INDIA’S FIRST LONG RANGE HYPERSONIC MISSILE
- India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted the flight test of its first long-range hypersonic missile on November 17, off the coast of Odisha.
- This achievement marks a significant milestone for India, positioning it among a select group of nations capable of developing and testing such advanced military technology.
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE TEST
The Defence Minister Rajnath Singh described the test as a historic moment, highlighting it as a major step for India in the field of advanced military technologies. With this success, India joins a small group of countries that have the ability to develop and test hypersonic missiles.
- The missile was launched from APJ Abdul Kalam Island, off the coast of Odisha.
- This location is named after India’s former president and renowned missile scientist, APJ Abdul Kalam.
KEY FEATURES
- Range: The missile has the ability to strike targets over 1,500 kilometers away and can carry different types of payloads.
- Indigenous Development: The missile was developed by several DRDO laboratories, along with industry partners.
- The core development took place at the APJ Abdul Kalam Missile Complex in Hyderabad.
What is a Hypersonic Missile?
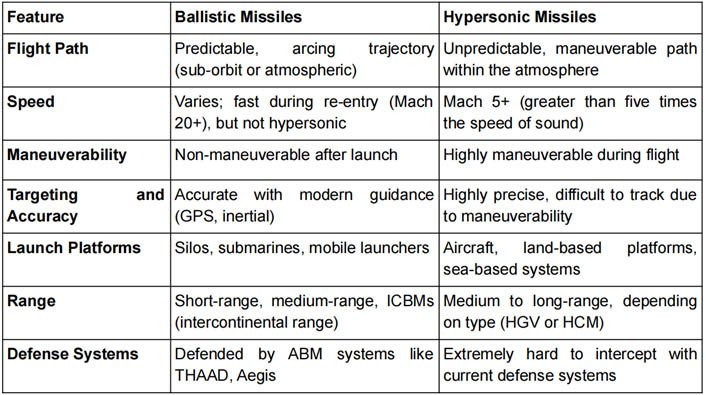
- A hypersonic missile is a missile that travels at speeds of at least Mach 5, which is five times the speed of sound (around 1 mile per second).
- Hypersonic missiles are much faster and more maneuverable than traditional ballistic missiles, which follow a fixed, predictable path.
TYPES OF HYPERSONIC MISSILES
- Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGV): These are launched from a rocket and then glide towards the target.
- Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCM): These missiles are powered by scramjets (air-breathing engines), which help maintain high speeds after the initial launch.
- Long-Range Strike: Hypersonic missiles can strike distant targets, including highly protected or time-sensitive targets like moving missiles or critical facilities.
- Difficult to Track: Due to their high speed and low flight path, hypersonic missiles are hard to detect using traditional radar systems or surface-based sensors.
- Kinetic Energy: Hypersonic missiles use kinetic energy (energy from motion) to destroy targets, including structures that are hard to penetrate using conventional weapons, such as underground facilities.
CHALLENGES OF HYPERSONIC MISSILES
- Heat and Friction: The extreme speeds create significant heat due to air resistance, requiring special materials that can withstand such conditions.
- Precision Maneuverability: The missile must be extremely precise in its movement, which makes the design and operation of these missiles highly complex.
- Communication Difficulties: It is difficult to maintain communication with a hypersonic missile during flight due to its high speed and altitude.
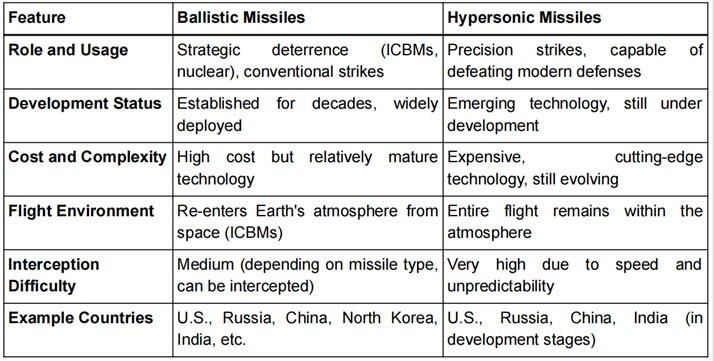
- Cost: Developing and producing hypersonic missiles is much more expensive than traditional ballistic missiles due to their cutting-edge technology.
GLOBAL RACE IN HYPERSONIC TECHNOLOGY
- Russia: Russia is a leader in hypersonic missile development. In 2022, Russia used a hypersonic missile for the first time during the Ukraine conflict, targeting an underground warehouse in Ivano-Frankivsk.
- China: China is also advancing in hypersonic missile technology, with several successful tests of its own hypersonic weapons.
- United States: The U.S. is heavily investing in hypersonic missile technology. In May 2023, the U.S. Army awarded Lockheed Martin a $756 million contract to develop a ground-based hypersonic missile system, known as the Long Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW).
- Other Countries: Several nations, including France, Germany, Australia, Japan, Iran, and Israel, are also working on developing hypersonic m
BALLISTIC MISSILE V/S HYPERSONIC MISSILES

Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


