Current Affairs (7th May 2021)
5G trial &its important for Indian telcos
Context:
- The Department of Telecommunications allowed private telcos Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio Infocomm and Vi (formerly Vodafone Idea) and well as state-run telco Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited (MTNL) to start trials for 5G technology as well as its applications in various sectors. The trials will last for 6 months for now.
- Chinese firms Huawei and ZTE will not be participating in the forthcoming trials as these were not marked on the priority list.
Why are the trials for 5G technology important for telcos?
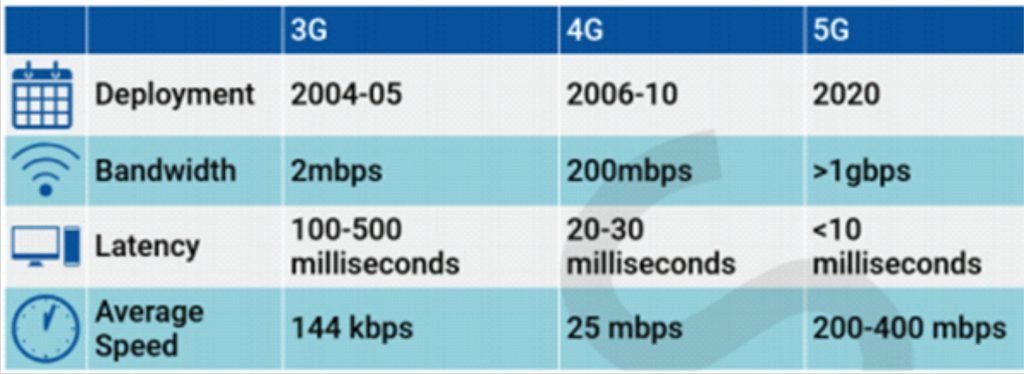
- 5G or fifth generation is the latest upgrade in the long-term evolution mobile broadband networks.
- It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G networks.
- It is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra-low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability and a more uniform user experience to more users.
- 5G mainly works in 3 bands, namely low, mid, and high-frequency spectrum — all of which have their uses and limitations.
- The telecom market in India is left with only three private telcos, with the rest having surrendered to the low returns on investments over the years.
- Apart from the private telecommunication companies, the two state-run companies, MTNL and Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited have also survived but are making losses.
- To increase their average revenue per user, it is pertinent for telcos to start offering the new 5G technology as soon as possible.
- For that, however, they will have to conduct trials in a variety of circumstances, including in semi-urban and rural areas, which remains an untapped market for them.
- Apart from the telcos, it is also important that the government be ready to roll out the new technology as soon as possible.
What will 5G trials in India entail for now?
- In the initial phase, these trials will be for 6 months, including a 2-month period for procurement and setting up of the equipment.
- In these 6 months, telcos will be required to test their set up in urban areas, semi-urban areas as well as rural areas.
- During this period, the telcos will be provided with experimental spectrum in various bands, such as the mid-band of 3.2 GHz to 3.67 GHz, the millimeter wave band of 24.25 GHz to 28.5 GHz, and others.
Model insurance villages
Context:
- Recently, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has come out with the concept of model insurance villages to offer comprehensive insurance protection in rural areas.
About:
- The idea behind the model village concept is to offer comprehensive insurance protection to all the major insurable risks that villagers are exposed to and make available covers at affordable or subsidised cost.
- IRDAI suggested a minimum of 500 villages in different districts of the country in the first year and increased to a minimum of 1,000 villages in subsequent two years.
- In these model villages, insurance companies will have to work towards covering the entire populations and their properties, farms, machineries, vehicles, and different village-level services, among others.
- IRDAI has stated that insurance companies need to study the risk profile of villages, their insurance needs and design their products accordingly.
- To make the premium affordable, financial support from governments as well as institutions such as NABARD and CSR funds must be explored.
- IRDAI advised Insurance companies to tap various initiatives of the rural development ministry as well as network of SHG members and bank correspondent Sakhis (BC Sakhis) for insurance product distribution and servicing.
Offerings Under Model Insurance Village (MIV):
- Weather index products or hybrid products combining weather index and indemnity-based insurance protection for various crops that remain uncovered under Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY).
- Flexible farm insurance package policies targeting comprehensive needs of crops, livestock, farmer, farm implements.
- Separate products for high value agriculture, contract farming and corporate farming community as their needs are different.
- Even states can be offered macro insurance covers based on predefined parametric weather indexes covering large complex risks arising out of natural catastrophes affecting the agriculture ecosystem and rural economy.
Significance
- This will boost insurance penetration and make people of the village aware of the concept of insurance and its benefits.
- The model villages are expected to tackle losses due to natural calamities like floods and earthquakes. There is no catastrophe insurance in the country now.
Challenges in Providing Insurance To Rural Areas:
- Lack of awareness about the concept of insurance and its benefits among the rural population.
- Limited choice of insurance products with various flexible features.
- Weak network of insurance companies and intermediary presence in rural areas.
- Lack of technology & underdeveloped market with constraints in offering affordable covers.
