S400 Air Defence Deal
The Hindu
GS 2: Agreements Involving India &/or Affecting India’s Interests
Context:
- The delivery schedule for the S-400 long range air defence systems is on track for the end of 2021 despite the COVID-19 pandemic.
About S 400 Triumf:
- The S-400 Triumf, previously known as the S-300 PMU-3, is an anti-aircraft weapon system developed in the 1990s by Russia’s Almaz Central Design Bureau as an upgrade of the S-300 family.
- It has been in service with the Russian Armed Forces since 2007.
- China was the first foreign buyer to make a government-to-government deal with Russia in 2014, while Saudi Arabia, Turkey, India and Belarus have all acquired, or expressed interest, in the system since.
- In 2017, the S-400 was described by The Economist as “one of the best air-defence systems currently made” and an official of Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) said it “is among the most advanced air defense systems available”.
- Max. target speed: 4.8 km/s (17,000 km/h; 11,000 mph; Mach 14)
- Operational range: 40 Km to 400 Km
- It is a long-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) system.
- This system is for the Indian Air Force (IAF) and will help in further enhancing the air defence (AD).
Background
- In the last three years, since 2018, the defence trade between India and Russia was $15 billion because of some big ticket defence deals.
- According to the Russia CAATSA was not targeted against Russia but against third countries cooperating with Russia.
What is CAATSA, and how did the S-400 deal fall foul of this Act?
- Countering America’s Adversaries through Sanctions Act (CAATSA) was passed unanimously by the US Congress and signed reluctantly by US President Donald Trump.
- Enacted on August 2, 2017, its core objective is to counter Iran, Russia and North Korea through punitive measures.
- It primarily deals with sanctions on Russian interests such as its oil and gas industry, defence and security sector, and financial institutions, in the backdrop of its military intervention in Ukraine and its alleged meddling in the 2016 US Presidential elections.
Greece’s Wall – Afghan Refugee Crisis
Indian Express
GS 2: International Relations
Context:
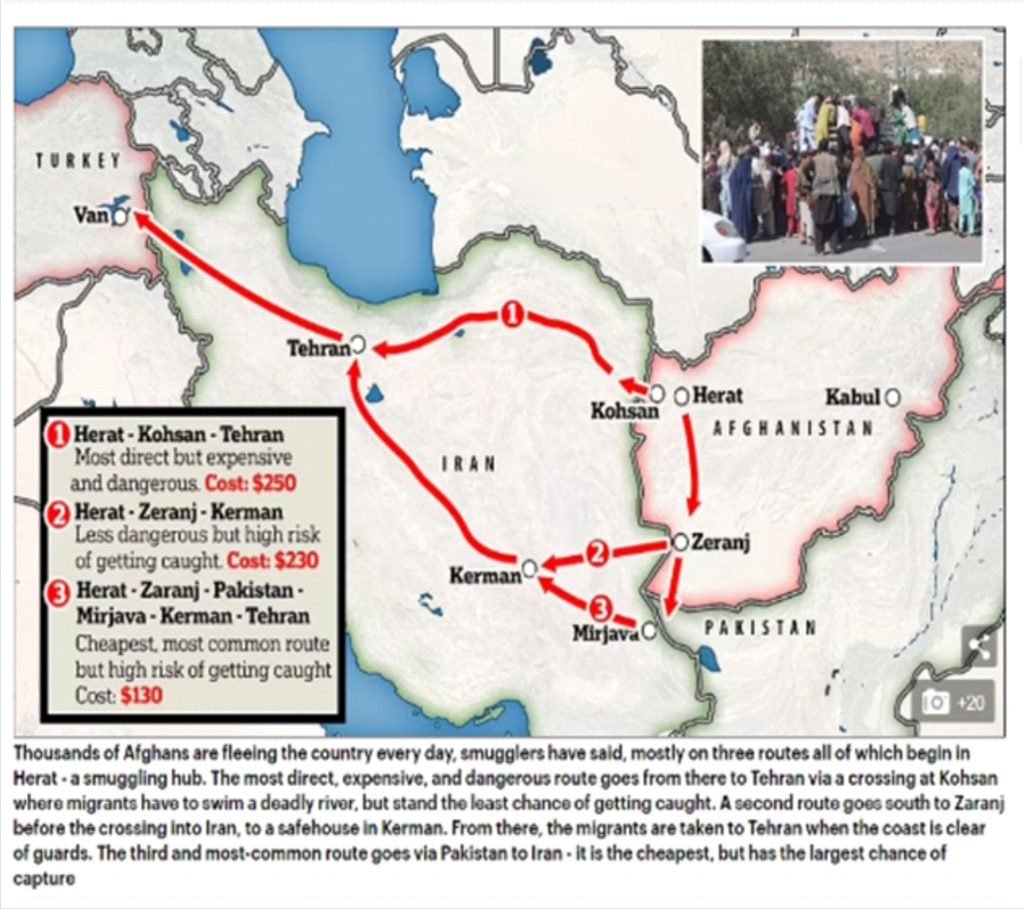
- To avoid heavy migration of Afghan citizens into Greece via Turkey, and then further into Europe, following the Taliban takeover of Afghanistan, Greece has built a 40-km long wall and installed a hi-tech surveillance system on its border with Turkey.
Afghan refugee crisis:
- The Taliban takeover of Afghanistan has given way to a new refugee crisis.
