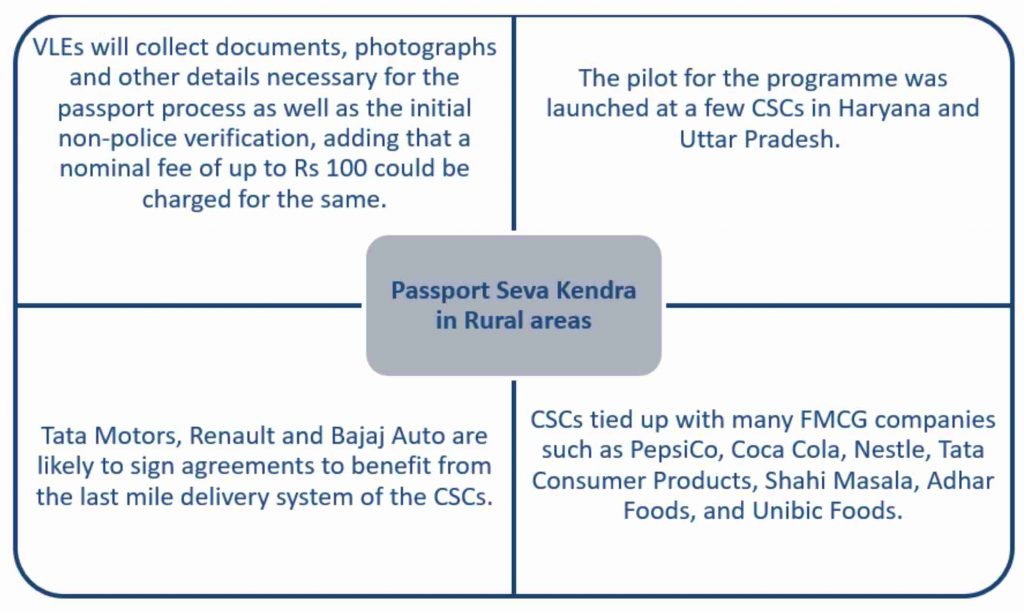
Passport Service Collection Centres
The Indian Express
GS 3: Economy
Context:
- The Common Services Centres (CSC)has received approvals to manage and operate Passport Seva Kendra kiosks in rural areas.
About:
- CSC is a special purpose vehicle of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It has over the past three years tied up with partners, both in the public and private sector.
- Last April, the CSC allowed village-level entrepreneurs (VLEs) the option to launch a Grameen e-store.
- It was initially launched for easy delivery of essential items in villages, gram panchayats and other rural areas.
- These e-stores soon started selling non-essential items like soft drinks, biscuits, soaps, shampoos, pencils, pens, electric and electronic appliances.
- VLEs of every CSC creates a personalised app depending on the need and availability of goods for his surrounding areas, and delivers those to customers.
- The government has collaborated Migrocer to create a master app, which has a database of 80,000 products.
- The goods can be procured either directly from farmers or self-help groups or from nearby retailers, wholesalers or supermarkets.
Millet Farming
Livemint
GS 3: Economy
Context:
- The United Nations General Assembly recently adopted a resolution declaring 2023 the International Year of Millets.
- It was also proposed by India to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
About:
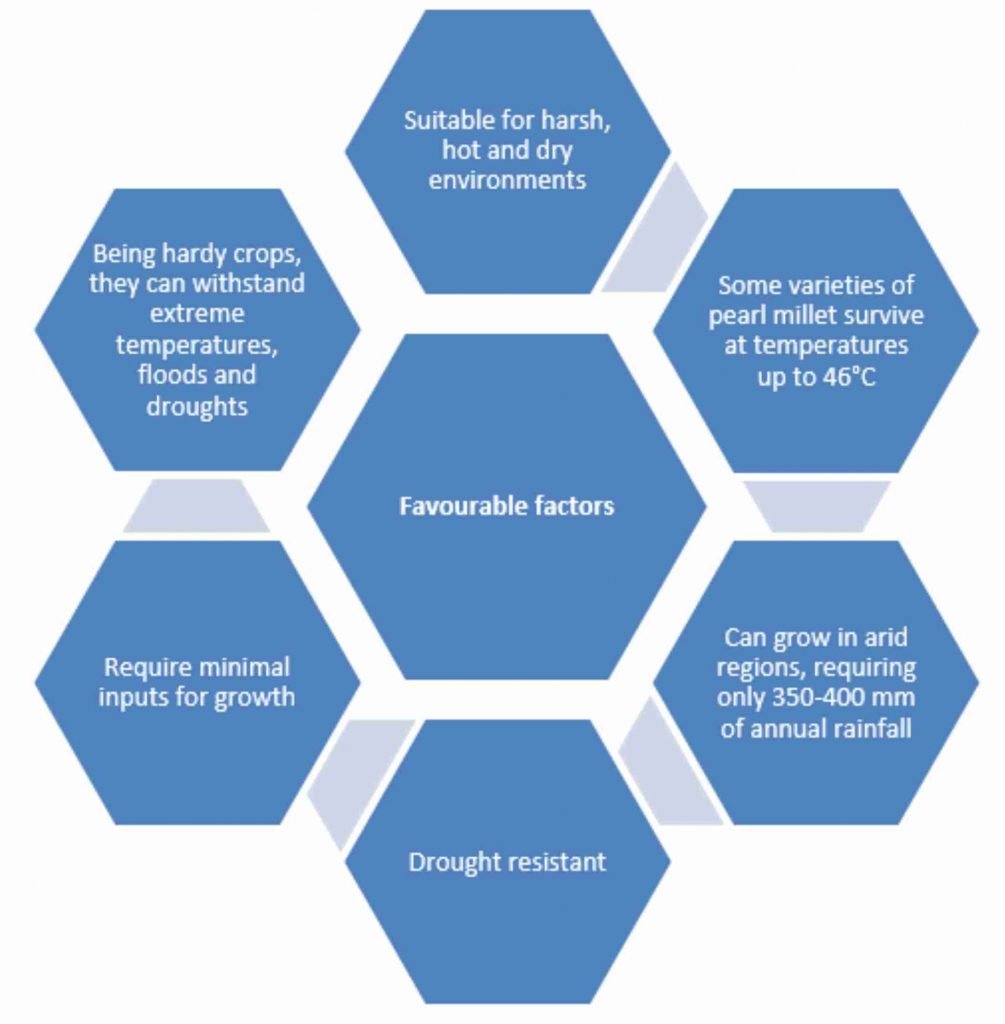
