INDIA RISES TO 15TH POSITION IN FDI DESTINATIONS
Why in News?
Released: June 19, 2025 |
Published by: United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
INDIA’S FDI PERFORMANCE
Global Ranking
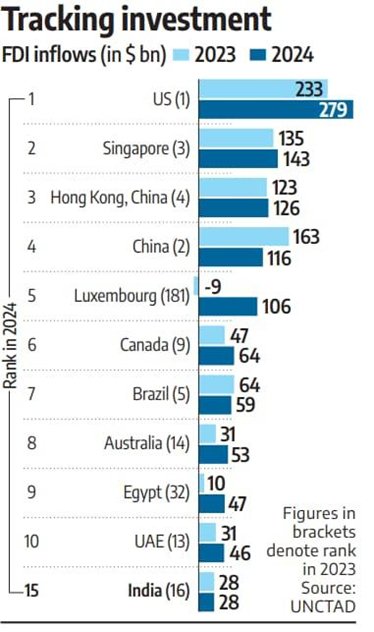
- In 2024, India rose to the 15th position globally for FDI inflows, improving from 16th in 2023.
- This rise occurred despite an 11% decline in global FDI flows, marking India as a stable destination for foreign investment.
FDI Inflows and Trends
- India maintained $28 billion in FDI inflows in 2024, the same level as 2023.
- This stability is considered a positive sign after a significant 43% drop in 2023 from the previous year.
OTHER FDI METRICS
- According to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), net FDI (excluding repatriation) stood at approximately $29 billion for FY25.
- Data from the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) indicated FDI equity inflows of $50 billion, representing a 13% increase in FY25.
India’s Standing in Developing Asia
- India attracted 46% of all international private equity investment in developing Asia, making it the leading recipient in the region.
INVESTMENT CATEGORIES
Greenfield Projects
- India retained its 4th position globally for greenfield project announcements.
- In 2024, a total of 1,080 greenfield projects were announced.
- The projected capital expenditure surged over 25%, reaching $110 billion—almost one-third of Asia’s total greenfield investments.
- This growth reflects strong long-term industrial investment interest in India.
International Project Finance (IPF)
- India ranked among the top five countries for IPF deals, with 97 transactions.
- However, India slipped from its 2nd place ranking in 2023.
OUTWARD FDI
- India improved its position in outward investments, ranking 18th globally in 2024.
- Outward FDI flows reached $24 billion, up from 23rd position and lower volumes in 2023.
KEY SECTORS ATTRACTING INVESTMENT
- Renewable Energy
- Semiconductors
- Basic Metals
- Digital Infrastructure
- Notably, Microsoft committed $3 billion to build out cloud and AI infrastructure in India.
- The report also highlighted M&A activity, such as:
- Walt Disney’s $3 billion merger with Viacom18, forming a majority Indian-owned joint venture.
- International pharmaceutical operations being sold to Indian companies.
GLOBAL FDI CONTEXT
Global Trends
- Global FDI dropped by 11% in 2024, marking the second consecutive year of decline.
- This decline excludes volatile conduit flows through select European countries.
- The outlook for 2025 remains pessimistic due to geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainty.
TOP FDI DESTINATION COUNTRIES
| Rank | Country | FDI Inflows |
| 1 | United States | $279 billion |
| 2 | Singapore | (Moved up) |
| 3 | Hong Kong | (Moved up) |
| 4 | China | $116 billion (29% decline) |
Regional Patterns
- Africa: FDI rose by 75%, largely driven by a megaproject in Egypt.
- Developing Asia: Received $605 billion in FDI (a slight 3% decline).
- ASEAN (Southeast Asia): FDI grew by 10%, defying global trends.
FDI IN SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
- Investment in SDG-related sectors fell sharply in 2024:
- Infrastructure, renewable energy, water/sanitation, agrifood: Down 25–33%.
- Only the health sector saw modest growth (from a low base).
- International Project Finance (IPF) fell 26% globally, severely affecting Least Developed Countries (LDCs).
DIGITAL ECONOMY INVESTMENTS
- FDI into the digital economy increased by 14% in 2024.
- However, 80% of greenfield digital projects in the Global South were concentrated in just 10 countries, including India.
- This highlights an uneven distribution of digital investment across developing nations.
WHAT IS FDI?
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) refers to an investment made by a person or company based in one country into a business or asset located in another country. Unlike portfolio investment (such as buying stocks or bonds), FDI involves significant ownership, control, or influence over the foreign business.
KEY FEATURES
- Long-Term Interest: FDI implies a lasting interest in the foreign enterprise, not just a short-term financial investment.
- Ownership or Control: It usually involves acquiring at least 10% of the equity in a foreign company, giving the investor some control over management decisions.
- Active Participation: The investor often participates in the decision-making and operations of the foreign business.
TYPES OF FDI
| Type | Description |
| Greenfield FDI | Establishing a new business or facility in a foreign country (e.g., factory, office). |
| Brownfield/ M&A | Acquiring or merging with an existing foreign company. |
| Joint Ventures | Partnering with a local company to operate a business together. |
Examples
- Amazon investing in warehouse infrastructure in India (Greenfield FDI).
- Tata Motors acquiring Jaguar Land Rover in the UK (Brownfield/M&A).
- Toyota forming a joint venture with Kirloskar Group in India.
BENEFITS & RISKS
- Brings in capital, technology, and expertise.
- Creates employment and boosts infrastructure.
- Increases exports and integrates the local economy into global supply chains.
Risks and Concerns
- Can lead to foreign dominance in key sectors.
- Potential for profit repatriation, where profits are sent back to the investor’s home country.
- Risk of exploitation of natural resources or local labor.
FDI IN INDIA
India receives FDI across multiple sectors including:
- Information Technology
- Telecommunications
- Pharmaceuticals
- Renewable Energy
- Retail and E-commerce
The Indian government regulates FDI through policies published by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT). Some sectors allow 100% FDI through the automatic route, while others require government approval.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


