USA PRESIDENTIAL ELECTIONS

- On 6 Nov 2024, Donald Trump won the US elections. The US media hasannounced Trump’s win.
- His rival Kamala Harris has secured 226 electoral colleges, while Trump surpassed the 270 – the majority mark.
- He will be the second Republican to get a second term in office in 20 years. George Bush, a Republican, was president from 2001 to 2009.
THE ELECTIONS
- On November 5, 2024,The 2024 United States presidential election was held where U.S. citizens chose between former President Donald Trump (Republican) and Vice President Kamala Harris (Democrat) for the office of the 47th President.
- Unlike the direct election system used in countries like France, the United States elects its president through a more complex, multi-stage process.
- The election process is governed by the S. Constitution, which states that the winner is determined not by the popular vote, but by the Electoral College.
- The popular vote is the total number of votes cast by people in an election.
- In a presidential election in the U.S., it shows how many people voted for each candidate.

IS PRESIDENT OF USA PART OF THE CONGRESS?
NO
What is Congress?
- Congress is the legislative branch of the U.S. government. It’s the part of the government that makes laws.
- Congress is bicameral, meaning it has 2 houses:
- The Senate and
- The House of Representatives.
WHO IS A SENATOR?
- A Senator is a member of the Senate, which is the upper house of Congress.
- There are 100 Senators in total from 50 states, with 2 Senators from each state. No matter how big or small the state is, each has equal representation in the Senate.
- Senators serve 6-year terms. Every two years, about one-third of the Senate is up for re-election.
WHO IS A REPRESENTATIVE? (IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES)
- A Representative is a member of the House of Representatives, which is the lower house of Congress.
- There are 435 Representatives in total. Each state gets a number of Representatives based on its population. States with more people, like California, have more Representatives than smaller states like Wyoming.
- Representatives serve 2-year terms. All 435 seats are up for election every two years.
There are 535 members in Congress (100 Senators + 435 Representatives).
WHAT IS AN ELECTORAL COLLEGE FOR THE PRESIDENT?
- The Electoral College is a system used in the United States to elect the president and vice president.
- It’s not a direct popular vote where the person with the most votes wins.
- Instead, theS. uses a group of electors from each state to decide who wins.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
- Electors in Each State:
- Each state has a certain number of electors based on its population.
- Electors are not Senators or Representatives.
- Senators and House Representatives are elected to serve in Congress.
- Electors, on the other hand, are chosen specifically for the purpose of voting in the Electoral College during the presidential election.
HOW ELECTORAL VOTES ARE ASSIGNED?
- How Electoral Votes Are Assigned:
- Each state gets electoral votes equal to the total number of Senators plus the number of House Representatives. So, every state gets at least 3 electoral votes (2 Senators + 1 Representative).
- For example:
- California, the most populous state, has 54 electors (2 Senators) + (52 Representatives) = 54 electoral votes
- Wyoming, one of the smallest states, has 3 electors (2 Senators + 1 Representative).
- Formula:
- Electoral Votes for a State = Number of Senators (always 2) + Number of House Representatives (based on population).
- Total Electoral Votes:
- There are 538 total electoral votes (100 Senators + 435 Representatives + 3 votes for Washington D.C.).
- Washington DC got 3 electoral votes from the 23rd AA in 1961.
- To win the presidency, a candidate needs 270 electoral votes.
- There are 538 total electoral votes (100 Senators + 435 Representatives + 3 votes for Washington D.C.).
- The Popular Vote:
- On Election Day (the first Tuesday after the first Monday in November), voters in each state cast their ballots for a presidential candidate.
- When voters vote, they are really voting for a slate of electors pledged to that candidate.
- In 48 states out of 50, the candidate who wins the popular vote receives all of that state’s electoral votes.
- The exceptions are Maine and Nebraska, which divide their votes differently based on proportional system.
- If 57% of voters in California vote for Kamala Harris, then all 54 of California’s electors (the electoral votes) will be pledged to vote for Kamala Harris in the Electoral College.

- If 56% of voters in Texas vote for Donald Trump, then all 40 of Texas’s electors will be pledged to vote for Donald Trump.
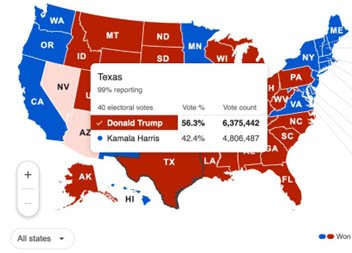
ROLE OF ELECTORS AFTER POPULAR VOTE
- Meeting of the Electors:
- After the popular vote, the electors meet in December in their state capitals to cast their votes for president and vice president.
- Most electors vote based on the results of the popular vote in their state (but they are not legally required to in every state).
- Faithless Electors: If an elector votes for someone other than the candidate they promised to support, they are called a faithless elector.
- Some states have rules against this, and faithless electors can be replaced.
- In 2016, there were seven faithless electors, but their votes didn’t change the overall result.
- Counting the Votes:
- In January, Congress counts the votes of the electors during a joint session.
- If a candidate gets 270 electoral votes, they are declared the winner.
WHAT HAPPENS IF THERE IS A TIE?
A tie in the Electoral College is rare but not impossible. It has occurred twice in U.S. history:
- 1800: Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr had the same number of electoral votes.
- 1824: Andrew Jackson, John Quincy Adams, and two other candidates had split votes. If there is a tie, or if no candidate receives a majority of electoral votes, the decision is thrown to the S. House of Representatives.
- House of Representatives: In this case, each state’s congressional delegation casts one vote to choose the President. A majority of 26 votes is needed to win.
- The Senate would then select the Vice President, with each Senator casting one vote. A majority of 51 votes is required.
If no winner is chosen by January 20 (Inauguration Day), the Vice President becomes the Acting President until a decision is reached.
CRITICISMS OF THE ELECTORAL COLLEGE
- Winner-Takes-All System: In most states, the candidate who wins the popular vote in that state gets all the electors, which can make the system feel unfair, especially if a candidate wins the popular vote nationally but loses the electoral vote.
- Disproportionate Influence: Small states like Wyoming have more power per person because they have a minimum of 3 electors, regardless of their small population.
- Popular Vote vs. Electoral Vote: In 2000 (George W. Bush vs. Al Gore) and 2016 (Donald Trump vs. Hillary Clinton), the winner of the popular vote did not win the election because the other candidate had more electoral votes. This makes people question whether the system truly reflects the will of the people.
PROBABLE IMPACTS ON INDIA
- Trade: India’s exports can be dented as tariff wars between India & USA was the hallmark of previous presidency term of Donald Trump.
- Defence Cooperation: This can strengthen further with more tech transfers happening to India. Trump is keen on containing China.
- Immigration: This can be a challenging domain due to the inward & protectionist tendencies of Donald Trump. Visa delays can be eminent.
- Cut on outsourcing: Trump has been vocal about bringing industries back to America (which have been outsourced to developing countries like China & India)
- Geopolitical Conflicts:
- Russia- Ukraine War: Can be a decisive moment in the war as Trump talks about stopping funds to Ukraine.
- West Asia: Trump has been very tough on Iran. USA’s support to Israel will increase.
Note: Connect with Vajirao & Reddy Institute to keep yourself updated with latest UPSC Current Affairs in English.
Note: We upload Current Affairs Except Sunday.


