HEALTHCARE IN INDIA
AYUSHMAN BHARAT
Launched in 2018, Ayushman Bharat is a transformative health initiative aimed at achieving universal health coverage for the most vulnerable populations in India, particularly in rural areas. The program is designed to provide comprehensive healthcare across all levels — primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
ABOUT AYUSHMAN BHARAT
The Ayushman Bharat programme was launched in 2018 to address health issues at all levels – primary, secondary, and tertiary.
It has two components:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY), earlier known as the National Health Protection Scheme (NHPS)
- Ayushman Arogya Mandir (earlier known as Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs))
Ayushman Bharat is an integrated approach comprising health insurance and primary, secondary and tertiary healthcare.
Targeted Beneficiaries: 12 Crore Households.
HWCs & PM JAY
The HWCs are aimed at improving access to cheap and quality healthcare services at the primary level.
PM-JAY will cover the financial protection for availing healthcare services at the secondary and tertiary levels.
Ayushman Bharat is the largest government-funded healthcare programme in the world with over 50 crore beneficiaries.
AYUSHMAN AROGYA MANDIR / HEALTH & WELLNESS CENTRES (HWCs)
HWCs are being created by converting the existing primary health centres and sub centres.
They provide comprehensive primary health care (CPHC) including a child and maternal health services, non-communicable diseases, and also diagnostic services, and free essential drugs.
HWCs are important because they offer CPHC that is critical to enhancing health outcomes. Primary healthcare plays a vital role in preventing many disease conditions. Providing CPHC decreases morbidity and mortality at a lower cost and greatly reduces the requirement for secondary and tertiary care.
PM JAN AROGYA YOJANA (PM JAY)
- It is the largest government-funded health insurance scheme in world.
- The scheme offers eligible families an insurance cover of 5 lakh per annum per family. (no cap on family size)
- This amount is intended to cover all secondary and most tertiary care expenditures incurred.
- The cover will include pre and post-hospitalization expenses. It will also cover all pre-existing conditions. 3 days of pre-hospitalization and 15 days of post-hospitalization like medicines and diagnostics are covered.
- The beneficiary will also receive a defined transport allowance per hospital.
- The beneficiaries can take cashless treatment from any empanelled hospital anywhere in the country. This includes both public and private hospitals. By default, all government hospitals in the states that are implementing the scheme will be empanelled.
WHO IS ELIGIBLE?
The scheme is targeted to cover 12 crore families (deprived rural families and identified occupational category of urban worker’s families)
The beneficiaries are identified by latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
The beneficiaries are different in rural & urban areas.
RURAL AREA BENEFICIARIES
Out of the total seven deprivation criteria for rural areas, PM-JAY covered all such families who fall into at least one of the following six deprivation criteria (D1 to D5 and D7) and automatic inclusion(Destitute/ living on alms, manual scavenger households, primitive tribal group, legally released bonded labour) criteria:
D1– Only one room with kucha walls and kucha roof
D2– No adult member between ages 16 to 59
D3– Households with no adult male member between ages 16 to 59
D4– Disabled member and no able-bodied adult member
D5– SC/ST households
D7– Landless households deriving a major part of their income from manual casual labour
URBAN AREA BENEFICIARIES
For urban areas, the following 11 occupational categories:
- Ragpicker
- Beggar
- Domestic worker
- Street vendor/ Cobbler/hawker / other service provider working on streets
- Home-based worker/ Artisan/ Handicrafts worker/ Tailor
- SWEEPER / SANITATION WORKER / MALI
- CONSTRUCTION WORKER / PLUMBER /MASON / LABOUR / PAINTER / WELDER / SECURITY GUARD / COOLIE AND OTHER HEAD-LOAD WORKER
- Transport worker/ Driver/ Conductor/ Helper to drivers and conductors/ Cart puller/ Rickshaw puller
- Shop worker/ Assistant/ Peon in small establishment/ Helper/Delivery assistant / Attendant/ Waiter
- Electrician/ Mechanic/ Assembler/ Repair worker
- Washer-man/ Chowkidar
ROLE OF NHA
- NHA is the apex body responsible for implementing Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana.
- It has been entrusted with the role of:
- designing strategy, building technological infrastructure and
- implementation of National Digital Health Mission to create a National Digital Health Ecosystem.
- To implement the scheme at the State level, State Health Agencies (SHAs) in the form of a society/trust have been set up by respective States.
RECENT UPDATE

HOW IS IT PERFORMING?
As of September 12, 2024, there are 1,74,453 AAMs across the country, comprising:
-
- 1,12,617 Sub Health Centres (SHCs)
- 23,903 Primary Health Centres (PHCs)
- 5,123 Urban Primary Health Centres (UPHCs)
- 5,632 Urban Health and Wellness Centres (UHWC)
- 12,178 Ayush-related Centres
- As of September 9, 2024, 4 crore Ayushman cards have been issued under the scheme.
- The scheme is operational in 33 States and Union Territories (UTs), with the exceptions of Delhi, West Bengal, and Odisha.
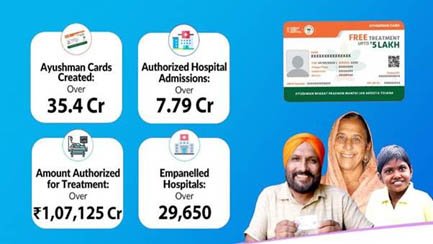
- The scheme has authorized 79 crore hospital admissions, with a total expenditure of Rs 1,07,125 crore for these admissions.
- Initially, the scheme covered 74 crore vulnerable families, which was expanded to 12 crore families in January 2022, reflecting the population growth of India (11.7% increase since 2011).
- Further, it was expanded to include 37 lakh Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs), Anganwadi Workers (AWWs), and Anganwadi Helpers (AWHs) and their families.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.

