WHY ARE TENSIONS HIGH IN ARCTIC?
- The Arctic, once isolated and difficult to access, is now a center of geopolitical tensions.
- The accelerating melting of ice due to climate change is making it more accessible for exploration.
- This opening creates new opportunities for natural resource extraction, new trade routes, and military positioning.
- The absence of a clear legal framework like Antarctica’s Treaty leads to disputes over sovereignty and territorial claims, heightening conflict risks.
KEY FACTORS DRIVING TENSIONS
- Climate Change Impact
- Melting Ice: Rapid ice melting is opening up new areas that were previously blocked by sea ice, allowing access to previously inaccessible regions.
- New Opportunities:
- Resources: Countries are eyeing Arctic resources like fossil fuels, rare earth elements, copper, and untouched fishing grounds.
- Trade Routes: The emerging shipping routes through the Arctic are reducing travel time between Europe and Asia, providing a major advantage for global trade.
- Legal Frameworks and Governance :
- UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea): The Arctic is governed by UNCLOS, which allows countries to claim rights over areas within their Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) and beyond, if they can prove natural prolongation of their continental shelf.
- Claims Extension: Countries such as Canada, Denmark, and Russia are submitting overlapping claims to the Arctic seabed, which are being reviewed by the UN Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS).
- Freedom of Navigation: The waters between the Arctic territories are classified as international waters, leading to disputes over which countries have the right to control them.
- Control Over Arctic Territory :
- Arctic Council: This is an intergovernmental forum made up of eight countries that have sovereignty over parts of the Arctic land. However, territorial disputes arise over the waters and seabed.
- Members: Canada, Denmark (via Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, and the United States.
- Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs): While each country has sovereignty over its own EEZ, disputes occur when countries attempt to extend their claims beyond 200 nautical miles to claim more of the Arctic seabed.
- Arctic Council: This is an intergovernmental forum made up of eight countries that have sovereignty over parts of the Arctic land. However, territorial disputes arise over the waters and seabed.
- Military and Infrastructure :
- Russian Military Presence: Russia has the largest infrastructure in the Arctic, including a fleet of nuclear-powered icebreakers, making it the dominant military and logistical power in the region.
- Arctic Ports: Russia has been developing key ports like Murmansk to solidify its military presence and strengthen trade routes.
KEY PLAYERS & INTERESTS
Russia
- Territorial Claims: Russia has made extensive claims to the Arctic seabed, including the Lomonosov Ridge, a subsea mountain range under the Arctic Ocean.
- Military Build-Up: Russia has greatly increased its military presence, building new bases, holding large military exercises, and expanding its fleet of icebreakers.
- Strategic Importance: Russia sees the Arctic as crucial for its national security and access to valuable natural resources, especially amid Western sanctions following the Ukraine conflict.
United States
- Greenland’s Importance: Greenland is strategically valuable for its location and for hosting the U.S. Pituffik military base, a key asset in Arctic defense.
- Northwest Passage Dispute: The U.S. insists that the Northwest Passage through Canada’s Arctic Archipelago is an international waterway, while Canada claims it as internal waters.
- Military Presence: The U.S. maintains military bases in Alaska and operates an icebreaking fleet through the Coast Guard, but it lacks the extensive infrastructure that Russia has.
Canada
- Northwest Passage Dispute: Canada asserts that the Northwest Passage is part of its internal waters, which is contested by the U.S. as an international waterway.
- Security and Sovereignty: To assert control over Arctic resources and protect its interests, Canada has strengthened its military presence in the region.
Denmark (Greenland)
- Strategic Position: Greenland is of strategic value due to its location between North America and Europe and its rich natural resources.
- Independence Movement: Greenland has been pushing for more autonomy from Denmark, and Denmark has responded by strengthening security to prevent Russian or Chinese influence in the region.
China
- Arctic Interests: In 2018, China declared itself a “Near-Arctic State” and began investing in Arctic resources, particularly rare earth minerals.
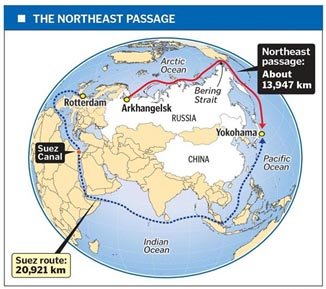
- Polar Silk Road: China is looking to use the Northeast Passage as part of its Belt and Road Initiative, transforming it into a key trade route between Asia and Europe.
- Icebreaker Development: China is also building a nuclear-powered icebreaker to access the Arctic and facilitate its growing presence there.
TENSIONS & DISPUTES
Greenland and U.S.-Denmark Relations
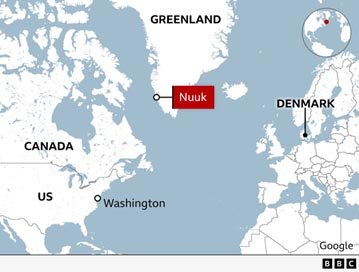
- Trump’s Offer to Buy Greenland (2019):S. President Trump’s attempt to buy Greenland for national security reasons caused diplomatic tension with Denmark, which rejected the offer.
- Security Concerns: Denmark has increased its focus on Greenland’s security to deter external threats, particularly from Russia and China, both of which are expanding their influence in the region.
Canada-U.S. Northwest Passage Tensions
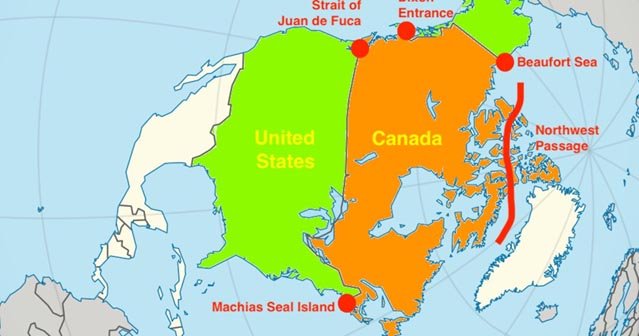
- Sovereignty vs. International Waters: Canada claims the Northwest Passage as internal waters, giving it control over navigation, while the U.S. views it as international waters, meaning all countries should have access to it.
- This disagreement is becoming more important as the passage is increasingly navigable due to melting ice.
Russia vs. NATO Members
- Svalbard Dispute: Russia has suggested that Norway’s Arctic island of Svalbard should fall under its control, a claim Norway, a NATO member, strongly rejects.
- NATO’s Arctic Presence: After Russia’s actions in Ukraine, NATO has increased its military presence in the Arctic, especially after Sweden and Finland joined NATO. This has raised fears of military escalation.
- Strategic Importance: The Greenland-Iceland-UK (GIUK) gap, located in the Arctic, is critical for NATO’s naval defense against Russian submarines and is a key strategic area.
GEOPOLITICAL & STRATEGIC IMPORTANCE
Resource Richness
- Oil & Gas: The Arctic region is estimated to hold around 13% of the world’s undiscovered oil and 30% of its untapped natural gas reserves, mainly under the seabed.
- Minerals: Greenland, in particular, is rich in rare earth elements that are essential for electronics and green technologies, making it a highly sought-after resource.
- Fishing: As the ice melts, the Arctic’s fish stocks are becoming more accessible, leading to competition for fishing rights.
New Shipping Routes
- Northeast Passage: This route along Russia’s Arctic coast can save up to 8,000 kilometers on shipping trips between East Asia and Europe, greatly reducing transportation costs.
- Polar Silk Road: China’s Belt and Road Initiative aims to establish the Northeast Passage as a key global trade route, furthering China’s influence in Arctic geopolitics.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


