SDG 13:URGENT ACTION TO COMBAT CLIMATE CHANGE

Overview
Goal 13 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) emphasizes urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. Climate change, primarily driven by human activities, threatens life on Earth and is occurring at an alarming rate.
TARGETS & GOALS
- Strengthen Resilience: Enhance the resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards in all countries.
- Integrate Climate Measures: Incorporate climate change considerations into national policies, strategies, and planning.
- Improve Education and Awareness: Enhance education and institutional capacity regarding climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- Financial Commitments: Mobilize $100 billion annually from developed countries to support developing nations in climate action, ensuring transparency in implementation and operationalizing the Green Climate Fund.
- Capacity Building: Promote effective planning and management for climate change in least developed countries and small island states, focusing on women, youth, and marginalized communities.
KEY ISSUES
Climate Crisis
- Global Impact: Climate change will affect every person, in every country, across all continents. Its repercussions include extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and ecosystem disruption.
- Cataclysmic Threat: Without immediate action, the looming climate cataclysm could undo significant development progress and provoke mass migrations, leading to instability and conflict.
Current Trends
- Temperature Targets: To limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, greenhouse gas emissions must be cut by nearly 50% by 2030. Current trajectories are far from meeting this target.
- Historical Context: The period from 2010 to 2019 was the warmest decade recorded, resulting in severe natural disasters, including wildfires, hurricanes, and floods.
CONSEQUENCES OF INACTION
- Rising Temperatures: If unchecked, global temperatures could rise beyond 3°C, severely impacting ecosystems and exacerbating issues like food and water scarcity, leading to potential conflicts.
- Mortality Rates: From 2010 to 2020, highly vulnerable regions (home to 3.3–3.6 billion people) experienced 15 times higher human mortality rates from climate-related disasters compared to less vulnerable areas.
Facts and Figures
- IPCC Recommendations: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) states that deep, rapid, and sustained reductions in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are essential across all sectors. Immediate action is crucial.
- Current Insufficiencies: The pace and scale of current climate action are inadequate to effectively address climate change. Increasingly frequent extreme weather events pose grave risks to every region on Earth.
SOLUTION & STRATEGIES
Raising Ambition
- Global Commitment: The Paris Agreement (2015) marked a significant milestone, with all countries pledging to address climate change. However, greater action is needed to achieve established targets.
- Sectoral Transformation: A comprehensive overhaul of energy, industry, transport, food, agriculture, and forestry systems is necessary to keep global temperature rise below 2°C, ideally below 1.5°C.
Financial Investment
- Climate Finance Overview: According to UNFCCC, climate finance flows averaged $803 billion annually in 2019-2020, a 12% increase from previous years, but still inadequate to meet climate goals. Fossil fuel investments surpassed climate financing for adaptation and mitigation in 2020.
- Developing Countries’ Efforts: By 2019, at least 120 of 153 developing countries had undertaken activities to formulate National Adaptation Plans, marking a 29-country increase from the previous year. However, progress in meeting the 2020 disaster risk reduction target has been slow.
SDG 13 & INDIA
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 13 aims to take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. The goal emphasizes integrating:
- climate change measures,
- disaster risk reduction, and
- sustainable resource management

into national development strategies. It seeks to enhance resilience and adaptive capacity, including strengthening human and institutional capabilities for mitigation, adaptation, and early warning systems. Recognizing that climate change transcends national boundaries, international cooperation is essential.
SDG INDIA INDEX
To assess India’s progress towards Goal 13, five national-level indicators have been identified, capturing two of the five SDG targets for 2030.
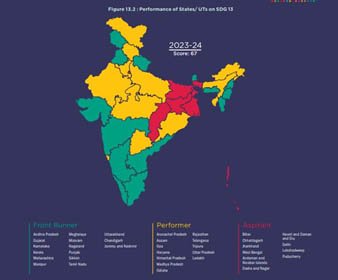
- State Scores: Ranges from 30 to 81.
- UT Scores: Ranges from 13 to 80.
- Top Performers:
- States: Sikkim and Tamil Nadu.
- UT: Chandigarh.
