Hypersonic Technology
Indian Express
GS 3: Defence Technology
Context:
- Recently, it has been reported that China tested a nuclear-capable hypersonic glide vehicle that circled the globe before speeding towards its target.

About:
- Chinese military launched a rocket that carried a hypersonic glide vehicle.
- It was launched on a Long March rocket, which is used for the space programme.
- Hypersonic speeds are 5 or more times the speed of sound.
- The missile has demonstrated an advanced space capability.
- It circled the globe, flew through low-orbit space before cruising down towards its target. However, it missed its target by about two-dozen miles.
- The development has caught USA intelligence by surprise.
- Several countries, including the US, Russia and China, are developing hypersonic missiles which travel at a speed five times that of sound.
- Though slower than ballistic missiles, they are harder to intercept and can be manoeuvred.
Implications for India:
- This move by China certainly needs to be watched closely by the world, especially India considering its issues along the LAC with China in the recent past.
- Such capabilities highlight the threat for India’s space assets along with the surface assets.
- The offence system operating at hypersonic speeds would mean the requirement to develop defence systems at these speeds.
- India too is working on hypersonic technologies.
- DRDO successfully flight-tested the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV), with a capability to travel at 6 times the speed of sound in September 2020.
- A solid rocket motor of Agni missile took it to an altitude of 30 km where the cruise vehicle separated as planned.
- The hypersonic combustion sustained and the cruise vehicle continued on its desired flight path at a velocity of six times the speed of sound for more than 20 seconds.
- In December 2020, an advanced Hypersonic Wind Tunnel (HWT) test facility of the DRDO was inaugurated in Hyderabad.
- It is a pressure vacuum-driven, enclosed free jet facility that simulates Mach 5 to 12.
Western Disturbances
Hindustan Times
GS 1: Geography
Context:
- Recently, Uttar Pradesh recorded Heavy rain due to the low-pressure zone caused by western disturbance and lower cyclonic circulations.
About:
- Western Disturbance (WD) is an extra-tropical storm that originates in the Mediterranean region.
- It travels from the “western” to the eastern direction.
- Disturbance means an area of “disturbed” or reduced air pressure.
- Equilibrium exists in nature due to which the air in a region tries to normalize its pressure.
- The WD is not always the harbinger of good weather.
- It travels from the “western” to the eastern direction.
- In the term “extra-tropical storm”, the storm refers to low pressure.
- “Extra-tropical” means outside the tropics (as WD originates outside the tropical region).

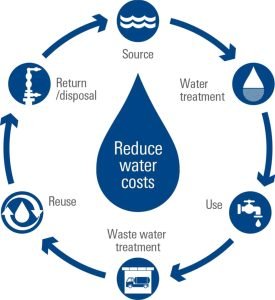
Management of Water
The Hindu
GS 3: Environment and Conservation
Context:
- Head of the panel drafting new water policy calls for ‘nature-based solutions’ for storage, supply.
- Changing patterns and intensity of precipitation require greater emphasis on agility, resilience, and flexibility in water management.
New Policy needed:
- There is a need to take very serious cognisance of the current context of climate change and the grave crisis of water facing the country.
- Recent estimates suggest that if the current pattern of demand continues, about half of the national demand for water will remain unmet by 2030.
- With water tables falling and water quality deteriorating, a radical change is needed in the approach to water management.
- Changing patterns and intensity of precipitation, as also rates of discharge of rivers, show that it can no longer be assumed that the water cycle operates within an invariant range of predictability.
- This requires greater emphasis on agility, resilience, and flexibility in water management so that there could be an adequate response to the heightened uncertainty and unpredictability of the future.
Recommendations of the proposed NWP:
Demand management is Key
- Shift focus from endlessly increasing the supply of water towards measures for demand management. This means diversifying the cropping patterns to include less water intensive crops.
- It also needs to lower the industrial water footprint, among the highest in the world by reducing freshwater use and shifting to recycled water.
- Cities must mandatorily shift all non-potable uses, like flushing, fire protection, vehicle washing, landscaping etc. to treated wastewater.
