CHINA’S CHANG’E 6 MOON MISSION
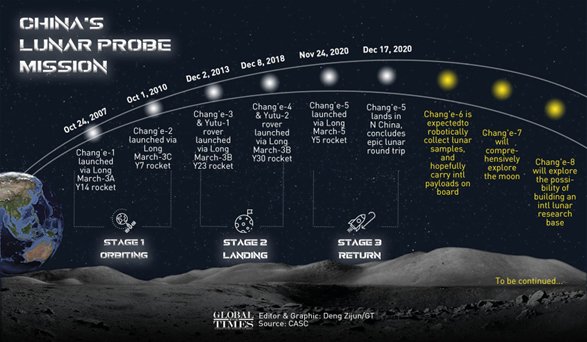
On Friday (May 3), China launched its second mission to the far side of Moon.
If successful, it will be the world’s first mission to bring back samples from the part of the Moon that the Earth never gets to see.
The mission, known as Chang’e-6, lifted off from the Wenchang Space Launch Center. Around 30 minutes after the launch, the spacecraft separated from the rocket and began its five-day-long journey towards the Moon.
China is the only country to achieve a soft-landing on the far side of the Moon. In 2019, its Chang’e-4 mission landed on the region and explored the Moon’s Von Karman crater with the help of a rover.
ABOUT THE FAR SIDE OF THE MOON
The Moon’s far side is often referred to as the dark side because it cannot be seen from the Earth, not because it does not catch the Sun’s rays. The Moon is tidally locked with the Earth and therefore, we see only one side of the Moon, also known as the near side.
The far side has been under the spotlight in recent years as it is very different from the near side.
“It has a thicker crust, more craters and fewer maria, or plains where lava once flowed,”
WHY EXPLORE THE FAR SIDE OF THE MOON?
- Examining the samples from the far side can help scientists solve mysteries about the origin and evolution of the Moon — till now, scientists have only been able to analyse samples from the near side.
- The far-side samples can also give answers to the longstanding question: why is it different from the near side?
Going to the far side, getting samples and doing different kinds of geophysical measurements is really important to figuring out this really long, long-standing mystery.
WHAT WILL CHANG’E 6 DO?
The Chang’e-6 is a 53-day-long mission. After reaching the Moon’s orbit, the mission’s orbiter will circle the natural satellite while its lander will descend into the 2,500-kilometre-wide South Pole-Aitken basin on the lunar surface.
“The impact that created the basin — among the largest in the history of the solar system — is thought to have dug up material from the lunar mantle. If that material can be retrieved, scientists can learn more about the history of the Moon’s insides.
After collecting samples through scooping and drilling, the lander will launch an ascent vehicle, which will transfer the samples to the orbiter’s service module. This module will then return to the Earth.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