- Millets include sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet and several small millets (kodo, little, foxtail, proso and barnyard).
- All millets, maize, and barley together are called coarse cereals.
- Millets were one of the oldest foods known to humans. But they were discarded in favour of wheat and rice with urbanization and industrialization.
- India is the largest global producer of millets, with a 41% market share.
- A compound annual growth rate of 4.5% is projected for the global millet market in the coming decade.
Significance of millets:
- Provide food, nutrition, fodder, and livelihood security.
- Help mitigate the effects of climate change with low carbon footprint of 3,218-Kg equivalent of CO2 per hectare.
Concerns:
- Market and economic barriers.
- Low demand, especially in urban markets.
- Unjust pricing and value wringing by intermediaries.
- Low remuneration leading to farmer distress.
- Lack of input subsidies and price incentives.
- Subsidised supply of fine cereals through the PDS and change in consumer preferences leading led to a shift from the production of millets (jowar in particular) to soybean, maize, cotton, sugarcane, and sunflower.
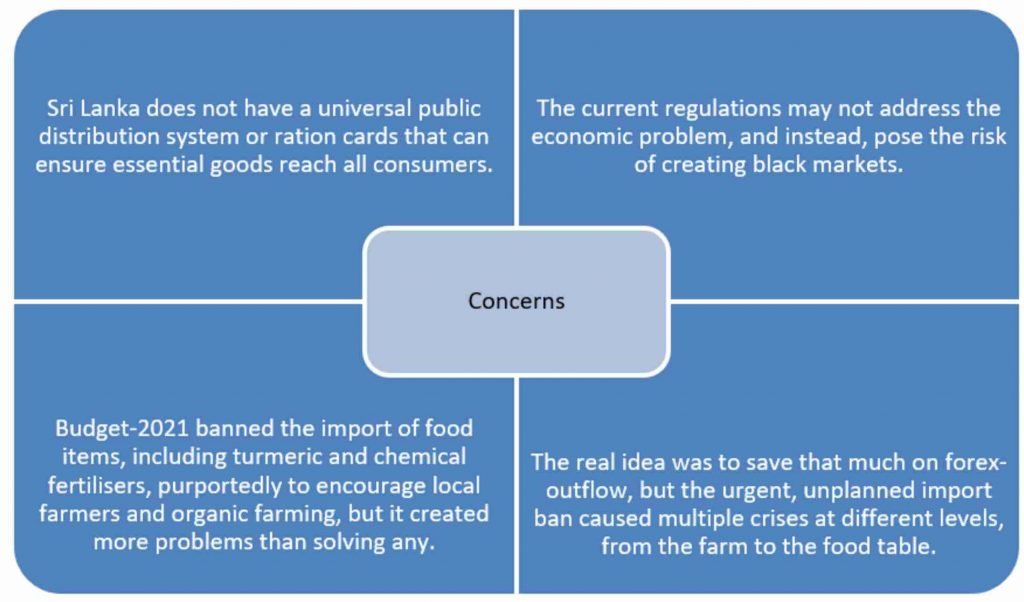
‘Food Emergency’ in Sri Lanka
Indian Express
GS 2: International Relations
Context:
- The President of Sri Lanka has declared a food emergency under the public security ordinance to maintain the supply of food items such as sugar and rice at fair prices.
