Current Affairs (29th July 2021)
Gold Ore Reserves
Context:
- Recently, Union minister of mines reported in the Rajya Sabha about the gold ore reserves.
About:
- India has 83 million tonnes of gold ore reserves as of April 1, 2015, according to National Mineral Inventory data.
- Out of these, 17.22 million tonnes were placed under reserves category and the rest under remaining resources category.
- The largest reserves of gold ores are in Bihar (44 per cent), followed by Rajasthan (25 per cent), Karnataka (21 per cent), West Bengal (3 per cent), Andhra Pradesh (3 per cent), Jharkhand (2 per cent).
- The remaining 2 per cent reserves are in Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu. The cost of extraction of any mineral, including gold, varies from mine to mine.
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is actively engaged in geological mapping, followed by mineral exploration and surveys, of various mineral commodities with an aim to identify potential mineral rich zones and establish resources.
- Every year, according to approved annual Field Season Program, GSI takes up mineral exploration projects in various parts of the country for augmenting mineral resources.
- The Government of India recently amended the Minerals Evidence of Mineral Contents Rules to allow auction of composite licence at G4 level for deep-seated minerals, including gold.
- This is expected to bring more participation from private players with advanced technology in the field of exploration and mining of deep-seated minerals, which is expected to reduce the cost of extraction of gold.
Earth Overshoot Day
Context:
- According to Worldwide Fund for Nature (WWF), humanity currently uses 74 per cent more than what the planet’s ecosystems can regenerate — or 1.7 Earths.
- From Earth Overshoot Day until the end of the year, humanity operates on ecological deficit spending.
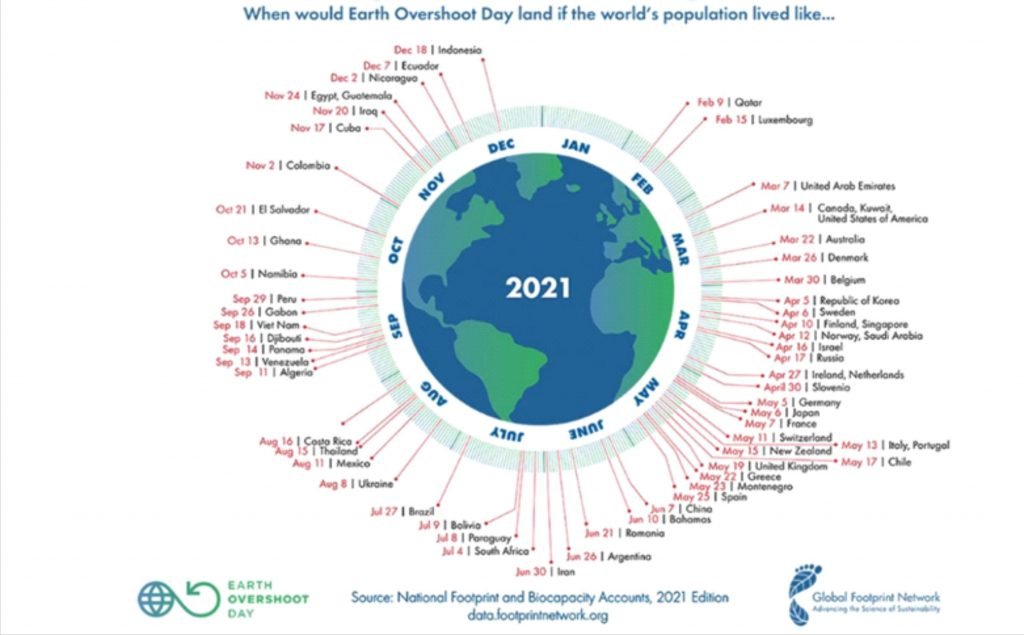
About:
- There was also the 5 per cent decrease in ‘global forest biocapacity’ due to a rise in deforestation of the Amazon’s rainforests.
- Some 1 million hectares of rainforest were lost in Brazil alone, which is home to the largest swathe of Amazonian rainforest.
- Even worse, there would be a 43 per cent year-over-year increase in deforestation in 2021.
- The carbon footprint of transportation will be lower this year than pre-pandemic levels. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from road transport and domestic air travel will be five per cent below 2019 levels.
- CO2 emissions due to international aviation will be 33 per cent below 2019 levels. This is according to estimates from the International Energy Agency.
- But global energy-related CO2 emissions will increase 4.8 per cent from last year as economies try to recover from the impact of COVID-19. Global coal use is estimated to constitute 40 per cent of the total carbon footprint.
Suggestions:
- A business-as-usual scenario will simply not work if the date for World Overshoot Day is to be pushed behind.
- It suggested a number of measures such as cutting down on food wastage, commercial technologies for buildings, industrial processes and electricity production and cutting down on transportation.
World Drowning Prevention Day
Context:
- At least 236,000 people drown every year; drowning is among the top 10 leading causes of death for children and youth aged between one and 24 years, the WHO noted on the first World Drowning Prevention Day marked July 25, 2021.
