UNION BUDGET 2025-26
On 1 Feb 2025, Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2025-26 in Parliament.
WHO PREPARES IT?
The national budget is prepared by the budget division under the Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), the Ministry of Finance and is presented to the Parliament for discussion and approval.

ENGINES OF DEVELOPMENT

CORE OBJECTIVES OF THE BUDGET
- The budget focuses on 5 key objectives:
- Accelerating Growth: Aiming for faster economic progress.
- Securing Inclusive Development: Ensuring that growth benefits all sections of society.
- Invigorating Private Sector Investments: Boosting investment from the private sector to create jobs and increase economic output.
- Uplifting Household Sentiments: Enhancing the financial confidence and well-being of households.
- Enhancing Spending Power of India’s Middle Class: Increasing the disposable income of the growing middle class in India.
BUDGET THEME
- India’s Growth Story
- India’s economy is the fastest-growing among major global economies, and structural reforms over the past decade have positioned the country as a rising global power. The focus for the next five years is on realizing “Sabka Vikas” (development for all) with balanced growth across regions.
- The Vision of “Viksit Bharat”
- The vision for a developed India includes:
- Zero Poverty: Eradicating poverty for all citizens.
- Quality Education: Providing 100% access to good education for every child.
- Affordable Healthcare: Ensuring access to high-quality healthcare for all.
- Skilled Workforce: Ensuring every Indian is skilled and employed.
- Women’s Economic Participation: Aiming for 70% women in the workforce.
- Agriculture: Positioning India as the “food basket of the world” through better support for farmers.
- The vision for a developed India includes:
KEY DEVELOPMENT MEASURES
- The budget outlines measures targeting ten areas of development:
- Spurring Agricultural Growth and Productivity: Boosting farm productivity and sustainability.
- Building Rural Prosperity and Resilience: Ensuring rural areas thrive economically.
- Inclusive Growth: Ensuring no one is left behind as the country grows.
- Boosting Manufacturing and “Make in India”: Focusing on self-reliance and strengthening India’s manufacturing sector.
- Supporting MSMEs: Strengthening small and medium-sized enterprises to drive growth.
- Employment-led Development: Creating more jobs through strategic economic policies.
- Investing in People, Economy, and Innovation: Fostering innovation and talent development to drive future growth.
- Securing Energy Supplies: Ensuring sustainable and secure energy sources.
- Promoting Exports: Expanding India’s reach in global markets.
- Nurturing Innovation: Focusing on research, innovation, and technology for the future.
TRANSFORMATIVE REFORMS
- Over the next five years, reforms will focus on six crucial areas to enhance India’s growth and global competitiveness:
- Taxation: Streamlining tax policies for ease of doing business.
- Power Sector: Modernizing energy production and consumption.
- Urban Development: Improving urban infrastructure and development.
- Mining: Strengthening the mining sector for sustainable growth.
- Financial Sector: Reforming financial systems to support economic development.
- Regulatory Reforms: Simplifying regulations for a more business-friendly environment.
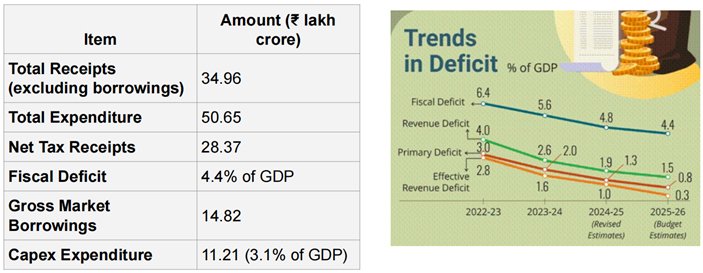
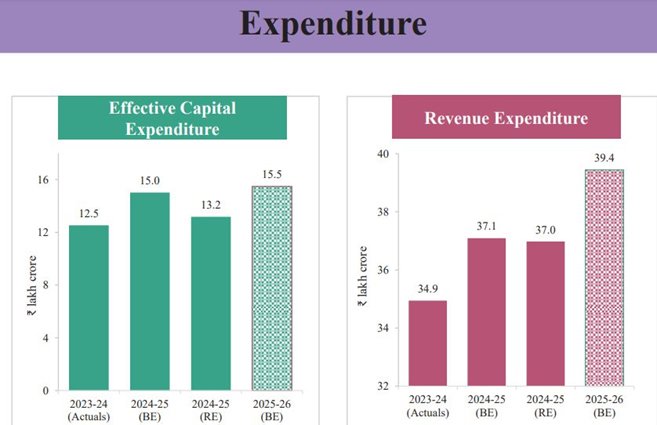
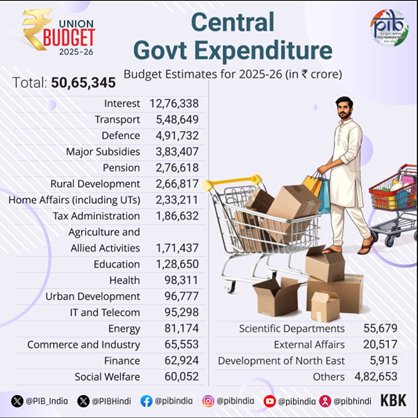
KEY INDICATORS
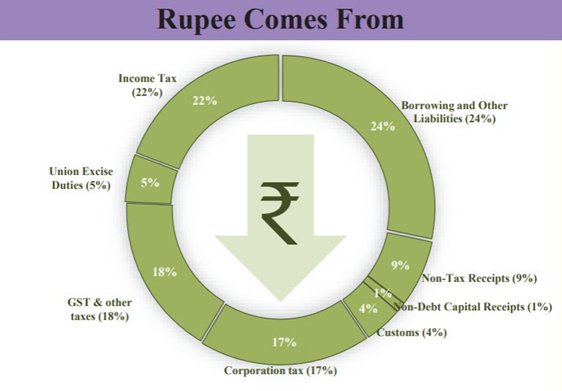
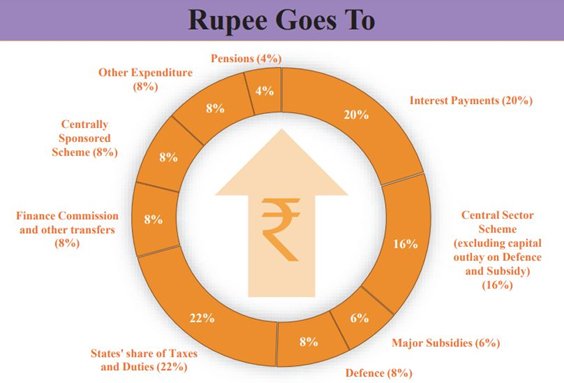

