ICC ISSUES ARREST WARRANT FOR NETANYAHU
- On November 21, 2024, the International Criminal Court (ICC) issued arrest warrants for Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, his former Defence Minister Yoav Galant, and Hamas leader Mohammed Deif.
- The ICC accused them of war crimes and crimes against humanity related to the ongoing conflict in Gaza.
- The decision follows a series of violent clashes between Israel and Hamas, most notably the October 2023 Hamas attack on Israel that killed hundreds and triggered Israel’s large-scale military offensive in Gaza.
ABOUT ICC
- About
- It is a permanent court to prosecute serious international crimes committed by individuals.
- It tries crimes such as genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity, and aggression.
- The court was established to fight global impunity and bring to justice criminals under international law, regardless of their rank or stature.
- It is different from the United Nations’ International Court of Justice, also at The Hague.
- HQ
- The Hague, The Netherlands
- Statute
- Before the ICC became functional in 2002, its founding treaty was adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1998 in Rome, Italy, thereby making it the Rome Statute.
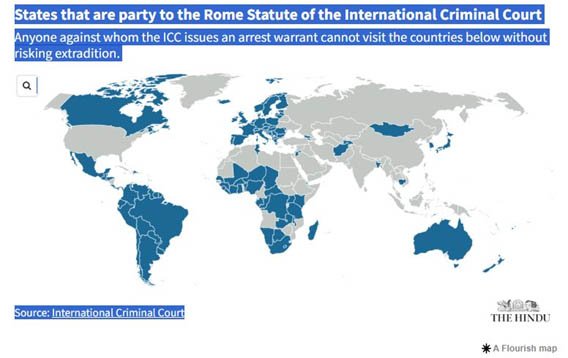
MEMBERSHIP
- To become a member of the ICC or State party to the Rome Statute, countries have to sign the statute and ratify it under their respective legislatures.
- 123 countries are currently members of the ICC, with African countries making up the largest bloc.
- Notably, countries including India, China, Iraq, North Korea and Turkey never signed the Rome Statute.
- Others including the US, Russia, Israel and Syria signed, but never ratified it.
HOW DOES ICC FUNCTION?
- Judges & Prosecutors
- The court carries out its investigations through the Office of the Prosecutor and has 18 judges.
- Both the judges and prosecutors hold non-renewable nine-year terms.
- Process
- There are pre-trial, trial, and appellate benches in the ICC.
- The prosecutor conducts a preliminary examination in a matter, before seeking permission from pre-trial judges to open a full investigation.
- The initial examination must conclude that the crimes in question are of sufficient gravity.
KEY POINTS OF ICC DECISION
- Warrants for Israeli Leaders:
- Benjamin Netanyahu and Yoav Gallant are accused of intentionally depriving civilians in Gaza of basic necessities, including food, water, medicine, and fuel.
- The ICC’s three-judge panel found reasonable grounds to believe that both men knowingly and intentionally engaged in actions that led to widespread suffering for Gaza’s civilian population.
- The charges include murder, attacks on civilians, and persecution.
- Warrant for Hamas Leader Mohammed Deif:
- Mohammed Deif, a senior Hamas military commander, was accused of committing crimes against humanity during the October 2023 attacks.
- These included murder, extermination, torture, rape, and other forms of sexual violence, as well as war crimes such as taking hostages and attacking civilians.
- The attacks by Hamas on October 7, 2023, killed around 1,200 Israelis and led to the abduction of 250 people.
- Impact of the Warrants:
- While the warrants place Netanyahu, Gallant, and Deif as internationally wanted figures, the practical impact is uncertain, as neither Israel nor Hamas are members of the ICC.
- The United States and Israel, both non-members, have rejected the ICC’s authority and dismissed the warrants as “political” and “anti-Semitic.”
- Two of the Hamas leaders named in the request for arrest warrants, Yahya Sinwar and Ismail Haniyeh, were killed during the conflict, and thus the warrants for them were withdrawn.
- Legal and Political Reactions:
- Israel’s Response: Israeli officials, including Netanyahu’s office, rejected the ICC’s decision, calling it “absurd” and “false”.
- Israel has long maintained that it has the right to self-defence and would not cooperate with the court’s actions.
- S. Support for Israel: U.S. President Joe Biden expressed strong backing for Israel’s right to defend itself, calling the ICC’s actions “disgraceful”.
- Hamas Response: Hamas also condemned the warrants, claiming that they were part of an effort to delegitimize its struggle against Israeli occupation.
- Challenges in Enforcement:
- The ICC lacks its own police force and relies on cooperation from member states to enforce arrest warrants.
- Since Israel and the U.S. are not members of the court, these warrants may not have immediate practical
- Netanyahu and Gallant may face challenges when traveling to ICC member states (such as the EU and UK), which are required to detain suspects under arrest warrants.
- However, as demonstrated by Russian President Vladimir Putin’s recent travel to Mongolia, which is an ICC member, non-cooperation from certain states could limit the impact of the warrants.
- The ICC’s Jurisdiction:
- While Israel is not a member of the ICC, the court has the authority to prosecute individuals from non-member states if crimes occurred on the territory of a member state or if those crimes were referred to the court by the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- Israel’s legal arguments against the ICC’s jurisdiction, including its claim that the court should allow Israel to investigate alleged war crimes itself, have been dismissed by the ICC.
- Separate Legal Issues:
- In addition to the ICC case, Israel is also dealing with a separate case at the International Court of Justice (ICJ), where it is accused of genocide by South Africa. Israel denies the accusation, claiming that it is acting in self-defence against Hamas militants.
CONCLUSION
The ICC’s arrest warrants for Benjamin Netanyahu, Yoav Gallant, and Mohammed Deif represent a significant development in the ongoing Israel-Hamas conflict and the pursuit of accountability for war crimes. While the practical impact of the warrants remains uncertain, the case signals the international community’s willingness to address allegations of war crimes and crimes against humanity committed by both state and non-state actors in the conflict. This decision also underscores the growing tension between the ICC and non-member states like Israel, which continues to reject the court’s authority.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


