SDG 10: REDUCE INEQUALITY WITHIN & AMONG COUNTRIES
SDG 10: Reduce Inequality Within and Among Countries
- Objective: Aim to reduce inequality both within countries and between them.
- Importance: Inequality hinders sustainable development, economic growth, and social progress, while affecting individuals’ well-being and sense of fulfillment.
TARGETS FOR GOAL 10
- 10.1: Achieve income growth for the bottom 40% at a rate higher than the national average by 2030.
- 10.2: Promote the social, economic, and political inclusion of all by 2030, regardless of personal characteristics.
- 10.3: Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities by eliminating discriminatory laws and practices.
- 10.4: Implement policies to progressively achieve greater equality, focusing on fiscal, wage, and social protection measures.
- 10.5: Improve the regulation of global financial markets and strengthen their implementation.
- 10.6: Enhance the representation of developing countries in international economic and financial institutions.
- 10.7: Facilitate safe, regular, and responsible migration, promoting well-managed migration policies.
- 10.A: Implement special treatment for developing countries in trade agreements.
- 10.B: Encourage development assistance and financial flows to countries in greatest need.
- 10.C: Reduce transaction costs of migrant remittances to less than 3%.
EXAMPPLES OF INEQUALITY:
- Healthcare Access:
- Women and children face preventable diseases due to lack of services; high maternal mortality rates in under-resourced regions.
- Discrimination:
- Groups like older persons, migrants, and refugees experience discrimination, limiting their opportunities.
- Global Disparities:
- Inequality affects both developing and wealthy nations, with persistent poverty and discrimination issues.
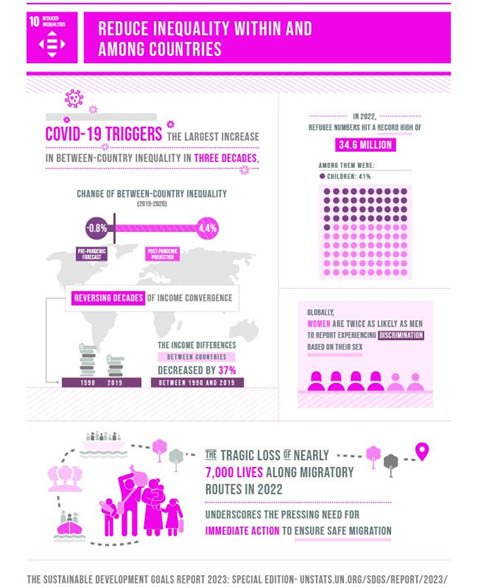
CURRENT CONTEXT
- Trends in Inequality:
- Before COVID-19, the income of the poorest 40% was growing faster than the average.
- The pandemic reversed this trend, increasing inequality, especially across countries.
- Impact of COVID-19:
- Largest rise in between-country inequality in three decades.
- Vulnerable groups faced disproportionate impacts, worsening poverty and marginalization.
Importance of Reducing Inequalities
- Social and Economic Development:
- High inequality stalls growth, creates barriers to education, healthcare, and job opportunities, and perpetuates poverty cycles.
- Sense of Fulfillment:
- Inequality leads to disenfranchisement, affecting mental health and contributing to social unrest.
- Environmental and Health Impacts:
- Contributes to societal issues like crime, disease, and environmental degradation, particularly affecting marginalized communities.
Examples of Inequality
- Healthcare Access:
- Women and children face preventable diseases due to lack of services; high maternal mortality rates in under-resourced regions.
- Discrimination:
- Groups like older persons, migrants, and refugees experience discrimination, limiting their opportunities.
- Global Disparities:
- Inequality affects both developing and wealthy nations, with persistent poverty and discrimination issues.
TACKLING DISCRIMINATION
- Global Interconnectedness:
- Poverty and discrimination are global challenges requiring collaborative solutions; even wealthy countries have disadvantaged communities.
- Intersectionality:
- Discrimination can overlap (e.g., women with disabilities face unique barriers), necessitating holistic strategies that address multiple forms of inequality.
Achieving Equality for All
- Transformative Policies:
- Policies must be universal and inclusive, focusing on the needs of marginalized groups and involving them in decision-making.
- Investment in Key Areas:
- Critical investments in education, healthcare, social protection, and decent work opportunities, especially for youth and vulnerable populations.
Actions to Reduce Inequality
- Empowering Inclusive Growth:
- Governments should promote economic policies that empower marginalized communities to ensure growth benefits all.
- Eliminating Discriminatory Practices:
- Establish legislative frameworks to abolish laws that perpetuate inequality.
- Enhancing Global Cooperation:
- Foster collaboration to amplify the voices of developing nations in international economic decisions, promoting equitable global trade and finance.
- Safe Migration Policies:
- Create well-managed migration policies to support those fleeing poverty, conflict, and discrimination in search of better opportunities.
SDG 10 & INDIA
Sustainable Development Goal 10 aims to reduce inequalities within and among countries. In India, this goal focuses on reducing income inequalities and inequalities of outcome by ensuring access to equal opportunities for all individuals, regardless of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, religion, or economic status.
It also emphasizes enhancing the representation of developing countries in international decision-making processes.