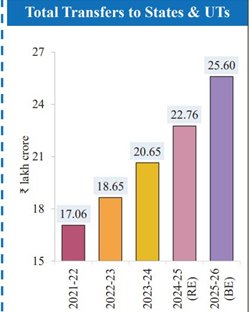
TRANSFERS TO STATES
PARTS OF THE BUDGET

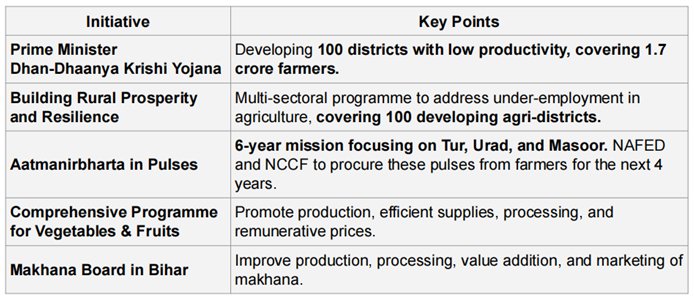
AGRICULTURE AS FIRST ENGINE OF GROWTH

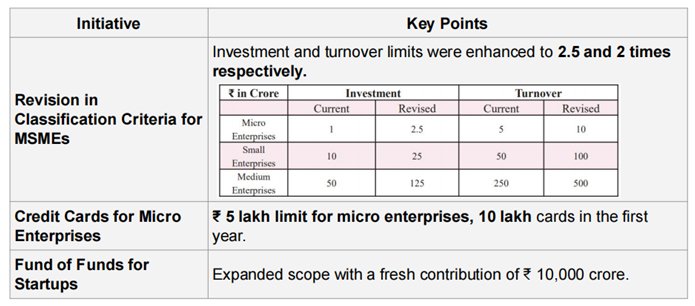
MSME AS SECOND ENGINE OF DEVELOPMENT

INVESTING IN PEOPLE (3RD ENGINE)
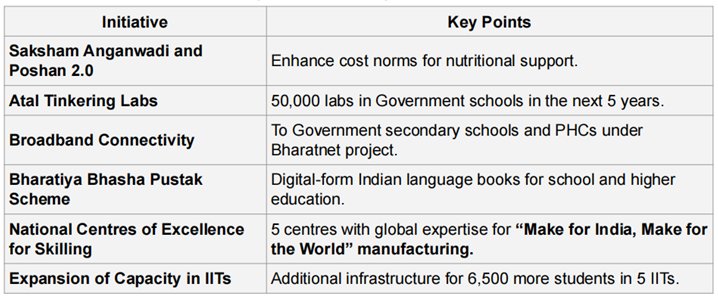
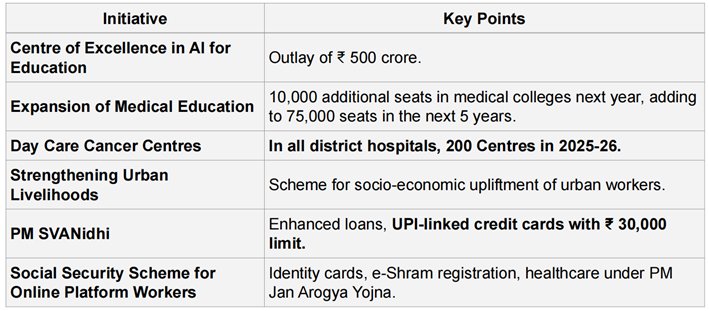
INVESTING IN THE ECONOMY (3RD PILLAR)

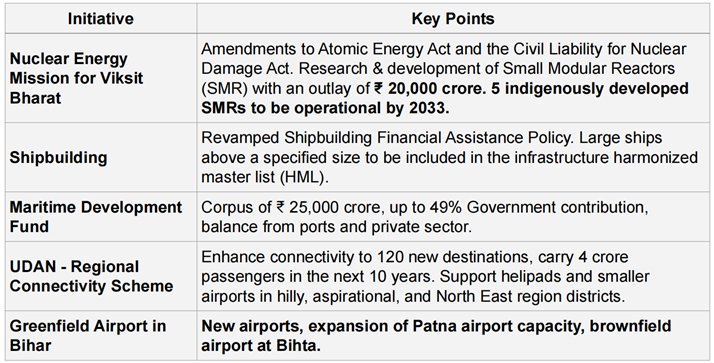

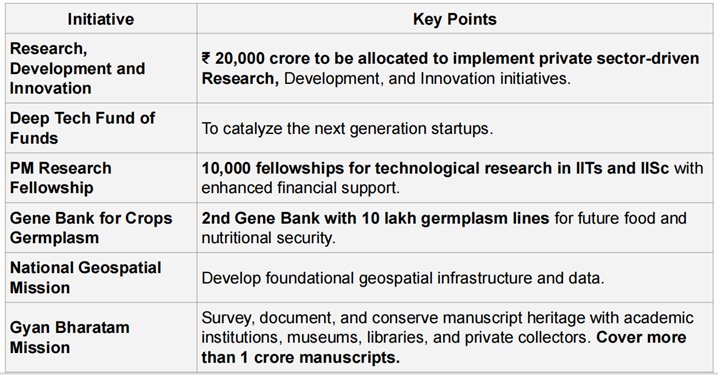
INVESTING IN INNOVATION (3RD PILLAR)
EXPORTS AS THE FOURTH ENGINE OF DEVELOPMENT

REFORMS AS FUEL


PART B: TAXATION REFORMS
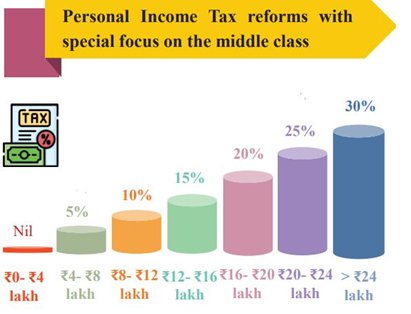
- No Personal Income Tax: Up to income of ₹ 12 lakh (average income of ₹ 1 lakh per month other than special rate income such as capital gains) under the new regime.
