EV batteries : Can the West catch up with China?
Context- The Shanghai Auto Show is opening its doors to car enthusiasts all over the world on Tuesday, after it was canceled last year due to China’s strict zero-COVID curbs.
A slew of Chinese and foreign automakers taking part in the event are girding to impress the visitors by unveiling their latest models and technologies, particularly electric vehicles (EVs).
The EU, meanwhile, aims to speed up the switch to EVs by effectively banning the sale of new petrol and diesel cars in the bloc from 2035.
(Credits- VDE Renewables)
Demand for EV batteries to skyrocket
- News agency Reuters estimates that the world’s top automakers are planning to invest nearly $1.2 trillion (€1.08 trillion) in EVs and batteries through 2030.
- According to the International Energy Agency, the share of battery-powered cars in total auto sales worldwide will jump from about 10% in 2021 to more than 60% by 2030.
- All these tens of millions of vehicles will need plenty of batteries — the single most-expensive component in an electric vehicle, accounting for about 30-40% of its cost.
- Given the anticipated surge in demand, governments and companies are racing to secure adequate supplies.
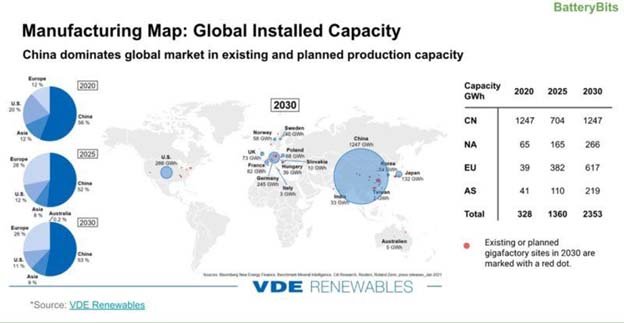
- But there’s one country that’s clearly in the lead when it comes to battery tech : China.
- The Asian giant dominates battery production, accounting for almost 75% of global manufacturing capacity, according to BloombergNEF.
- Chinese firms also control various stages of the supply chain — from mining and refining to final assembly
- China’s dominance of the sector stems from the fact that the Chinese government has prioritized electric vehicle technology for years, spending billions of dollars in government subsidies and tax breaks to support the sector.
- It has also promoted the setting up of EV infrastructure and encouraged people to buy EVs instead of combustion-engine cars.
- “Beijing has signaled early on that electric vehicles will be a strategic national priority, inducing Chinese firms to invest in mining, raw material refining and battery technologies,” said Gregor Sebastian, a researcher on China’s industrial policy.
No green transition without Chinese batteries?
- Many Western automakers like Tesla and General Motors currently rely on Chinese firms like Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., (CATL) — the world’s biggest producer of EV batteries — for their battery needs.
- Ford Motors recently announced that it’s licensing CATL’s lithium-iron-phosphate technology for use in a new battery plant it will set up in the US state of Michigan.
- The deals show that foreign automakers who want to ditch their gas-guzzling internal combustion engines for electric ones won’t be able to do it without turning to Chinese-made batteries.
But they have also drawn criticism from some in the West.
- Biden administration, with the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), is trying to take Chinese battery cells out of US EV manufacturing supply chains for vehicles manufactured in North America.
- The IRA funnels some $370 billion into subsidies for energy transition, including tax breaks for US-made EVs and batteries.
- To be eligible for the incentives, companies must source a certain percentage of the components and minerals for EV batteries from the US or its free trade partners.
How does EU fare in battery tech?
- The EU has also been pushing for a domestic EV battery industry for years. In 2017, the bloc launched the European Battery Alliance to kick-start local production. The goal was to get European suppliers to meet 90% of the region’s battery needs by 2030.
- “European countries like Germany have important technologies for certain parts of the EV battery tech value chain, for instance in recycling, and have been at the forefront of trialing new battery chemistries like sodium-ion batteries,” said Sebastian.
- But he stressed that Europe’s battery industry lacks scale and faces difficulties to bridge the gap from initial development to widespread commercialization. “In certain parts of the value chain, like the refining of raw materials, Europe is almost entirely dependent on East Asian firms.”
- Companies like Volkswagen (VW) have plans to invest in mines to secure raw materials for battery making.
- As part of its €180 billion ($199.8 billion) five-year spending plan, VW has allocated up to €15 billion for its three announced battery plants and some raw material sourcing.
- Some EU countries like Hungary, meanwhile, have been wooing foreign manufacturers, including Chinese ones, to set up battery plants.
Conclusion- The EV battery industry remains in flux. European firms’ best bet to overtake China would be on new, upcoming technologies like solid-state batteries that are not yet dominated by any firm.
Source- Indian Express
NEWS- EV batteries : Can the West catch up with China?
Syllabus- GS-3; Renewable Energy and Climate change


