ECONOMIC SURVEY 2024
- The Economic Survey is a comprehensive review or annual report of Indian economy during the closed financial year.
- Prepared by: The Economics Division of the Department of Economic Affairs of the Finance Ministry under the guidance of the India’s Chief Economic Advisor (CEA).
- It is typically published a day before the Union Budget.
- The survey has evolved over the years, becoming more comprehensive and analytical
THE HISTORY
- The first Economic Survey was published in 1950-51 as a “white paper” within the budget papers
- Initially, the survey relied on secondary data due to the scarcity of readily available figures and analysts
- Over time, the survey has expanded in scope and become a primary data source for those outside the government
- However, since 2021-22, the Economic Survey has reverted to its classic template, focusing on hard facts and less on opinions
1: OVERALL ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE
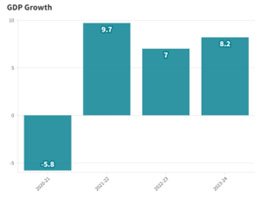
- GDP Growth: India’s real GDP grew by 8.2% in FY24, exceeding 8% in three out of four quarters.
- Projected Growth: India’s real GDP is anticipated to grow between 6.5% and 7% in fiscal year 2024-25.
- Global Context: India’s growth is notable, given the challenging global economic environment with 3.2% global growth in 2023.
- Recovery: The real GDP in FY24 was 20% higher than its level in FY20, a feat achieved by very few major economies post-pandemic.
- India has continued to reduce its fiscal deficit, going against the global trend of increasing deficits. According to recent data, the fiscal deficit has decreased from 6.4% of GDP in FY 23 to 5.6% of GDP in FY 24.
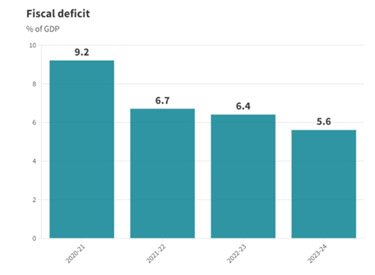
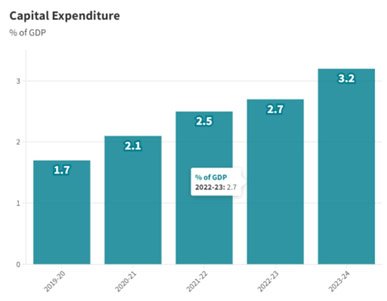
- India’s capital expenditure in FY24 reached ₹9.5 lakh crore, a 28.2% year-over-year increase, and nearly triple the level of FY20.
- The government’s focus on capital expenditure has been a key factor in driving economic growth despite global uncertainty.
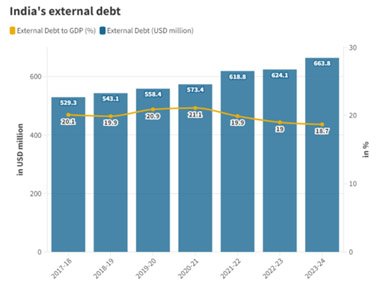
- India’s external debt indicators remain stable, with external debt at 18.7% of GDP as of March 2024.
- Additionally, foreign exchange reserves cover 97.4% of total debt, indicating a comfortable position.
2: INFLATION & MONETARY POLICY
- Inflation Rate: Retail inflation moderated to 5.36% in FY24, the lowest since the pandemic.
- Core Inflation: Dropped to a four-year low in FY24.
- RBI Actions: The Reserve Bank of India raised the repo rate by 250 basis points from May 2022 to combat inflationary pressures.
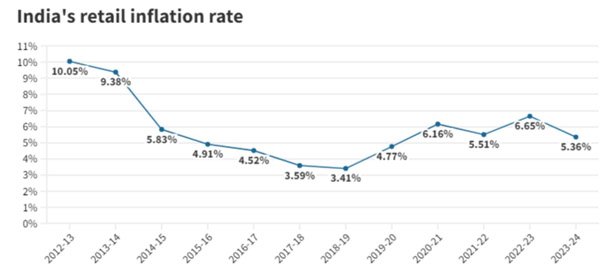
- Future Outlook: RBI projects inflation to fall to 4.5% in FY25 and 4.1% in FY26, assuming normal monsoons and no external shocks.
3: EXTERNAL SECTOR
- Current Account Deficit (CAD): Narrowed to 0.7% of GDP in FY 24, down from 2.0% in FY23.
- Services Exports: Grew by 4.9% to USD 341.1 billion in FY 24, driven by IT/software and business services.
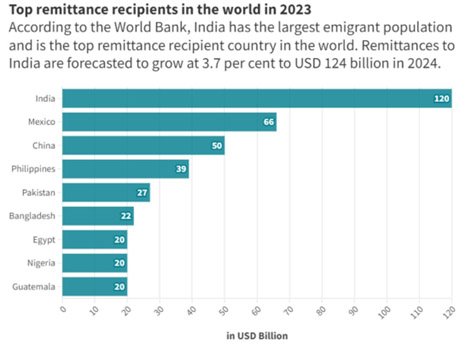
- Remittances: India remains the top global remittance recipient, reaching USD 120 billion in 2023.
