UN WORLD WATER DEVELOPMENT REPORT, 2025
- The World Water Development Report (WWDR) is a flagship publication of UN-Water (the United Nations coordination mechanism for water and sanitation) that provides an authoritative assessment of global water and sanitation issues.
- It evaluates the state, use, and management of freshwater resources around the world.
- Theme for 2025: Mountains and Glaciers: Water Towers.
- The report is launched annually on World Water Day (March 22) with a specific theme each year.
- The report offers policy recommendations, best practices, and in-depth analyses for decision-makers to address water challenges globally.
- It is published by UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) on behalf of UN-Water and coordinated by the UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme.
History of World Water Day (March 22)
- 1992: First proposed at the UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in Rio de Janeiro (a global conference focusing on sustainable development).
- 1993: Officially established by the United Nations General Assembly.
ABOUT UN WATER
- UN-Water coordinates the UN’s work on water and sanitation, with over 30 UN organizations working on these issues across various sectors.
- Its goal is to ensure UN members and partners “deliver as one” in addressing water and sanitation challenges globally.
Core Activities:
- Informing policy processes and addressing emerging water issues.
- Supporting monitoring and reporting on water and sanitation.
- Building knowledge and inspiring action for water sustainability.
KEY MILESTONES
- SDG 6 (Sustainable Development Goal 6, which focuses on water and sanitation): Shaped SDG 6—ensuring the sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
- Contributed to agreements like:
- The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (an international framework aiming to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all),
- Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (a global framework for reducing disaster risks), and
- The Paris Climate Agreement (an international treaty to combat climate change).
GLOBAL WATER TRENDS
- Water Withdrawals: (The total amount of water that is taken from a water source for use in various sectors like agriculture, industry, and domestic use):
- Agriculture: 72% (water used for irrigation, livestock, and other agricultural purposes).
- Industry: 15% (water used in manufacturing processes).
- Domestic use: 13% (water used for household activities such as drinking, cooking, and cleaning).
- Freshwater withdrawals grew by 14% from 2000 to 2021 (average annual increase of 0.7%).
- Water Stress:
- Water stress: A situation where demand for water exceeds the available amount in a region or season.
- 25 countries (home to 1/4 of the world’s population) face extremely high water stress annually.
- 4 billion people experience severe water scarcity at least part of the year.
MOUNTAIN AREAS & WATER
- Area: 33 million km² (24% of global land excluding Antarctica).
- Population: Approx. 1.1 billion people (15% of the world’s population).
- 34% live in urban areas, 31% in towns, 35% in rural areas.
- Water Contribution:
- Mountains provide 55-60% of global annual freshwater flows.
- Rivers like the Amu Darya, Colorado, Nile, Indus, and São Francisco depend heavily on mountain waters (up to 90% of their annual flow).
CRYOSPHERE & WATER IMPACT
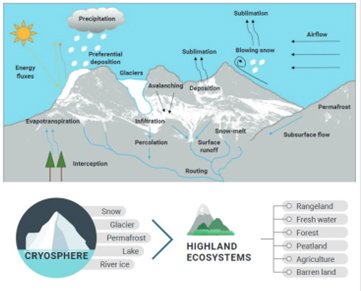
- Cryosphere: The frozen water part of the Earth’s surface, including glaciers, ice sheets, snow, and permafrost.
- Glacier retreat: The process of glaciers shrinking and losing ice due to warming temperatures.
- 26-41% of glacier mass is projected to be lost by 2100 due to warming.
- Glacial lakes (lakes formed from melting glaciers) are increasing, raising the risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) (Sudden and catastrophic releases of water from glacial lakes due to the failure of a natural dam).
MOUNTAIN AGRICULTURE & LIVELIHOODS
- 648 million people in rural mountain areas depend on agriculture and pastoralism (the raising of livestock) for their livelihoods.
- 35-40% of the mountain population experiences food insecurity (lack of consistent access to sufficient food).
- Forests: Cover 40% of mountain areas, protect against landslides, regulate water flow, and reduce soil erosion.
Climate-related hazards such as droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures affect 25% of agriculture in developing countries, causing 80% of livestock and crop damage in mountain areas.
HUMAN SETTLEMENTS & DISASTER RISKS
- 3,151 GLOF (Glacial Lake Outburst Flood) events were recorded from 850 to 2022, with over US$56 billion in economic losses and 39,000 deaths in mountain regions between 1985 and 2014.
- Adaptation finance: Funds allocated for adjusting to the impacts of climate change. US$187 billion annually is needed for climate adaptation in mountain regions, yet only US$13.8 billion was available in 2022, creating a significant gap.
INDUSTRY & ENERGY IN MOUNTAINS
- Water-intensive industries like lithium extraction (mining process for lithium, which is key in battery production) and cryptomining (the process of mining digital currencies like Bitcoin, which requires large amounts of water) increase water demand in mountain areas.
- Hydropower: 95% of global pumped storage hydropower (PSH) (a type of hydroelectric power generation that stores energy by pumping water to a higher elevation) is located in mountain areas, crucial for electricity storage.
- 85% of hydroelectric power in Latin America comes from mountain regions.
MOUNTAIN ECOSYSTEM & ENVIRONMENT
- Mountains host 25 of the world’s 34 biodiversity hotspots (regions with a high level of endemic species that are under threat from human activities).
- Ecological pressure: The strain on ecosystems caused by human activities such as development, resource extraction, and pollution.
- 57% of global mountain areas face intense pressure from human activities.
REGIONAL HIGHLIGHTS
- Sub-Saharan Africa:
- Africa’s mountains cover 20% of its land area, with 252 million people living in mountain regions.
- 132 million rural mountain people are vulnerable to food insecurity.
- Glacier loss is projected to affect Mount Kenya and the Rwenzori Mountains by 2030 and Mount Kilimanjaro by 2040.
- Europe and Central Asia:
- In the Alps, river discharge (The flow of water in rivers) is expected to decrease by 45% due to reduced glacier runoff by 2100.
- Latin America and the Caribbean:
- The Andes provide 50% of Amazon River flow and have lost 30-50% of glaciers since the 1980s.
- 85% of hydroelectric power in Latin America comes from mountain regions.
- Asia and the Pacific:
- The Tibetan Plateau and Himalayas store more ice and snow than any region outside Antarctica and the Arctic.
- Glacier melt in the Himalayas is 65% faster than in the previous decade.
- By 2100, glaciers in the region may shrink by 30-50% under 1.5°C-2°C warming scenarios.
- Arab Region:
- Snow contributes 50-60% of Lebanon’s river and spring water volume, feeding into groundwater aquifers.
ABOUT UNESCO
- Full Name: United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
- Founded: 1945, headquartered in Paris, France.
- Mission: Promote peace, sustainable development, and human rights through education, science, and culture.
India’s Membership: India has been a member since UNESCO’s founding in 1946. Primary Goal: Advance peace, human rights, and sustainable development through global collaboration.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