- 400,000 Afghans have fled their homes since the start of 2021, including almost 300,000 since May 2021.
- Afghan nationals enter Turkey from Iran and then, via land or sea enter Greece to eventually get into Europe.
Stance of Greece and Turkey:
- The European Union and Greece have been in talks to help each other in the possibility of massive migration from Afghanistan.
- EU nations should collectively act towards supporting the countries in the region “which will be affected by the migration wave”.
- EU should help the Afghan citizens in Afghanistan and in neighbouring countries like Iran.
- But the cooperation on migration should be promoted based on mutual understanding and interests.
- Because, the EU is not ready and does not have the capacity to handle and afford another major migration crisis like the one in 2015.
National Monetisation Plan
PIB
GS 3: Government Policies & Interventions
Context:
- Recently, the Government of India has launched the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP).
About:
- The NMP estimates aggregate monetisation potential of Rs 6 lakh crores through core assets of the Central Government, over a four-year period, from FY 2022 to FY 2025.
- The plan is in line with Prime Minister’s strategic divestment policy, under which the government will retain presence in only a few identified areas with the rest tapping the private sector.
- The pipeline has been developed by NITI Aayog, in consultation with infrastructure line ministries, based on the mandate for ‘Asset Monetisation’ under Union Budget 2021-22.
- NMP is envisaged to serve as a medium-term roadmap for identifying potential monetisation-ready projects, across various infrastructure sectors including roads, ports, airports, railways, warehousing, gas & product pipeline, power generation and transmission, mining, telecom, stadium, hospitality, and housing.
- Under the plan, private firms can invest in projects for a fixed return using the InvIT route as well as operate and develop the assets for a certain period. Some assets such as warehouses and stadiums can also be given on a long-term lease for operations. Thus, it will involve the participation of the private firms in the infrastructure sector.
- The objective of this initiative is to enable ‘Infrastructure Creation through Monetisation’.
- The programme will include only brownfield assets that are either languishing or have not been fully monetised. There would be no transfer of ownership of assets or land. The primary ownership of the assets will continue to be with the Government with the framework envisaging hand back of assets to the public authority at the end of transaction life.
Urban employment scheme
The Hindu
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Context:
- The Tamil Nadu government will implement an urban employment scheme on the lines of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) at a cost of ₹100 crore to improve the livelihood of urban poor.
About:
- Till now it is a pilot scheme and the government would soon come out with guidelines for providing wages under the scheme.
- In the FY22 it will be implemented in two zones in the Greater Chennai Corporation.
- Objective:
- To provide employment to urban poor, who had lost their jobs because of the COVID-19 pandemic as recommended by the committee headed by former RBI Governor C Rangarajan.
- The State government had submitted a memorandum to the Centre seeking funds for an urban employment scheme but was yet to get a response.
Immune cells in Corals
Down to Earth
GS 3: Science and Technology
Context:
- Specialised immune cells exist in certain varieties of sea corals and anemones, found a new study.
- These cells help understand how the organisms protect themselves from viruses and bacteria in the marine ecosystem.
Background:
- The newly discovered phagocytic cells were identified in cauliflower coral and starlet sea anemone by scientists at the Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University of Miami and the Ben Gurion University of the Negev.
- At least three per cent of the total cell population of these organisms are phagocytic that fight infections, the study found.
- Immune cells ingest and destroy foreign and damaged cells through a process called phagocytosis.
- Phagocytosis was observed in the unique immune cells that engulfed and digested the antigens as well as the damaged cells of the organisms. At least two populations of these immune cells were identified.
Multi-Mode Hand Grenades (MMHG)
PIB
GS 3: Defence and Security
Context:
- The first batch of Multi-Mode Hand Grenades (MMHG), manufactured by Economic Explosives Limited (EEL), following Transfer of Technology from Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory of Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO), was handed over to the Indian Army in Nagpur, Maharashtra on August 24, 2021.
Benefits:
- The grenade is not just more lethal but is safer to use. It has a distinctive design that gives flexibility of employment in both defensive (fragmentation) and offensive (stun) modes.
- It has a highly accurate delay time, very high reliability in usage and safe for carriage.
- These new grenades will replace Grenade No 36 of World War I vintage design, which had been continuing in service till date.
Background:
- The EEL had signed a contract with Ministry of Defence on October 01, 2020 to supply 10 lakh modern hand grenades for Indian Army and Indian Air Force.
- The deliveries would be spread over two years from the bulk production clearance, which was accorded to EEL in March 2021. The first order has been delivered within five months.

GM Soya Cake
PIB
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Context:
- Government of India has relaxed the rules for import of crushed and de-oiled GM soya cake (Non-living organism only).
About:
- Application of provision as in Condition 6(b) of General Notes Regarding Import Policy Schedule — I (Imports) of the ITC (HS) 2017 has now been relaxed to allow imports of 12 Lakh Metric ton of crushed and de-oiled GM soya cake (only Non-living organism) under ITC HS codes 23040020 and 23040030 from Nhava Sheva port and LCS Petrapole, till 31st October, 2021.
- The said relaxation comes after clarification and prior permission from the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change that “Since soya de-oiled and crushed (DOC) cake does not contain any living modified organism, this Ministry has no concerns and no objection for import of soya cakes from an environmental angle”.
- This decision will positively impact farmers, poultry farmers, and fishermen.

