STRAIT OF HORMUZ CLOSURE THREAT
Context: June 2025
Trigger: U.S. airstrikes on Iran’s nuclear facilities
Reaction: Iran’s Parliament passed a motion recommending closure of the Strait of Hormuz
WHY IN NEWS?
- In June 2025, following U.S. military strikes on Iran’s nuclear facilities, Iran’s Parliament approved a resolution to close the Strait of Hormuz as retaliation.
- The final decision rests with Iran’s Supreme National Security Council, which operates under the Supreme Leader.
- This move has raised global concerns about oil supply disruptions and economic instability.
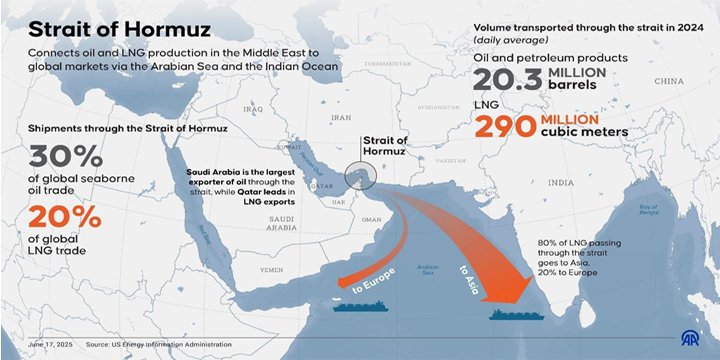
ABOUT STRAIT OF HORMUZ
| Feature | Details |
| Location | Between Iran (north) and Oman & UAE (south) |
| Width | ~50 km at entrance; ~33 km at narrowest point |
| Function | Connects Persian Gulf to Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea |
| Legal Status | Lies within territorial waters of Iran and Oman |
| Importance | World’s busiest oil transit chokepoint |
| Volume of Trade | ~20 million barrels/day (~20% of global oil supply) |
| Annual Value | ~$600 billion in oil and gas trade (U.S. EIA estimate) |
| Main Exporters | Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Kuwait, Qatar |
| Main Importers | India, China, Japan, South Korea |
WHAT COULD HAPPEN IF THE STRAIT IS CLOSED?
1. Oil Prices Could Surge
- Oil prices may jump from $77 to $120–$150 per barrel.
- This would raise fuel costs globally and affect domestic inflation in many countries.
2. Stock Markets and Trade Would Suffer
- Global stock markets may react negatively due to uncertainty.
- Central banks could revise inflation and interest rate outlooks.
3. Global Supply Chains Will Be Affected
- Increased shipping times (10–14 days longer via Cape of Good Hope).
- Higher freight and insurance costs, especially for oil shipments.
4. Higher Costs for Manufacturing Countries
- Countries like India, China, Japan, and South Korea will face higher energy and manufacturing costs.
- These costs will be passed on to consumers, increasing global inflation.
IMPACT ON INDIA
India’s Oil Dependency
- India imports ~88% of its crude oil needs.
- India consumes ~5.5 million barrels per day (bpd).
- 1.5 to 2 million bpd comes through the Strait of Hormuz.
- ~4 million bpd comes via other global routes.
BREAKDOWN OF IMPORT ROUTES (KPLER ESTIMATES)
| Route | Share of Imports | Main Source Countries |
| Strait of Hormuz | ~40% | Iraq, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Kuwait |
| Suez Canal | ~33% | Russia |
| Cape of Good Hope | ~17% | West Africa, Americas |
| Other Routes | ~10% | Southeast Asia, Far East |
KEY RISKS FOR INDIA
| Risk Category | Specific Effects |
| Oil Price Hike | Increased import bill, inflation, fiscal burden |
| Freight & Insurance | Longer routes → Higher transport costs and delivery delays |
| Currency Depreciation | Pressure on rupee → Wider current account deficit |
| Trade Disruption | Container shortages may affect exports and imports (esp. Europe-Asia corridor) |
WHAT DID INDIA’S OIL MINISTER SAY?
Minister Hardeep Singh Puri (June 23, 2025):
- “We have diversified our oil sources in the past few years.
