Current Affairs (5th February 2021)
Lithium deposits
Context:
- Atomic Minerals Directorate for Exploration and Research (AMD) have conducted a preliminary surveys on surface and limited subsurface which have shown the presence of Lithium resources of 1,600 tonnes in the pegmatites of Marlagalla – Allapatna area, Mandya district, Karnataka.
LITHUM AND ITS USES:
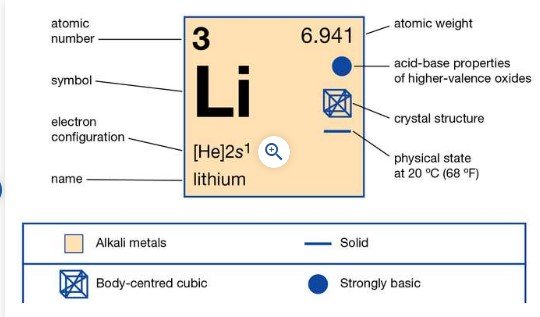
- Soft, silvery-white metal
- Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element.
- Highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in mineral oil.
- It is an alkali metal and a rare metal.
- Highest specific heat capacity of any solid element.
- Its single balance electron allows it to be a good conductor of electricity.
- Flammable and can even explode when exposed to air and water.
- Used in ceramics, glass, telecommunication and aerospace industries.
- Used in Lithium ion batteries, lubricating grease, high energy additive to rocket propellants, optical modulators for mobile phones.
AERO-INDIA 2021
CONTEXT:
- The Inaugural ceremony for Aero India 2021, Asia’s largest Aerospace and Defence Exhibition, was held at Air Force Station, Yelahanka, Bengaluru between February 03-05, 2021.
ABOUT AERO-INDIA:
- Biennial air show and aviation exhibition held in Bengaluru, India at the Yelahanka Air Force Station.
- Organised by the Defence Exhibition Organisation, Ministry of Defence.
- First edition of the air show was held in 1996.
- Aero India 2021 is the 13th edition of Aero India.
- This year Aero India 2021 has been organised in hybrid mode with a concurrent virtual exhibition to encourage maximum participation.

Square Kilometre Array
CONTEXT:
- The Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO) Council held its maiden meeting recently among organisations from ten countries like Australia, Canada, China, India, Italy, New Zealand, South Africa, Sweden, the Netherlands and the UK and they approved the establishment of the world’s largest radio telescope.
- SKAO is a new intergovernmental organisation dedicated to radio astronomy and is headquartered in the UK.
RADIO TELESCOPES
- Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can detect invisible gas and, therefore, they can reveal areas of space that may be obscured by cosmic dust.
- Since the first radio signals were detected by physicist Karl Jansky in the 1930s, astronomers have used radio telescopes to detect radio waves emitted by different objects in the universe and explore it.
- The Arecibo telescope in Puerto Rico, which was the second-largest single-dish radio telescope in the world, collapsed in December 2020.
- The telescope was built in 1963 and because of its powerful radar, scientists employed it to observe planets, asteroids and the ionosphere, making several discoveries over the decades, including finding prebiotic molecules in distant galaxies, the first exoplanets, and the first-millisecond pulsar.
Significant of SKA telescope
- The telescope, proposed to be the largest radio telescope in the world, will be located in Africa and Australia whose operation, maintenance and construction will be overseen by SKAO.
- The completion is expected to take nearly a decade at a cost of over £1.8 billion.
- It will tell the beginning of the universe, how and when the first stars were born, the life-cycle of a galaxy, exploring the possibility of detecting technologically-active civilisations elsewhere in our galaxy and understanding where gravitational waves come from.
- Telescope will accomplish NASA’s scientific goals by measuring neutral hydrogen over cosmic time, accurately timing the signals from pulsars in the Milky Way, and detecting millions of galaxies out to high redshifts.

