INS ARIGHAT
Event: On August 29, 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh commissioned INS Arighat, India’s second nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN), at an event in Visakhapatnam.
ABOUT INS ARIGHAT
- Name and Design:
- Name Meaning: ‘Destroyer of enemies’ in Sanskrit.
- Class: Arihant-class, following the lead submarine INS Arihant.
- Construction Timeline: Construction began in 2017 at the Ship Building Centre, Visakhapatnam.
- Specifications:
- Displacement: 6,000 tonnes.
- Length: 112 meters.
- Speed: Surface speed of 12-15 knots; underwater speed of up to 24 knots.
- Power: Powered by 83 MW pressurised light-water reactors allowing for extended submerged durations.
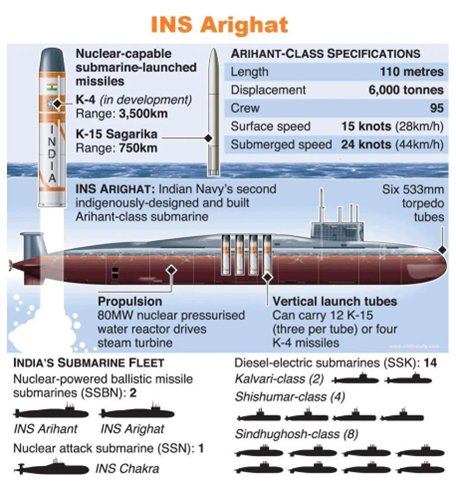
- Armament:
- Missiles: Capable of carrying either up to 4 (K-4 SLBMs) with a range exceeding 3,500 kilometers or 12 (K-15 SLBMs) with a range of around 750 kilometers.
- Additional Armament: Equipped with torpedoes for enhanced combat capability.
HISTORY OF THE INDIAN SUBMARINE PLAN
- INS Arihant:
- Launch: 2009, Commissioned:
- Significance: First nuclear-powered submarine in India’s fleet, establishing India’s nuclear triad with its first deterrence patrol completed in 2018.
- Development Timeline:
- Origins: Began over 30 years ago with collaboration from private companies and the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO), including significant assistance from Russia.
WHY IT MATTERS?
- Enhancing Nuclear Capabilities:
- Nuclear Triad: The addition of INS Arighat boosts India’s nuclear triad capabilities, which include the ability to launch nuclear missiles from land, air, and sea platforms.
- Technological Advancements:
- Stealth Capabilities: INS Arighat features advanced stealth technology, including improved sonar systems and quiet propulsion, which enhance its ability to operate undetected and respond swiftly to threats.
STRATEGIC ROLE & NUCLEAR TRIAD
- Nuclear Triad:
- Components: The triad includes land-based missiles, air-launched missiles, and sea-based missiles.
- Impact: INS Arighat enhances India’s ability to conduct a credible retaliatory strike, which is crucial for maintaining a strong deterrent posture.
- Nuclear Deterrence:
- Sea-Based Component: INS Arighat enhances India’s sea leg of the nuclear triad, complementing land and air-based systems, and supports India’s “no first use” nuclear policy.
- Strategic Balance:
- Defense Minister’s Statement: Rajnath Singh emphasized that INS Arighat will play a key role in maintaining regional peace and balance, reflecting its importance in India’s defense strategy.
FUTURE PLANS
- Current Fleet:
- Composition: India’s submarine fleet includes 16 conventional submarines alongside INS Arighat and INS Arihant.
- Additional Submarines:
- Planned: 2 larger SSBNs, each with eight missile tubes, are being built. INS Aridaman is expected to be commissioned next year, with a fourth SSBN to follow.
- Global Context:
- Status: With INS Arighat, India joins a select group of nations with operational nuclear-powered submarines, including the US, Russia, UK, France, and China. This positions India as a significant naval power with advanced strategic capabilities.
WHAT COMMISSIONING OF INS ARIGHAT MEANS TO INDIA?
- Pride and Achievement:
- Exclusive Club: India has now become part of an elite group of countries capable of building and operating nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines, reflecting major advancements in defense and scientific technology.
- Credit to the Navy:
- Role: The Indian Navy has been crucial in the development and operationalization of the SSBN program, highlighting its expertise and the complexity of submarine construction and operation.
- Significance of INS Arighat:
- Increased Self-Reliance: Compared to INS Arihant, the INS Arighat incorporates a higher proportion of locally-made components (60% vs. 30%), showcasing improved self-reliance and technological capability.
OPPORTUNITIES & CHALLENGES
- Opportunities:
- Innovation and Growth: High local content in SSBNs like INS Arighat presents opportunities for further innovation, job creation, and industrial growth in the defense sector.
- Challenges:
- Technical and Operational: Addressing the technical, operational, and training challenges associated with advanced submarine technology will enhance India’s defense capabilities and expertise.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.

