CONFLICT IN DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO
What is Happening in Congo?
- The M23 rebels, a group led by ethnic Tutsis, have launched a major attack in eastern Congo.
- Tutsi are an ethnic group primarily inhabiting Rwanda and Burundi in the Great Lakes region of Africa
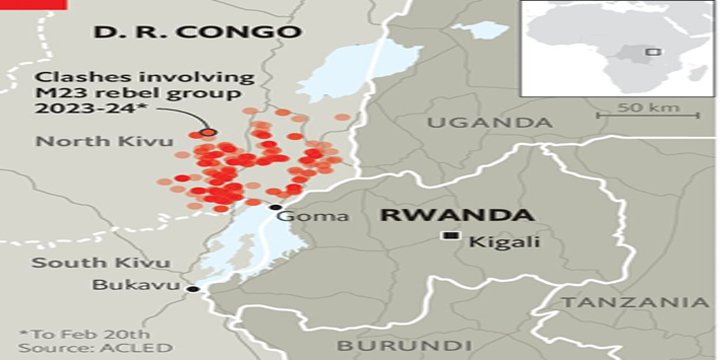
- They took over the city of Goma in North Kivu province on January 27, 2025, and are now moving southward toward the capital of South Kivu, Bukavu.
- By January 30, Goma was fully controlled by the rebels, with many civilians fleeing the city due to the violence.
- The fighting has also spilled into nearby areas, with soldiers from Rwanda and Burundi reportedly involved, raising concerns that the conflict could spread.
- Thousands of people have been forced to leave their homes, adding to the millions already displaced by earlier fighting. This has made an already difficult humanitarian situation even worse.
WHO ARE M23 REBELS?
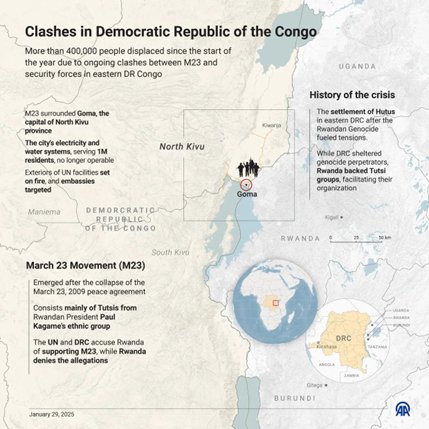
- The M23 (March 23 Movement) group gets its name from a 2009 peace agreement that ended a previous rebellion.
- The current rebellion began in 2022, with M23 accusing the Congolese government of not keeping promises made in that peace deal, such as including Tutsis in the army and government.
- The group mainly represents the Tutsi ethnic group, which has faced persecution in the region.
- M23 wants to protect Tutsis from violent attacks by another group called the FDLR, which is made up of Hutus responsible for violence against Tutsis in both Congo and Rwanda.
- The Forces Démocratiques de Libération du Rwanda (FDLR), or the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda, is a Hutu armed group operating in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
- In addition to their political and ethnic concerns, M23 has also gained control of important mining areas, which generate a lot of money from minerals like coltan. This funding helps support their efforts.
WHY IS RWANDA INVOLVED?
- Rwanda is accused of supporting the M23 rebels, providing them with weapons and soldiers.
- A UN report from 2022 suggests Rwanda is involved in the fighting, although Rwanda denies it.
- The Rwandan government says it’s only protecting itself from the FDLR, which has long been a threat to Tutsi communities.
- Rwanda also claims that the Congolese government is working with the FDLR.
- The conflict between Tutsi and Hutu groups goes back to the 1994 Rwandan genocide, when Hutus killed nearly a million Tutsis.
- Many of the people involved in the genocide fled to Congo, and some formed the FDLR, continuing their attacks on Tutsis.
WHY ARE THE M23 REBELS FIGHTING?
- The M23 rebels are fighting because they feel the government has not kept its promises from the 2009 peace deal.
- These promises included including Tutsis in the military and government, which hasn’t happened.
- They also want to protect Tutsis from attacks by the FDLR.
- Another major reason for the fighting is control over the region’s valuable minerals, like coltan, cobalt, and gold, which are in high demand worldwide.
INTERNATIONAL & REGIONAL IMPACT
- The violence has caused a huge amount of suffering.
- More than a million people have had to leave their homes, and many have sought refuge in neighboring countries like Uganda and Rwanda.
- The destruction of infrastructure, such as hospitals and schools, is making life even harder for those who remain.
- There is a risk that this conflict could escalate into a wider regional war, especially with Rwanda and Burundi involved. Tensions between these countries and others in the region are high because of the instability in eastern Congo.
- International Response Global organizations like the UN, the EU, and the US have condemned the violence and called for a ceasefire.
- The UN has sent peacekeeping troops, but the situation remains tense, and diplomatic efforts have struggled to make a lasting impact.
- The ongoing fighting has disrupted Congo’s mining industry, which is crucial for both the country’s economy and the global market.
CONCLUSION
The conflict in Congo is a complex mix of ethnic tensions, political struggles, and control over valuable resources. M23’s rebellion, the failure of peace agreements, and the involvement of neighboring countries like Rwanda and Burundi have made the situation even more dangerous. Despite global efforts to stop the violence, finding a lasting solution remains difficult due to the deep-rooted issues at play.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.