Supply-side reforms:
- Country is running out of sites for further construction of large dams, while water tables and groundwater quality are falling in many areas.
- There is mounting evidence across the globe in favour of “nature-based solutions” for water storage and supply.
- Thus, the NWP places major emphasis on the supply of water through rejuvenation of catchment areas, which needs to be incentivised through compensation for ecosystem services, especially to vulnerable communities in the upstream, mountainous regions.
- Renewed thrust on local rainwater harvesting to catch the rain where it falls, when it falls, must be combined with demarcation, notification, protection, and revival of traditional local water bodies in both rural and urban areas.
- This would form part of the urban blue-green infrastructure for improved water levels and quality, as also flood mitigation.
Pricing the water:
- Economic services (like industrial and commercial use) be charged at a rate where the O&M (Operation and Management) costs and part of the capital cost would be the basis for the water service fees.
- At the same time, concessional rates should be provided for vulnerable social sections.
Rise of Prices of Natural Gas, Coal and Electricity
Bloomberg
GS 3: Infrastructure
Context:
- The rise of prices of natural gas, coal and electricity are putting extra pressure on oil markets and boosting the demand as industries and power generators are seeking to switch to liquid fuels.
How are oil prices decided?
- Supply and demand – The concept of supply and demand is the mechanism by which the prices of crude oil are controlled.
- OPEC as producers have no influence over the demand for petroleum but they tend to change its supply in order to influence the price.
- In order to keep prices of the oil stable, OPEC countries usually maintain a quota of oil supply.
- Speculations – Another mechanism of pricing is the future supply based on some speculations.
- These are the supply and demand based on speculations of suppliers and consumers.
Reasons for the current oil demand:
- Fuel switching from gas and coal to oil and crude is the reason for increased demand.
- Soaring natural gas prices have spiked the price by 300% .
- Agencies like IEA’s forecast on oil demand contributes for the reluctance of OPEC to open the taps.
Way ahead:
- Top exporter Saudi Arabia has started cutting its official selling price to its core customers to ease the price of Brent crude oil futures.
- On the demand side, China’s industrial slowdown, collapse of real estate giant Evergrande, rising inflation pressure and COVID-19 disruptions could undermine oil demand growth over the next 12 months.
- But in the near term, a repeat of a cold winter across the Northern Hemisphere could cause major energy supply shortages in many leading industrial hubs.
Review of IMF role
Indian Express
GS 2: International Organisations
Context:
- In the backdrop of the 2021 annual meetings of the World Bank Group and the International Monetary Fund (IMF)in Washington, leading experts have suggested the need to review the role of the IMF.
Rationale
- Reforms due to changing economic weight of emerging countries, stressing on completing quota reforms and maintaining data integrity amid the World Bank discontinuing its Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) reports.
Experts Suggestions
- When it was alleged that the EoDB rankings were tweaked to inflate the ranks for China (in EoDB 2018) and Saudi Arabia, UAE and Azerbaijan (EoDB 2020);
- Experts stressed the need to complete quota reforms in the IMF amid changing dynamics of developed and emerging economies including India.
- A restructuring of the Article IV consultations, under which the IMF holds bilateral discussions with its members usually every year and its staff prepares a report, is also being sought.
- On IMF Quota Reform experts cited that
- Each member’s quota determines its voting power as well as its borrowing capacity.
- The US and China should jointly lead the efforts on transformation of relative quota shares in the IMF and associated reforms in the international monetary system.
- IMF should focus on lower income countries and support other developing countries’ market funds raising activities, as its Article IV consultation reports are utilised by credit rating agencies, impacting the fund raising capacity of countries like India.
- Most of the Asian countries including India can now raise funds on their own on the basis of strength of their forex reserves, and do not have to necessarily go to the IMF like in the past to stem the tide of the crisis.
- The second is that even though countries like India and others are no longer clients, there will still be occasions when because of the sudden rise in the price of petroleum products or something, there may be a need and therefore, they need to look at the problems that may arise because of certain situations.
- During the 1991 crisis, India was able to utilise funding facilities of the IMF and was able to tide over the difficult situation.