- A large volume of our supplies no longer come through the Strait of Hormuz.
- Our Oil Marketing Companies have supplies for several weeks and continue to receive energy through several routes.”
The Minister also:
- Held a high-level security review with officials from the Navy, Coast Guard, ONGC, and Defence Ministry.
- Reaffirmed the government’s commitment to ensure uninterrupted fuel supply.
HOW COULD IRAN BLOCK THE STRAIT?
| Method | Description |
| Naval Mines | Laid using submarines or small attack boats |
| IRGC Fast Boats | Swarm attacks using speedboats with anti-ship missiles |
| Submarine Warfare | Attacks on commercial or military vessels using submarines |
| Semi-submersibles | Hard-to-detect vessels targeting oil tankers |
Historical Reference: In the 1980s, during the Iran–Iraq war, similar tactics led to the “Tanker War” where both nations attacked commercial oil shipments.
U.S. Response:
- Fifth Fleet is stationed in Bahrain.
- Past success: Operation Earnest Will (1987–88) safely escorted Kuwaiti oil tankers.
WILL IRAN ACTUALLY CROSS THE STRAIT?
| Factor | Explanation |
| Loss of Own Oil Revenue | Iran earns ~$67 billion from oil exports (FY 2024–25) |
| China is a Key Buyer | China buys ~90% of Iranian oil – would be negatively impacted |
| Diplomatic Isolation | Gulf countries (Saudi Arabia, UAE) may turn hostile |
| U.S. and Allied Response | Risk of direct military conflict |
| Gulf Normalization Setback | Iran’s recent regional diplomacy could collapse |
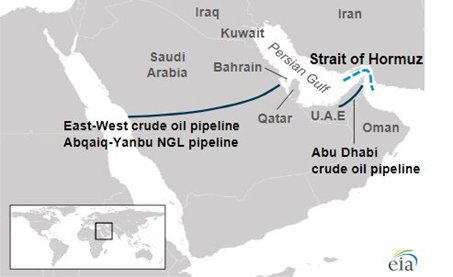
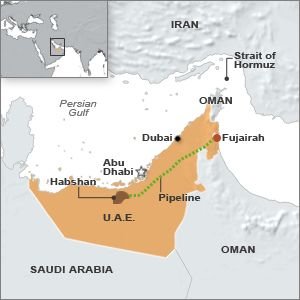
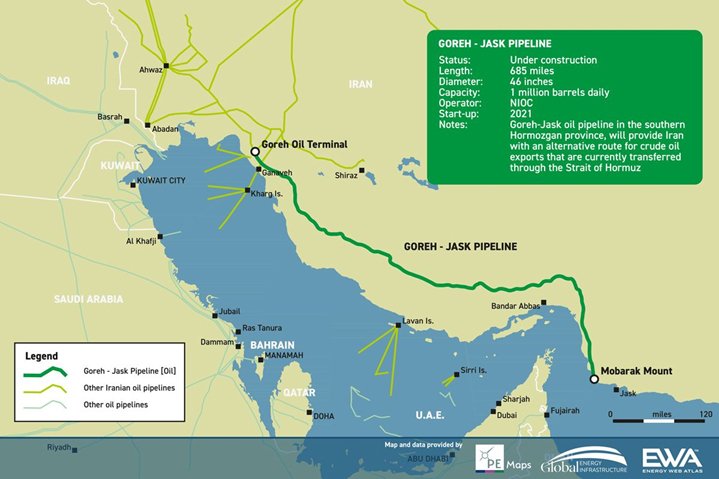
ARE THERE ANY EXPORT ROUTES?
| Country | Pipeline Name | Capacity (approx.) |
| Saudi Arabia | East–West Pipeline (Petroline) | 5 million barrels/day |
| UAE | Habshan–Fujairah Pipeline | 1.5 million barrels/day |
| Iran | Goreh–Jask Pipeline | ~350,000 barrels/day |
Limitation: These can handle ~3.5 million bpd, while the Strait handles ~20 million bpd.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.