Vaccine passport
CONTEXT:
- In an effort to reduce curbs on travel and public life, Denmark announced that it is in the process of rolling out a digital passport that would show if holders have been vaccinated against the coronavirus.
- Currently, Denmark is under a lockdown. Non-essential retail is closed, and bars and restaurants are only permitted takeaway orders.
ABOUT:
- The first step will be completed by the end of February 2021, when Danish citizens who have been vaccinated will be able to see a record on a government health website.
- After another three or four months, the digital passport and an app will be launched. It will function as an “extra passport” that people can carry on their mobile devices.
- Denmark, along with countries in northern Europe, has in recent years pushed for paperless communications in both the public and private sectors. The corona passport is considered a part of its effort to reduce bureaucracy by using electronic verification.
- Last year, the World Health Organisation had also said it was working on an e-vaccination certificate. Its “smart yellow card” would be a digitised version of the yellow vaccination booklets used in many countries, as per a Reuters report.
83 LCAs TEJAS
CONTEXT:
- At the 13th edition of Aero India in Bengaluru, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) was awarded the contract to manufacture 83 Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
ABOUT:
- This contract is the biggest Make in India defence contract till date.
- The contract includes 73 LCA Tejas Mk-1A fighter aircraft and 10 LCA Tejas Mk-1 trainer aircraft at a cost of ₹45,696 crore along with design and development of infrastructure sanctions worth ₹1,202 crore.
- The deliveries of all 83 aircraft shall be completed in eight years from now.
- Globally India is facing unprecedented levels of ‘uncertainty, volatility and interconnected threats’. In this regard he pitched for greater regional coordination.
- As part of efforts to boost defence exports, HAL displayed an ‘Atmanirbhar formation’ consisting of its platforms — LCA trainer, HTT-40 trainer, Intermediate Jet Trainer, Advanced Hawk Mk-132 and Civil Dornier Do-228.
HAL Tejas:
- The HAL Tejas is an Indian single-engine, fourth-generation, multirole light fighter designed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) in collaboration with Aircraft Research and Design Centre (ARDC) of HAL for the Indian Air Force and Indian Navy.
- It came from the LCA programme, which began in the 1980s to replace India’s ageing MiG-21 fighters.
- In 2003, the LCA was officially named “Tejas”.
- Tejas has a tail-less compound delta-wing configuration with a single vertical stabilizer. This provides better high-alpha performance characteristics than conventional wing designs.
- It integrates technologies such as relaxed static stability, fly-by-wire flight control system, multi-mode radar, integrated digital avionics system and composite material structures.
- It is the smallest and lightest in its class of contemporary supersonic combat aircraft.
- The Tejas is the second supersonic fighter developed by HAL after the HAL HF-24 Marut.
- Production of the Tejas Mark 1 for the Indian Air Force (IAF) began in 2016, at which time the naval version was undergoing flight tests for Indian Navy (IN).
- The first Tejas IAF unit, No. 45 Squadron IAF Flying Daggers was formed on 1 July 2016 with two aircraft.
- The indigenous content of the Tejas was 7% by value and 75.5% by number of line replaceable units in 2016.

INDIA MOTIVES:
- India has long witnessed unfortunate attempts to employ force to change the status quo along our unresolved border and India is vigilant and prepared to counter and defeat any misadventure and defend people and territorial integrity at all costs. India’s resolve towards this is shown by our growing defence capabilities.
- India plans to spend $130 bn on military modernisation in the next 7-8 years.
- India faced threats and challenges emanating from multiple fronts and it was a victim of state-sponsored terrorism, which was now a global threat.
Collection of DNA samples
CONTEXT:
- DNA Technology (Use and Application) Regulation Bill, 2019 allows investigating agencies to collect DNA samples from “suspects”.
- This Bill will give investigating agencies “unbridled power that is easily capable of misuse and abuse” and amount to a “threat to the life, liberty, dignity and privacy of a person”.

USE OF DNA:
- DNA testing is currently being done on an extremely limited scale in India, with approximately 30-40 DNA experts in 15-18 laboratories undertaking fewer than 3,000 cases a year.
- The standards of the laboratories are not monitored or regulated. The Bill aims to introduce the regulation of the entire process from collection to storage.
- Bill aims to provide for “the regulation of use and application of Deoxyribonucleic Acid [DNA] technology for the purposes of establishing the identity of certain categories of persons, including the victims, offenders, suspects, undertrials, missing persons and unknown deceased persons”.
ANALYSIS:
- Collection DNA of a “suspect” is questioned and in a blind crime or a crime involving a large number of persons (such as a riot), everybody is a suspect without any real basis.
- This would mean that thousands of persons could be subjected to DNA profiling on a mere suspicion.
- Such an unbridled power is easily capable of misuse and abuse by targeting innocents, against whom there is not a shred of evidence.
- Such an unbridled police power ought not to be conferred on anybody or any agency as it would amount to a threat to the life, liberty, dignity and privacy of a person.
- Bill would lead to the targeting of Muslims, Dalits and Adivasis.

CONCLUSION:
- Fears are not entirely unfounded and have to be addressed by the government and by Parliament as well.
- Its use in recent months has exposed a false encounter in which innocents were killed contradicting initial claims made that they were militants.