About:
- It empowers the authorities to seize stocks of staple foods and set their prices, to contain soaring inflation after a steep devaluation of its currency due to a foreign exchange crisis.
- Sri Lanka, a net importer of food and other commodities, is witnessing a surge in COVID-19 cases and deaths which has hit its tourism sector. It is one of the main foreign currency earners.
- Major sources of foreign exchange earnings — exports and worker remittances.
- Production shortages and logistical bottlenecks.
Way forward:
- The government has announced massive penalties for hoarders but that may not be enough to end food-panic and long queues at retail stores. The situation can ease only if the government pumps in more forex into the system.
Agencies Flag Surge in Number of Foreign Ultras in North Kashmir
The Hindu
GS 3: Internal Security
Context:
- Security agencies have pointed out a sudden spike in the number of foreign militants operating in north Kashmir.
Concerns:
Spike in number of foreign militants:
- According to the latest official data of the police, there are 40 to 50 foreign militants active in north Kashmir compared with just 11 local militants.
- There has been a marked increase in the presence of foreign militants in the ranks of insurgent groups such as the Jaish-e-Muhammad, Al-Badr, Lashkar-e-Taiba and The Resistance Front (TRF).
- Increasing number of recent high profile terror attacks have been attributed to non-local recruits. There have also been reports of foreign terrorist fighters offering to fund terror activities in India and arrange supply of sophisticated weapons, explosives and so on.
- This marks a changing trend in militancy in Kashmir which should concern the security agencies.
- The increase in foreign militants build-up had been visible in the past two months. Official sources have noted that this uptick cannot be connected with the recent situation in Afghanistan.
Increased militant activities in North Kashmir:
- It is for the first time in a decade that north Kashmir is witnessing heightened militant activities compared with south Kashmir.
- The three districts of North Kashmir – Baramulla, Bandipora and Kupwara had been relatively free from militant activities as compared to south Kashmir which has remained a hotbed of militant activities.
Security agencies response:
- The rising number of militants in north Kashmir, which is already over 50, has forced the security agencies to re-strategise their response to counter-terrorism.
- Mainstream leaders and elected grassroots representatives have been asked to be vigilant given the threat of attacks against them.
- Also, the security agencies have launched an aggressive counter-strategy against the militancy. A number of militants have been killed and a substantial number of overground workers have also been arrested.
- Overground workers are people who help militants, or terrorists, with logistical support, cash, shelter, and other infrastructure with which armed groups and insurgency movements can operate.
Pollen Calendar
Indian Express
GS 3: Economy
Context:
- Chandigarh now has its first pollen calendar, which can identify potential allergy triggers and provide a clear understanding for clinicians as well as allergy sufferers about their causes to help limit their exposure during high pollen loads.
About:
- About 20-30% of the population suffers from allergic rhinitis/hay fever in India, and approximately 15% develop asthma.
- Pollens are considered major outdoor airborne allergens responsible for allergic rhinitis, asthma, and atopic dermatitis in humans.
- Pollen calendars represent the time dynamics of airborne pollen taxa in graphical form in a particular geographical area. They yield readily accessible visual details about various airborne pollen taxa present throughout the year, with their seasonality in a single picture.
- Pollen calendars are location-specific, with concentrations closely related to locally distributed flora.
- Department of Community Medicine and School of Public Health, PGIMER, Chandigarh, examined the seasonal periodicities of airborne pollen spectrum and developed the first Pollen Calendar for Chandigarh city.
Account Aggregators
Indian Express
GS 3: Economy
Context:
- On September 2, 2021, eight of India’s major banks joined the Account Aggregator (AA) network that will enable customers to easily access and share their financial data.
- The eight major banks are: State Bank of India, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, IDFC First Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, HDFC Bank, IndusInd Bank and Federal Bank.
About:
- The framework, which has been under discussion since 2016 and in the testing phase for some time, will now be open to all customers.
- An Account Aggregator is a non-banking financial company engaged in the business of providing, under a contract, the service of retrieving or collecting financial information pertaining to its customer.
- It is also engaged in consolidating, organising and presenting such information to the customer or any other financial information user as may be specified by the bank.
- The AA framework was created through an inter-regulatory decision by RBI and other regulators including Securities and Exchange Board of India, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority, and Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) through an initiative of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC).
- An Account Aggregator allows a customer to transfer his financial information pertaining to various accounts such as bank deposits, equity, mutual fund and pension funds to any entity requiring access to such information.
- There are 19 categories of information that fall under ‘financial information’, besides various other categories relating to banking and investments.
- For sharing of such information, the FIU is required to initiate a request for consent by way of any platform/app run by the AA.
- Such a request is received by the individual customer through the AA, and the information is shared by the AA, after consent is obtained.
- It reduces the need for individuals to wait in long bank queues, use Internet banking portals, share their passwords, or seek out physical notarisation to access and share their financial documents.


