INDIA RUSSIA TRADE TARGET OF 100 BN USD BY 2030: DEVELOPMENTS AND CHALLENGES
India and Russia aim to achieve a USD 100 billion trade target well before 2030. This was discussed at the 25th India-Russia Intergovernmental Commission on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological, and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC) held in New Delhi. The session focused on strengthening bilateral ties and overcoming challenges in trade, connectivity, and strategic cooperation.
KEY HIGHLIGHTS FROM IRIGC-TEC
- Trade Target of USD 100 Billion:
- India and Russia are confident of reaching USD 100 billion in annual trade earlier than the 2030 target.
- Both countries agreed on the need for a more balanced trade relationship and have started efforts to tackle current trade constraints.
- Trade Progress and Diversification:
- Payment and Logistics: Significant progress has been made to resolve challenges related to payments and logistics. 90% of trade between India and Russia is now conducted using local or alternative currencies, minimizing reliance on freely convertible currencies.
- Diversifying Trade: The trade basket is diversifying beyond crude oil. Both countries are focusing on sectors like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, industrial equipment, and technology.
- Improving Connectivity and Talent Mobility:
- Emphasis was placed on improving connectivity between India and Russia, with key projects like the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), the Chennai-Vladivostok Corridor, and the Northern Sea Route.
- Both nations are also looking to promote the mobility of talent and skills development, especially for Russia’s growing needs in education and workforce collaboration.
- Future Steps for Economic Cooperation:
- Working groups and sub-groups were set up to finalize the economic cooperation program leading up to 2030.
- Key agenda items include enhancing market access, and advancing discussions on services, investments, and technology exchange.
INDIA RUSSIA TRADE: KEY DATA & FACTS
- Trade Targets:
- Initially, India and Russia had set targets of USD 50 billion in investment and USD 30 billion in trade by 2025.
- In FY 2023-24, bilateral trade reached a record high of USD 65.70 billion. India’s exports to Russia were valued at USD 4.26 billion, and imports from Russia at USD 61.44 billion.
- Trade Basket:
- Imports from Russia include oil, fertilizers, minerals, precious metals, and vegetable oils.
- Exports to Russia include pharmaceuticals, organic chemicals, electrical machinery, mechanical appliances, and iron & steel.
- Major Investments:
- Russian investments in India focus on sectors like oil and gas, petrochemicals, banking, railways, and steel.
- Indian investments in Russia are concentrated in the oil and gas sector and the pharmaceuticals
KEY CHALLENGES IN RUSSIA INDIA TRADE
- Trade Imbalance:
- India faces a trade deficit of nearly USD 57 billion with Russia, primarily due to crude oil imports.
- The trade imbalance is skewed in Russia’s favor, with India’s exports to Russia remaining lower compared to imports.
- Geopolitical Issues:
- India’s growing ties with the US and the Quad (a group of four major democracies) could limit deeper cooperation with Russia, especially in the context of the Ukraine war.
- Russia’s strengthening relations with China reduce its ability to balance the interests of both India and China, which affects India’s leverage in global forums.
- Sanctions and Compliance:
- Sanctions imposed by the European Union (EU) and Western countries on Russia complicate trade relations with India, with some Indian companies facing sanction risks.
- India must balance its defense and energy ties with Russia while respecting international sanctions.
- Diverse Trade Basket:
- Although energy trade (like discounted crude oil) has increased, efforts to expand into sectors such as automotive parts, electronics, and renewables have been slow.
- Russia’s declining international influence also limits its ability to engage with India in new economic areas.
- Connectivity Challenges:
- Projects like the INSTC and Chennai-Vladivostok Corridor are critical to improving India-Russia trade. However, India’s increasing interest in other routes, like the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, may reduce the strategic importance of the INSTC.
SPECIAL INITIATIVES TO ADDRESS TRADE CHALLENGES
- Special Rupee-Vostro Account:
- To overcome challenges posed by international sanctions, India introduced a Special Rupee-Vostro Account to facilitate payments in local currencies between Indian and Russian businesses.
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA):
- Both countries are working toward a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU). The agreement would help streamline trade processes and reduce barriers.
- Ongoing negotiations for a Bilateral Investment Treaty and the launch of an Investment Forum in Moscow are expected to strengthen economic cooperation.
- Facilitating Business Ventures:
- Russia is showing interest in India’s Make in India program, which could lead to joint ventures and more business opportunities between the two countries.
- The Authorized Economic Operators (AEO) agreement between India and Russia will simplify trade processes, allowing trusted exporters to benefit from smoother customs clearances.
- Energy Sector Cooperation:
- Both countries are focusing on large-scale energy initiatives, particularly in the nuclear and renewable energy sectors (solar and wind energy).
- Russian Business Centre:
- A Russian Business Centre has been established in New Delhi to facilitate business interactions, organize regional missions, and offer analytical support for improving bilateral economic ties.
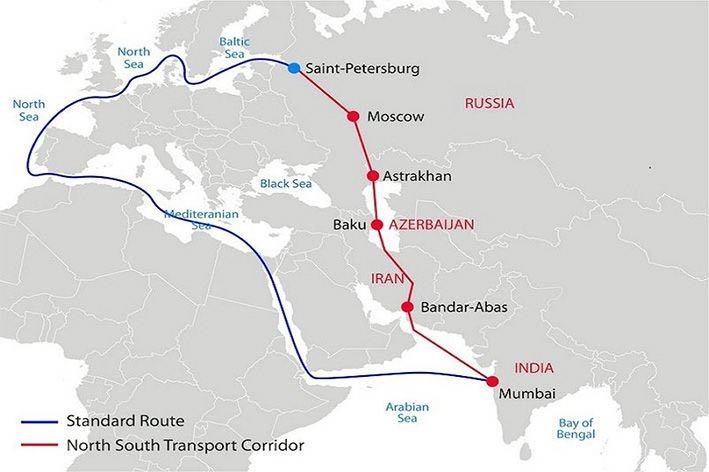
ABOUT INSTC
- About INSTC:
- The INSTC is a 7,200 km multimodal transit route that connects the Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea, extending to northern Europe via Petersburg, Russia.
- It was launched in 2000 under a trilateral agreement between India, Russia, and Iran.
- Geopolitical Importance:
- The INSTC connects ship, rail, and road routes between India, Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia, and Europe. It has the potential to enhance India’s connectivity with Central Asia and the Eurasian region.
- Membership:
- The member countries of the INSTC include India, Iran, Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkey, Ukraine, Belarus, Oman, and Syria. Bulgaria has joined as an observer.
PROSED ROUTE

Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