- Front Runners: Thirteen states and two UTs scored between 65 and 100.
- Aspirants: Four states and five UTs scored less than 50.
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
Fatalities Due to Extreme Weather Events
- SDG Target 13.1: Aims to strengthen resilience against climate-related hazards.
- Statistics: During extreme weather events in 2018–2019, India experienced 15 fatalities per crore population.
- Highest Fatalities: Himachal Pradesh (472 fatalities), followed by Arunachal Pradesh (221).
- Best Performer: Haryana (1 fatality per crore population).
- Extreme Weather Events: Includes cyclones, heavy rains, floods, landslides, etc.
Disaster Preparedness
- Scorecard: Assesses the disaster management systems of various states/UTs on a scale of 0–50.
- National Score: India’s score was 19.2 in 2019.
- Top States: Maharashtra (27.5), Gujarat (27).
- Lowest Score: Jharkhand (7.5).
- UT Performance: Delhi (25) and Chandigarh (24.5) are the highest.
Share of Renewable Energy
- INDC Commitment: India aims for 50% of total electricity generation from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030, with a target of 450 GW from renewables.
- Current Achievement: As of April 2024, 43.28% of India’s electricity generation came from renewable sources.
- Leading States: Himachal Pradesh (96.14%), Arunachal Pradesh (89.15%).
- Lowest Performer: Bihar (7.28%).
Air Pollution
- DALY Rate: The Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALY) rate due to air pollution is 3,469 per 100,000 population (2016).
- Lowest DALY: Nagaland (1,408).
- Highest DALY: Rajasthan (4,528).
Compliance with Environmental Standards
- National Compliance Rate: 94.86% of industries comply with environmental standards as per the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- States with 100% Compliance: Goa, Manipur, Nagaland, Sikkim.
- Lowest Compliance: Arunachal Pradesh (64.22%).
- UT Performance: Chandigarh leads with 100% compliance.
INITIATIVES TAKEN
National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC):
- Launched in 2008, this plan outlines India’s strategy to tackle climate change.
- Includes eight core missions in specific areas like solar energy, energy efficiency, sustainable habitat, water, Himalayan ecosystems, Green India, sustainable agriculture, and strategic knowledge.
Paris Agreement:
- India ratified the Paris Agreement in 2016, committing to reduce emissions intensity of GDP by 33-35% by 2030 compared to 2005
- Aims to achieve about 40% cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
- Targets creating an additional carbon sink of 2.5-3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through forest and tree cover.
Renewable Energy:
- India has set ambitious targets for renewable energy, aiming to achieve 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022.
- Various initiatives like the National Solar Mission, National Wind Energy Mission, and National Biofuel Policy are promoting renewable energy
Energy Efficiency:
- The National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency focuses on improving energy efficiency in various sectors like industry, buildings, and transportation.
- Initiatives like the Energy Efficient Lighting Program and Appliances Labeling Program have been implemented.
Sustainable Agriculture:
- The National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture aims to promote sustainable agriculture practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change.
- Initiatives include organic farming, precision agriculture, and climate-smart agriculture.
Forest Conservation:
- The National Mission for Green India focuses on increasing forest cover and restoring degraded ecosystems.
- Initiatives like afforestation programs and community-based forestry are being implemented.
Climate Finance:
- The Indian government has established the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change to support adaptation projects in vulnerable regions.
- India is also actively participating in international climate finance mechanisms like the Green Climate Fund.
Capacity Building:
- The Indian government is investing in capacity building to enhance understanding and expertise in climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- Initiatives include training programs for government officials, researchers, and civil society organizations.
International Cooperation:
- India is actively participating in international climate change negotiations and collaborating with other countries to address global challenges.
- India has been a strong advocate for climate justice and the need for developed countries to take greater responsibility for reducing emissions.
These are just some of the many steps taken by the Indian government to address SDG 13 -Climate Action. It is important to note that India faces significant challenges in achieving its climate goals, including rapid population growth, poverty, and dependence on fossil fuels. However, the government’s commitment to climate action and the progress made so far demonstrate a strong determination to address these challenges and build a sustainable future.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.