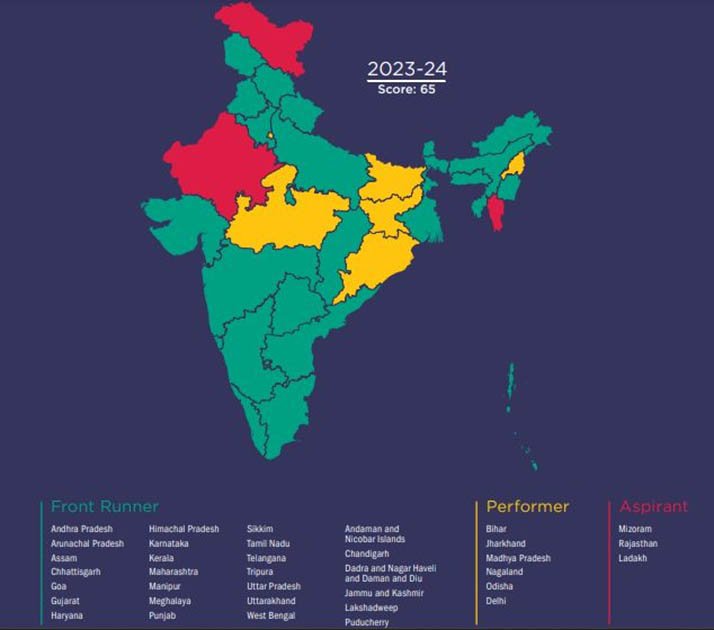
SDG 10 INDEX SCORE
- The SDG Index Score for Goal 10 ranges from 43 to 87 for states and 49 to 80 for UTs.
- Top Performers: Goa (States) and Puducherry (UTs) lead in scores.
- Front Runners: Twenty-one states and six UTs are categorized as Front Runners, with scores between 65 and 100 (excluding 100).
- Aspirants: Two states and one UT scored less than 50, indicating they are lagging.
KEY INDICATORS
- Income Inequality:
- Gini Coefficient: Measures wealth distribution; scores range from 0 (low inequality) to 1 (high inequality).
- Current Status: India’s Gini coefficient is 0.20 (NFHS-5, 2019–2021).
- Best and Worst Performers:
- Delhi: Best performance with a Gini of 0.08.
- Jharkhand: Highest inequality at 0.27.
- UTs: Ladakh has a Gini of 0.23, indicating significant inequality.
- Women in Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs):
- Reservation: The Indian Constitution mandates one-third of PRI seats for women.
- Current Representation:
- Overall: Women hold 45.61% of total seats in PRIs (2021).
- Top State: Uttarakhand at 56.02%.
- Lowest Representation: Uttar Pradesh at 33.34%.
- Best UT: Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu at 41%.
- Representation of SC/ST in State Legislative Assemblies:
- Current Data: 28.57% of seats in State Assemblies are occupied by Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST).
- Top States: Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland, with 98.3% representation.
- Note: This indicator is not ranked due to variations in mandated seats among states, particularly in the North-Eastern region.
- Female Professional and Technical Workers:
- National Ratio: The female-to-male worker ratio in professional and technical fields is 50.4%.
- Top States:
- Meghalaya (169.8%) and Kerala (101.6%) exceed the target of 100%.
- Lowest: Bihar at 31.5%.
- Best UT: Andaman and Nicobar Islands at 96.5%.
- Crimes Against SCs:
- Crime Rate: Approximately 29 crimes occur against SC members for every 100,000 SC population (2022).
- Highest Rate: Mizoram, with 411 crimes per 100,000 SC population.
- Crimes Against STs:
- Crime Rate: About 10 crimes occur against ST members for every 100,000 ST population.
- Highest Rate: Kerala, with 36 crimes per 100,000 ST population.
STEPS TAKEN BY GoI
- Social Welfare Schemes: Programs like the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (housing for all) and the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) provide support to marginalized communities and promote income security.
- Reservation Policies: Affirmative action policies in education and government jobs aim to uplift Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and Other Backward Classes.
- Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT): To reduce leakages and ensure that subsidies reach intended beneficiaries, the government has adopted DBT for various schemes, including LPG subsidies and cash transfers.
- Skill Development Initiatives: Programs like the Skill India Mission aim to enhance employability and income potential among disadvantaged groups through vocational training.
- Financial Inclusion: The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana has facilitated access to banking services for the unbanked population, promoting savings and financial literacy.
- Healthcare Initiatives: Schemes such as Ayushman Bharat provide health insurance coverage to low-income families, reducing the economic burden of healthcare costs.
- Education Programs: The Right to Education Act and initiatives to improve access to quality education in rural and underserved areas aim to bridge educational disparities.
- Women Empowerment Initiatives: Programs like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao focus on improving the status of women and girls, addressing gender inequality.
- Minimum Support Prices (MSP): The government guarantees MSP for certain crops to ensure that farmers receive fair compensation, helping reduce rural income inequality.
- Digital Initiatives: Efforts to improve digital infrastructure aim to bridge the urban-rural divide, facilitating access to information, services, and economic opportunities.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


