) that recognizes AC4 protein (viral effector) of ToLCNDV to restrict virus spread. These findings could be translated into development of resistance in susceptible cultivars of tomato through modern breeding or molecular approaches.