- Lack of industry-wide well-coordinated efforts to serve the rural insurance segment.
Way Forward
- Awareness and publicity: Focused publicity campaigns need to be carried out to make aware people about its benefits and features.
- Coordinated efforts needed: The support and involvement of the central government can be explored.
- It is also in line with the initiative and vision of the Centre’s “AtmaNirbhar Bharat Abhiyan”.
- Insurance product innovation: Make products Innovative, affordable, technology-based, in the form of package and/or combo policies that provide a flexible choice of risk protection & adequate risk coverage in rural and semi-urban areas which would attract the rural population.
Unfamiliar lineament among Assam earthquake factors
Context:
- An unfamiliar lineament is among the factors behind frequent earthquakes in northern Assam’s Sonitpur area.
- Sonitpur was the epicentre of the huge 6.4 earthquake after 33 years because of the tectonic complexity.
About:
- According to the Geological Survey of India (GSI), Sonitpur district lies within a tectonically complex triangular area bounded by the east-west trending Atherkhet Fault, the northwest-southeast trending Kopili Fault and a north-south trending lineament.
- A lineament is a linear feature in a landscape dictated by an underlying geological structure such as a fault.
- The two faults and the lineament, along with the oblique convergence of the Indian plate, have caused frequent earthquakes.
- Both the Atherkhet and Kopilli faults are active.However, Atherkhet and Kopili are not the only faults that impact the Sonitpur region.
- The Siang Fracture, Yemla Fault, Namula Thrust and Canyon Thrust are spread across the northeast and are active along with Main Himalayan Thrust, Main Boundary Thrust, Main Central Thrust and several subsidiary faults.
- The northeast is demarcated as Seismic Zone V, which indicates a zone with high vulnerability.
- The Indian plate is moving northeast toward the Eurasian plate in the Himalayan region, their oblique collision and release of stress and strain accumulated in the local tectonic or fault environments lead to earthquakes.
EU unveils plan to cut dependency on China
Context:
- The European Union (EU) has unveiled a plan to cut its dependency on Chinese and other foreign suppliers in six strategic areas after the pandemic-induced economic slump.
About:
- The six strategic areas include raw materials, pharmaceutical ingredients, and semiconductors.
- EU outlined the urgency of the task citing Europe’s reliance on China for about half of 137 products used in sensitive ecosystems, mainly raw materials, pharmaceuticals, and other products key to its green and digital goals.
- The updated industrial strategy plan was devised after the COVID-19 pandemic showed bottlenecks in supply chain.
- The executive European Commission plans to conduct in-depth reviews of supply chains in raw materials, batteries, active pharmaceutical ingredients, hydrogen, semiconductors and cloud and edge technologies, to decide how to deal with them.
- To reduce import dependency, EU countries could pool resources for Important Projects of Common European Interest (IPCEIs) in next-generation cloud, hydrogen, low-carbon industry, pharmaceuticals and a second IPCEI on cutting-edge semi-conductors.
Section 142 of The Social Security Code – 2020
Context:
- Section 142 of the Social Security Code, 2020 has been notified by Ministry of Labour & Employment covering applicability of Aaadhar.
About:
- The notification of section will enable Ministry of Labour and Employment to collect Aaadhar details for the database of beneficiaries under various social security schemes.
- National Data Base for unorganised workers (NDUW) is at an advanced stage of development by National Informatics Centre.
- The portal is aimed at collection of data for unorganised workers including migrant workers for the purpose of giving benefits of the various schemes of the Government.
- An inter-state migrant worker can register himself on the portal based on submission of Aaadhar alone.
- Union Minister of State (I/c) for Labour and Employment has clarified that the section under the Social Security Code has been notified only for collection of data of workers including migrant workers. No benefit will be denied to workers for want of Aaadhar.
India-UK summit
Context:
- Roadmap 2030 was adopted to elevate bilateral ties to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.
- British Prime Minister Boris Johnson has announced one billion pounds of new UK-India trade deals which includes an investment of 240 million pounds investment by Pune based Serum Institute of India (SII).
About:
- All in all, the announcement on a trade deal will create 6500 new jobs in the UK and includes over £533m of new Indian investment into the UK.
- £200 million of these deals will support low carbon growth.
- The roadmap aims to expand and deepen India-UK cooperation in the next decade in 5 areas–people-to-people relationship, trade, and prosperity, defense and security, climate action, and healthcare.
- Enhanced Trade Partnership (ETP) launched to unleash trade potential between two and by setting an ambitious target of more than doubling bilateral trade by 2030.
- Both will also consider an Interim Trade Agreement for delivering early gains.
- India-UK ‘Global Innovation Partnership’ was announced that aims to support the transfer of inclusive Indian innovations to select developing countries, starting with Africa.
- Launched comprehensive partnership on migration and mobility to facilitate greater opportunities for the mobility of students and professionals between the two countries.
- Decided to expand cooperation under Defence and International Security Partnership (DISP) agreed in 2015.
- Enhanced India-UK engagement within the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) framework as UK is a Dialogue Partner in IORA.