- Salaried Taxpayers: This limit will be ₹ 12.75 lakh for salaried taxpayers, due to a standard deduction of ₹ 75,000.
- Benefits: The new structure will substantially reduce the taxes of the middle class, leaving more money in their hands, boosting household consumption, savings, and investment.
- New Income-Tax Bill: To be clear and direct, making it simple to understand for taxpayers and tax administration, leading to tax certainty and reduced litigation.
- Revenue Forgone: About ₹ 1 lakh crore in direct taxes.
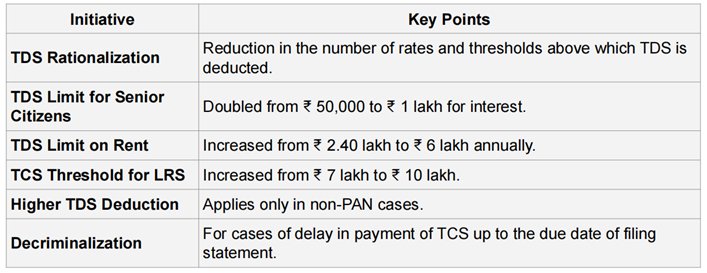
TDS/TCS RATIONALISATION
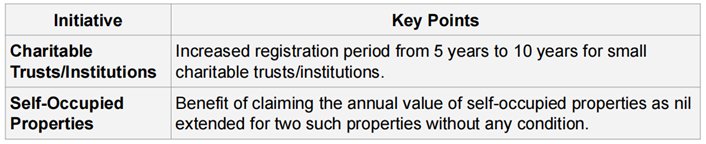
REDUCING COMPLIANCE BURDEN
EASE OF DOING BUSINESS