About:
- More than 90 per cent of drowning deaths occur in rivers, lakes, wells, and domestic water storage vessels in low- and middle-income Children and adolescents in rural areas are disproportionately affected.
- Over half the people drown in the WHO Western Pacific Region and WHO South-East Asia Region.
- Drowning death rates are the highest in the WHO Western Pacific Region — 27-32 times higher than those seen in the United Kingdom or Germany, respectively.
Suggestion:
- There is a need to provide safe places away from water to children, teach swimming to them as well as improve flood risk management to avert deaths caused by drowning.
- The WHO urged all stakeholders — governments, UN agencies, civil society organisations, the private sector, academia, and individuals —for a coordinated and multi-sectoral action on measures such as:
- Installing barriers controlling access to water
- Providing safe places away from water such as crèches for pre-school children with capable childcare
- Teaching swimming, water safety and safe rescue skills
- Training bystanders in safe rescue and resuscitation
- Improving flood risk management
Cloudbursts
Context:
- There have been a series of cloudbursts across the western Himalayan region. The ensuing flash floods have wreaked havoc in Himachal Pradesh, the Union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh and across the border, in the twin cities of Islamabad and Rawalpindi in Pakistan.
- A cloudburst occurred in the area around the holy cave shrine of Amarnath in south Kashmir causing flooding. The Amarnath Yatra has been cancelled for a second consecutive year due to the novel corona virus disease (COVID-19) pandemic.
What is Cloudburst?
- It is an extreme amount of precipitation in a short period of time to a small geographical area.
- Meteorologists say the rain from a cloudburst is usually of the shower type with a fall rate equal to or greater than 100 mm (4.94 inches) per hour.
- Cloudburst is basically a rainstorm and occurs mostly in the desert and mountainous regions, and in interior regions of continental landmasses due to the warm air current from the ground or below the clouds rushes up and carries the falling raindrops up with it.
- The rain fails to fall in a steady shower, which causes excessive condensation in the clouds as new drops form and old drops are pushed back into it by the updraft.
How is cloudburst different from rainfall?
- Rain is condensed water falling from a cloud while cloudburst is a sudden heavy rainstorm.
- A report in the Down to Earth said a cloudburst is different from rain only in the amount of rainfall recorded. Rain over 100 mm per hour is categorised as a cloudburst.
- Hence, cloudburst is a natural phenomenon, but occur quite unexpectedly, very abruptly, and rather drenching.
- In the Indian Subcontinent, it generally occurs when a monsoon cloud drifts northwards, from the Bay of Bengal or the Arabian Sea across the plains than on to the Himalaya that sometimes brings 75 millimetres of rain per hour.
Pneumonia
Context:
- As per the Sample Registration System Report (2010-13) of the Registrar General of India, Pneumonia contributes to 16.9% of infant deaths and it is the 2nd highest cause of infant mortality.
About:
- Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung affecting primarily the small air sacs known as alveoli.
Causes:
- Bacteria, viruses, or fungi can lead to pneumonia.
- Top causes include:
- Flu viruses
- Cold viruses
- RSV virus (the top cause of pneumonia in babies aged 1 or younger)
- Bacteria called Streptococcus pneumonia and Mycoplasma pneumonia.
Spread
- Pneumonia is contagious and can be spread through coughing or sneezing. It can also be spread through fluids, like blood during childbirth, or from contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms
- Cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
Vaccine
- Pneumonia caused by bacteria is easily preventable with vaccines. 3 doses of the primary vaccine (Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) are recommended to prevent it.
- Recently, the Serum Institute of India announced the launch of India’s first indigenously developed pneumococcal vaccine – Pneumosil.
- A new vaccine for one of the main viral causes of pneumonia is under development.
- India is planning for the nationwide roll out of PCV under Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP).
Status of Pneumonia in India:
- As per UNICEF data, more than one lakh children under the age of five years die every year in India due to pneumococcal disease.
- The top five contributors to India’s pneumococcal pneumonia burden in terms of the number of cases and deaths were Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Jharkhand.
Global Burden:
- The Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria and Pakistan account for more than half of all deaths due to pneumonia among children under 5.
Initiatives in fighting Pneumonia:
- Global Action Plan for Pneumonia and Diarrhoea (GAPPD): It is an effort led by the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF to accelerate disease prevention and control.
- Integrated Action Plan for Prevention and Control of Pneumonia and Diarrhoea (IAPPD): It was launched in the year 2014, to undertake collaborative efforts towards the prevention of diarrhoea and Pneumonia related under-five deaths.
- Global Forum on Childhood Pneumonia: It is an initiative of 9 leading health and children’s organisations including UNICEF, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and Gavi among others.
- Social Awareness and Actions to Neutralize Pneumonia Successfully (SAANS) Initiative: It aims to reduce child mortality due to pneumonia, which contributes to around 15% of deaths of children under the age of five annually.

