Hydroponics
- Hydroponics is the technique of growing plants using a water-based nutrient solution rather than soil, and can include an aggregate substrate, or growing media, such as vermiculite, coconut coir, or perlite.

- Hydroponic production systems are used by small farmers, hobbyists, and commercial enterprises.
- It is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture which involves growing plants, usually crops or medicinal plants, without soil, by using water based mineral nutrient solutions in aqueous solvents.
- Terrestrial or aquatic plants may grow with their roots exposed to the nutritious liquid or in addition, the roots may be mechanically supported by an inert medium such as perlite, gravel, or other substrates.
- Despite inert media, roots can cause changes of the rhizosphere pH and root exudates can affect rhizosphere biology and physiological balance of the nutrient solution by secondary metabolites.
Advantages of Hydroponic Farming :

- No Soil Involved :
- Since Hydroponic farming involves growing crops without soil, it is an ideal option for anyone who has limited accessibility to land.
- During the mid-nineties, Hydroponics was used for supplying fresh crops to the troops in the distant Wake Islands.
- Optimal Use of Location :
- Since every requirement of the plant is provided for and duly maintained in a structured system, Hydroponic Farming can be performed anywhere.
- Complete Control Over Climate :
- As with greenhouses, hydroponic growers have absolute control over the climate.
- They can adjust the temperature, the intensification of light, and the humidity levels as per their requirements.
- Saves Water :
- The plants grown in a Hydroponic system barely use around 10% of the water when compared to the conventionally field-grown plants.
- The water used here is drastically less because unlike conventional farming water is reused or re-circulated.
- Optimal Use of Nutrients :
- When it comes to Hydroponics Systems, you have absolute control over the nutrients as required by the plants.
- pH control :
- Since every mineral is directly in touch with water, you can always manually adjust and tweak the pH level as and when required.
- This will ensure that the plants receive optimal nutrient intake.
- Zero Weed :
- Trimming weeds is one of the most exhausting tasks for crop owners or gardeners.
- With tilling, ploughing, and hoeing, the process practically seems endless.
- Fewer Pests and Ailments :
- As with weeds, removing soil ensures that your plants are not as susceptible to soil-borne pests like gophers, groundhogs, or a bunch of birds.
- Fewer Insecticides and Herbicides Involved :
- Since Hydroponic Farming doesn’t involve any soil, the process also eliminates the need and use of chemicals.
- Over time, this enables to grow clean and healthy foods. Your safety is kept at priority and never compromised on at any point.
Disadvantages of Hydroponic Farming :
- Time Consuming :
- While the process of Hydroponic Farming might seem feasible and convenient, it is slightly time-consuming as well.
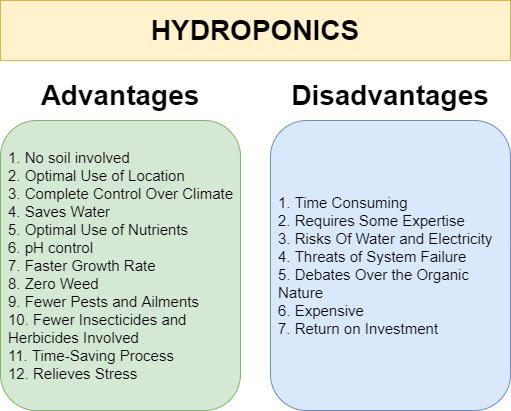
- Requires Some Expertise :
- The process of Hydroponic farming depends on a range of equipment that requires proper expertise.
- Risks of Water and Electricity :
- Two major factors in Hydroponic farming are electricity and water.
- So, unless you have adequate water or stable electricity, the Hydroponic system won’t thrive well.
- Expensive :
- Unlike conventional soil-based farming, Hydroponic Farming involves expensive equipment (at least for the first installation).
Syllabus : Prelims