EMPLOYMENT AND INVESTMENT

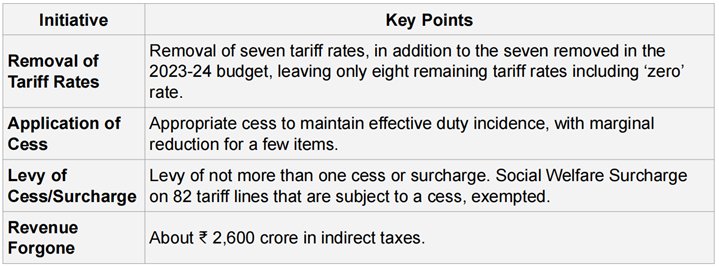
RATIONALISATION OF CUSTOMS TARIFF STRUCTURE FOR INDUSTRIALISATION GOODS
RELIEF ON IMPORT OF DRUGS
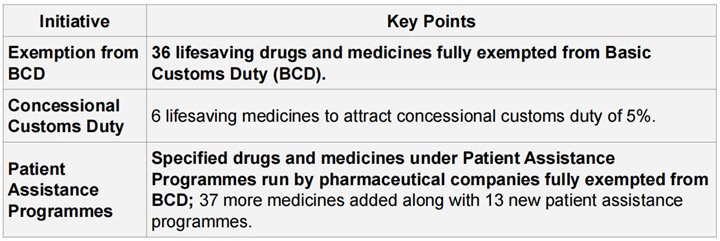
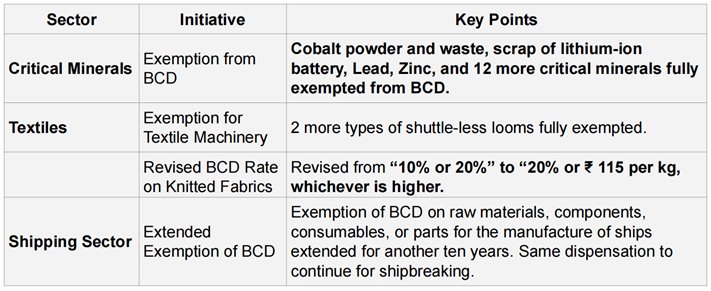
SUPPORT TO DOMESTIC MANUFACTURING & VALUE ADDITION

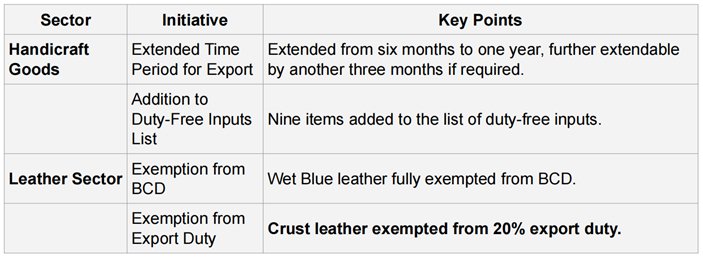
EXPORT PROMOTION
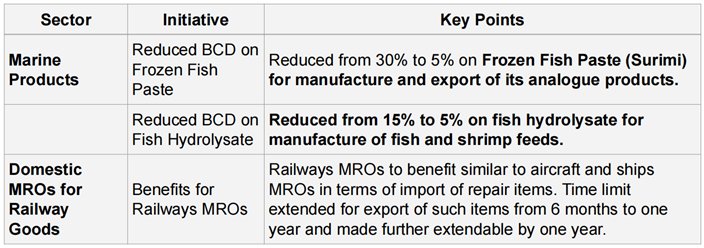
TRADE FACILITATION

CONCLUSION
Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that Democracy, Demography and Demand are key pillars of Viksit Bharat journey. She said that the middle class gives strength of India’s growth and the Government has periodically hiked the ‘Nil tax’ slab in recognition to their contribution. She said the proposed new tax structure will substantially boost consumption, savings and investment, by putting more money in the hands of the middle class.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