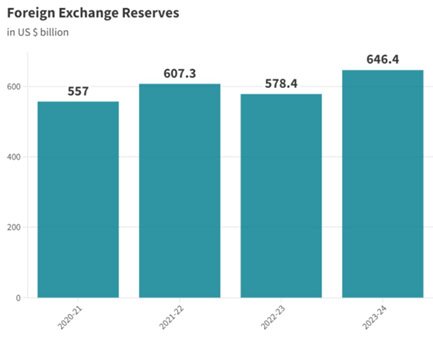
- Forex Reserves: Sufficient to cover more than 10 months of projected imports for FY25.
4: INVESTMENT & CAPITAL FORMATION
- Public Investment: Has been pivotal in sustaining capital formation in recent years.
- Private Sector Investment: Showing encouraging signs since FY22.
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation: Increased by 9% in real terms in 2023-24.
- Capital Markets: Primary capital markets facilitated capital formation of ₹10.9 lakh crore in FY24.
5: BANKING & FINANCIAL SECTOR
- Credit Growth: Bank credit growth was broad-based and in double digits.
- Non-Performing Assets (NPAs): Gross and net NPAs reached multi-year lows.
- Stock Market Performance: India’s market capitalization to GDP ratio is the fifth largest globally
6: EMPLOYMENT & LABOUR MARKET
- Unemployment Rate: Decreased to 3.2% in 2022-23.
- Formal Employment: Net payroll additions under EPFO have more than doubled over the past five years.
- Youth and Female Participation: Significant rise in workforce participation, offering opportunities for demographic and gender dividends.
7: AGRICULTURE & FOOD MANAGEMENT
- Sector Growth: Average annual growth rate of 4.18% at constant prices over the last five years.
- Allied Sectors: Livestock and fisheries showing robust growth (CAGR of 7.38% and 8.9% respectively from 2014-15 to 2022-23).
- Digital Initiatives: Implementation of Digital Agriculture Mission (2021–2025) and e-National Agriculture Market (e-NAM).
- Food Security: Free food grains provided to 81.35 crore beneficiaries under PMGKAY for an additional five years.
8: INDUSTRIAL GROWTH
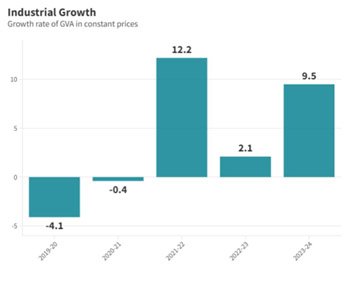
- Manufacturing Growth: Average annual growth rate of 5.2% in the last decade.
- Steel Production: India became a net exporter of finished steel over the past decade.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Significant growth since 2014, reaching 3.7% of global market share in FY22.
- MSME Support: ₹9,000 Crore allocated to the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) in Union Budget 2023-24.
9: SERVICE SECTOR

- Sector Growth: Estimated to have grown by 7.6% in FY24.
- PMI Performance: Services PMI above 50 since August 2021, indicating continuous expansion for 35 months.
- Global Services Exports: India’s share reached 4.4% of the world’s commercial services exports in 2022.
- E-commerce Growth: Indian e-commerce industry expected to cross USD 350 billion by 2030.
10: INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT
- National Highways: Construction increased from 11.7 km per day in FY14 to ~34 km per day by FY24.
- Railways: Capital expenditure increased by 77% in the past 5 years.
- Airports: New terminal buildings operationalized at 21 airports in FY24, increasing passenger handling capacity by approximately 62 million per annum.
- Clean Energy: New investment of ₹8.5 lakh crore (USD 102.4 billion) between 2014 and 2023.
11: CLIMATE CHANGE & SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
- Emission Reduction: Emission intensity of GDP reduced by 33% from 2005 levels by 2019.
- Renewable Energy: Non-fossil sources make up 45.4% of installed electricity generation capacity as of May 31, 2024.
- Mission LiFE: Initiative to create a mass movement for sustainable living based on conservation and moderation.
- International Leadership: India has led several global climate change mitigation efforts, including the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
12: SOCIAL SECTOR DEVELOPMENTS
- Education: Implementation of NEP 2020, focusing on foundational literacy and numeracy.
- Healthcare: Over 34.7 crore Ayushman Bharat cards issued, covering 7.37 crore hospital admissions.
- Women Empowerment: DAY-NRLM Program covers over 89 million women through 8.3 million Self Help Groups.
- Skill Development: Increased participation in government skill development programs under the ‘Skill India’ initiative.
13: CHALLENGES & FUTURE FOCUS AREAS
- Global Risks: Slowing global GDP growth and rising trade protectionism pose significant risks.
- Climate Adaptation: Aligning production patterns with agro-climatic characteristics and natural resources.
- Technology Integration: Balancing technological deployment (e.g., AI) with labor considerations in various sectors.
- Infrastructure Financing: Need for higher levels of private sector financing and resource mobilization.
- Data Management: Developing better systems for tracking infrastructure utilization and financial flows.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


